American Public Education Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
American Public Education Bundle
The American public education system faces significant competitive forces, from the bargaining power of teachers' unions to the growing influence of charter schools. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of educational provision.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore American Public Education’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of technology providers, including Learning Management System (LMS) platforms and specialized educational software, is a significant factor for American Public Education (APEI). This power is generally considered moderate to high. While the market offers several vendors, the costs associated with switching platforms can be substantial, impacting APEI’s operational flexibility.
Furthermore, certain highly specialized software solutions may have few viable alternatives, granting these suppliers considerable leverage. APEI’s reliance on a robust online infrastructure to effectively deliver its educational programs means that disruptions or unfavorable terms from these technology providers could have a material impact. For instance, in 2023, cloud computing services, a backbone for many LMS platforms, saw price increases driven by demand and hardware costs, a trend that could continue to affect APEI's technology expenditures.
The bargaining power of content developers and curriculum providers for American Public Education (APEI) is typically moderate. APEI's strategy involves significant in-house curriculum development, particularly for its niche programs such as military studies and nursing, which reduces reliance on external parties. For instance, in 2024, APEI continued to emphasize its proprietary curriculum for its key academic offerings.
However, there are instances where external content or licensing becomes necessary, especially for foundational general education courses or to meet specific accreditation standards. When APEI needs to source these external materials or licenses, the suppliers of such content gain a degree of influence. This can manifest in pricing negotiations or requirements for curriculum integration.
Accreditation bodies wield significant bargaining power over American Public Education (APEI). Their approval is not just a formality; it's a prerequisite for APEI's very operation and the recognition of its degrees. Without this crucial validation, APEI's ability to offer federal financial aid, a cornerstone of its student enrollment, would be critically undermined.
The landscape of accreditation is characterized by stringent requirements and a relatively limited pool of recognized accrediting agencies. This scarcity, coupled with the essential nature of their approval, grants these bodies substantial leverage over educational institutions like APEI. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Education continues to oversee recognized accrediting agencies, ensuring a centralized control that reinforces their power.
Supplier Power 4
The bargaining power of suppliers for American Public Education (APEI) is primarily influenced by its faculty and instructional staff. For highly specialized programs, such as nursing or cybersecurity, where there's a shortage of qualified educators, these faculty members can exert significant influence. This is especially true in 2024, as demand for skilled professionals in these fields continues to outpace the supply of experienced instructors.
Conversely, in general education or less specialized disciplines, APEI benefits from a broad pool of available adjunct and online instructors. This abundance of potential faculty members dilutes the individual bargaining power of any single instructor, allowing the university to maintain more control over compensation and contract terms. For instance, in 2023, the national average for adjunct faculty pay across various disciplines often remained modest, reflecting this dynamic.
- Faculty Specialization: The power of faculty as suppliers is directly correlated with the demand for their specific expertise.
- Instructor Pool Size: A larger pool of available instructors, particularly adjuncts and online educators, reduces individual bargaining power.
- Market Demand for Skills: Shortages in fields like healthcare and technology empower specialized faculty to negotiate better terms.
- Adjunct Compensation Trends: In 2023, adjunct faculty compensation nationally often reflected the high supply of instructors in many general education subjects.
Supplier Power 5
The bargaining power of suppliers for student support services, like proctoring or career counseling platforms, is generally moderate for American Public Education (APEI). While these services are important for keeping students engaged and helping them find jobs, APEI can usually find several companies offering similar solutions. This means APEI has some room to negotiate prices and terms.
For instance, in 2024, the online proctoring market saw increased competition, with new players emerging and existing ones offering tiered pricing models. This competitive landscape allows institutions like APEI to shop around. However, the quality of these services is crucial for student outcomes, so APEI must balance cost with effectiveness. A poorly chosen proctoring service, for example, could lead to student complaints and impact retention rates, a key metric for educational institutions.
- Moderate Supplier Power: Multiple vendors for student support services provide APEI negotiation leverage.
- Quality as a Differentiator: The effectiveness of services like proctoring and career counseling remains a critical factor in provider selection.
- Market Dynamics: Increased competition in areas like online proctoring in 2024 has given institutions more options and better pricing potential.
The bargaining power of suppliers for American Public Education (APEI) is largely influenced by its faculty and instructional staff, particularly in specialized fields. For 2024, the demand for qualified instructors in areas like nursing and cybersecurity remains high, granting these faculty members considerable leverage in negotiations. This contrasts with general education disciplines where a larger pool of adjuncts, as evidenced by modest compensation trends in 2023, limits individual instructor power.
The bargaining power of technology providers, including LMS platforms and specialized software, is generally moderate to high for APEI. Switching costs can be substantial, and reliance on these systems for program delivery means terms from providers can significantly impact operations. For example, the ongoing demand for cloud computing services, a foundation for many platforms, has driven price increases, a trend likely to continue affecting APEI's technology expenditures in 2024.
Accreditation bodies hold significant bargaining power over APEI, as their approval is essential for operation and financial aid eligibility. The limited number of recognized agencies, overseen by the U.S. Department of Education, reinforces their leverage. Similarly, suppliers of student support services like proctoring platforms have moderate power due to a competitive market in 2024, allowing APEI some negotiation flexibility, though service quality remains paramount.
What is included in the product
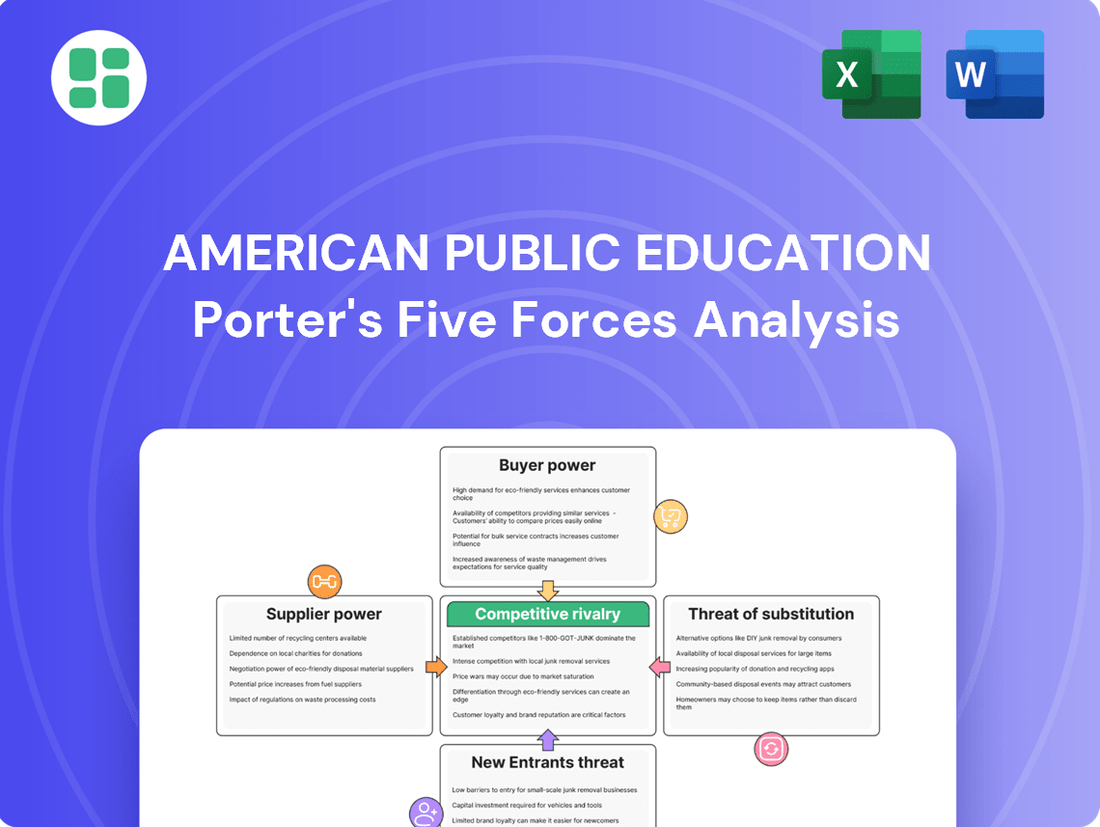
This analysis details the competitive forces impacting American Public Education, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing institutions.
Navigate the complex landscape of American public education by identifying and mitigating key competitive pressures, allowing for more effective resource allocation and strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of American Public Education's (APEI) customers, primarily students, is significant. This stems from a wide array of competing educational institutions, both online and brick-and-mortar, offering similar programs. Students can readily compare tuition fees, course structures, and learning formats, driving a focus on affordability and flexibility in educational choices.
American Public Education's (APEI) primary customer base, comprising adult learners and military/veteran segments, exhibits significant bargaining power. These individuals are keenly focused on value, prioritizing career progression, flexible learning options, and a demonstrable return on their educational investment. This makes them highly sensitive to tuition fees and the overall quality and relevance of APEI's offerings.
In 2023, APEI reported total revenue of $322.8 million, with a significant portion derived from these core demographics. The discerning nature of these students means that any perceived lack of value or excessive cost can lead them to seek alternatives, directly impacting APEI's enrollment numbers and financial performance.
Prospective students at American Public Education (APEI) possess significant bargaining power, largely due to the ease with which they can access information about alternative educational programs and institutions. Online searches, university rankings, and extensive student reviews empower them to compare offerings, tuition costs, and program outcomes, making informed choices. For instance, in 2024, the proliferation of online comparison tools and readily available accreditation information means a student can identify and evaluate competing institutions in mere minutes, significantly reducing the effort previously required to switch providers.
This increased transparency allows students to readily switch to providers that better meet their academic or career needs, or if they find more attractive pricing or a superior learning experience elsewhere. APEI's ability to retain students is therefore directly linked to its capacity to deliver value and satisfaction, as the cost of switching for a student is relatively low. This dynamic forces APEI to remain competitive in its program quality, pricing, and student support services to mitigate the threat of customer defection.
Buyer Power 4
The bargaining power of customers for American Public Education (APEI) is moderate. While various financial aid options like federal student aid and military benefits can buffer direct price sensitivity for some, the overall cost and perceived value remain critical decision factors for students. In 2023, APEI reported total revenue of $347.2 million, indicating a substantial market where student choices significantly influence the company's performance.
Students actively compare net costs and the return on investment from their education. This careful evaluation means APEI must continually demonstrate its value proposition to attract and retain students. The competitive landscape, with numerous institutions offering similar programs, further empowers students in their decision-making process.
- Financial Aid Impact: Federal student aid and military benefits offer some insulation from immediate price concerns, but students still scrutinize the total cost of attendance.
- Value Proposition Focus: APEI's ability to clearly articulate the career outcomes and earning potential associated with its degrees is crucial to mitigating customer price sensitivity.
- Competitive Environment: The presence of many alternative educational providers means students have options, increasing their leverage in negotiating or selecting institutions based on cost and quality.
Buyer Power 5
The bargaining power of customers, particularly students, is a significant factor for American Public Education (APEI). Student mobility is on the rise, with learners increasingly seeking flexibility and value. This trend is amplified by the growing acceptance of micro-credentials and alternative learning pathways, allowing students to acquire specific skills without committing to a full degree program. Consequently, students are less anchored to a single institution and can more easily transfer credits or pursue specialized training elsewhere, putting pressure on APEI to offer competitive pricing and relevant educational outcomes.
Several factors contribute to this heightened buyer power:
- Increased Student Mobility: Students are more willing and able to switch institutions or learning formats to find the best fit for their needs and budget.
- Rise of Micro-credentials: The demand for shorter, skill-focused certifications allows students to bypass traditional degree structures and seek targeted education.
- Alternative Learning Pathways: Online platforms, bootcamps, and competency-based education provide viable alternatives to traditional university models.
- Information Accessibility: Students have unprecedented access to information about program quality, costs, and outcomes across various educational providers, facilitating comparisons.
Students at American Public Education (APEI) wield considerable bargaining power due to the vast array of educational options available. They can easily compare tuition, program flexibility, and career outcomes across numerous online and traditional institutions. In 2024, the ease of accessing detailed program reviews and accreditation information online empowers students to make highly informed choices, driving APEI to focus on value and affordability to remain competitive.
The primary customer segments, including adult learners and military personnel, are particularly price-sensitive and seek a strong return on their educational investment. This focus on value means APEI must consistently demonstrate the relevance and career impact of its programs to prevent student attrition. For instance, in 2023, APEI's revenue of $322.8 million was directly influenced by the enrollment decisions of these discerning students.
The overall cost of attendance, even with financial aid, remains a critical factor. Students actively weigh net costs against potential future earnings, and the low switching costs associated with online education allow them to readily move to institutions offering better perceived value or lower prices. This necessitates APEI maintaining competitive pricing and a clear value proposition.
| Factor | Impact on APEI | 2023 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Information Accessibility | Empowers students to easily compare APEI with competitors. | Revenue: $322.8 million |
| Price Sensitivity | Drives demand for cost-effective education and clear ROI. | Tuition revenue is a significant component of total revenue. |
| Student Mobility | Increases the risk of student defection to alternative providers. | Enrollment figures are closely monitored for retention trends. |
What You See Is What You Get
American Public Education Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of American Public Education provides an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Competitive rivalry in the online postsecondary education sector is fierce, with a multitude of traditional universities, for-profit entities, and large non-profit online universities vying for students. This crowded market fuels aggressive marketing campaigns and price wars, as institutions try to differentiate themselves and attract learners.
For instance, in 2024, the online education market continued to see significant growth, with many established universities increasing their online program offerings. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics indicated that millions of students were enrolled in at least one online course, highlighting the broad appeal and intense competition for this student base.
American Public Education (APEI) operates in a higher education landscape increasingly shaped by demographic shifts. A significant factor is the projected enrollment cliff for traditional 18-24 year old students, a trend expected to intensify competition for this shrinking demographic. This necessitates a stronger focus on attracting and retaining adult learners and military personnel, segments where APEI has historically found success, but where rivals are also increasingly concentrating their efforts.
In 2024, the higher education sector continues to grapple with these enrollment challenges. For instance, projections from organizations like the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center indicate ongoing declines in first-time undergraduate enrollment for certain age groups. This competitive pressure means institutions are not only fighting for a smaller pool of recent high school graduates but also intensely competing for the attention and tuition dollars of adult learners seeking to upskill or change careers, and the crucial military student population.
American Public Education (APEI) faces intense rivalry from institutions differentiating through specialized programs, flexible learning formats like online and hybrid models, robust student support, and demonstrable career outcomes. APEI's strategic focus on military and veteran students, alongside its nursing programs via Hondros College of Nursing, carves out specific market segments, yet these niches are also highly competitive.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Technological advancements, particularly the integration of AI in education, are significantly intensifying competitive rivalry for institutions like American Public Education. This forces them to constantly innovate their course content and delivery methods to stay relevant.
Institutions must make ongoing investments in new technologies and teaching strategies to keep pace. For instance, the global AI in education market was projected to reach $20 billion by 2027, highlighting the scale of this technological shift and the pressure to adapt.
- AI-powered personalized learning platforms
- Virtual and augmented reality in classrooms
- Data analytics for student success prediction
Competitive Rivalry 5
Competitive rivalry within the online education sector, where American Public Education (APEI) operates, is intense. Established brands and strong alumni networks provide a significant edge in attracting and retaining students, especially in the digital realm where trust and perceived quality are crucial. For instance, in 2024, online universities with decades of history and robust professional connections often see higher enrollment rates and better student outcomes compared to newer entrants.
Reputation and brand recognition are paramount for APEI and its competitors. Institutions that have cultivated a strong reputation for academic rigor and career success benefit from word-of-mouth referrals and a more loyal student base. This is particularly true in the competitive online space where prospective students rely heavily on perceived quality and the credibility of the institution's brand.
- Brand strength significantly influences student acquisition in the online education market.
- Established institutions with strong alumni networks often outperform newer competitors.
- Trust and perceived quality are critical factors for attracting and retaining students online.
- APEI faces rivalry from institutions with long-standing reputations and extensive professional connections.
Competitive rivalry for American Public Education (APEI) is characterized by a crowded marketplace where established universities, for-profit providers, and large online institutions aggressively compete for students. This intense competition is further fueled by demographic shifts, such as the projected enrollment cliff for traditional-aged students, forcing institutions to focus on adult learners and military personnel, segments where APEI also operates and faces strong competition.
Institutions are differentiating themselves through specialized programs, flexible learning formats, and demonstrable career outcomes, intensifying the need for APEI to innovate. For example, in 2024, the demand for upskilling and reskilling continued to grow, increasing competition for adult learners seeking career advancement. Furthermore, technological advancements, including AI in education, are forcing all players to invest in new teaching strategies and platforms to remain competitive.
| Metric | 2023 (Approx.) | 2024 (Projection/Trend) | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Enrollment Growth | Steady growth, ~5-7% annually | Continued growth, potentially accelerated by AI tools | Increased competition for online students |
| Adult Learner Demand | High, driven by career changes | Very high, with a focus on micro-credentials | Intensified competition for this demographic |
| AI in Education Market | Significant investment, ~$15 billion | Projected to exceed $20 billion by 2027 | Pressure to adopt AI for competitive advantage |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for traditional public education is significant and growing. Alternative education models like micro-credentials, coding bootcamps, and specialized professional certificates are gaining traction. These programs often provide more focused, hands-on training for specific in-demand skills, allowing individuals to enter the workforce or advance their careers much faster than a traditional four-year degree.
For instance, the global online education market, which encompasses many of these alternative pathways, was valued at approximately $250 billion in 2023 and is projected to see robust growth. This indicates a clear shift in how individuals perceive value in education, with many prioritizing speed and direct applicability of skills over the broader, longer-term approach of public education institutions.
Employer-provided training and corporate learning initiatives are increasingly acting as substitutes for traditional public education. Companies are investing heavily in internal academies and specialized training programs to upskill their employees, directly addressing skill gaps and reducing reliance on formal degree programs. For instance, in 2024, many large corporations reported significant increases in their learning and development budgets, with some allocating over $1,000 per employee annually for upskilling.
The threat of substitutes in American public education is significant, primarily driven by the rise of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) and other affordable online learning platforms like Coursera and Udemy. These platforms provide accessible content that can replace traditional courses or even core knowledge acquisition, fulfilling specific learning needs outside of formal degree structures.
4
Vocational and technical training programs present a significant threat of substitutes to traditional American public education. These programs, particularly in high-demand areas like skilled trades or specific healthcare certifications, offer a more direct and often faster path to employment. For instance, in 2024, the demand for electricians and HVAC technicians remained exceptionally high, with projected job growth significantly outpacing the average for all occupations.
Individuals prioritizing immediate workforce entry over extended degree programs may find these shorter, skill-focused alternatives more appealing. The cost-effectiveness of vocational training, often involving lower tuition fees and shorter completion times, further enhances its attractiveness as a substitute. This can lead to a diversion of students, particularly those with clear career goals and a preference for hands-on learning, away from conventional public high schools and colleges.
- Faster Workforce Entry: Vocational programs offer quicker pathways to employment compared to multi-year degree programs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower tuition and shorter durations make these programs financially attractive substitutes.
- Demand for Skilled Trades: High demand in fields like construction and healthcare fuels the appeal of vocational training.
- Practical Skill Development: Focus on hands-on skills aligns with the needs of many employers seeking job-ready graduates.
5
The threat of substitutes in American public education is growing as self-learning resources become more accessible and effective. Platforms offering open educational resources, YouTube tutorials, and online communities allow individuals to acquire knowledge and skills outside traditional classroom settings. While these alternatives may not offer formal credentials, they can effectively substitute for certain aspects of formal education, especially for driven learners.
These substitutes present a significant challenge to traditional public education models. For instance, the global Open Educational Resources (OER) market was valued at approximately $2.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. This indicates a strong and increasing preference for accessible, often free, learning materials.
- Growing Accessibility: The internet provides a vast repository of knowledge, making it easier than ever to learn new subjects independently.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many self-learning resources are free or significantly cheaper than traditional tuition fees.
- Flexibility: Learners can study at their own pace and on their own schedule, fitting education around other commitments.
- Skill-Specific Learning: Online platforms often excel at providing targeted instruction for specific skills, which can be more appealing than broad academic curricula for some individuals.
The threat of substitutes to traditional American public education is substantial, driven by alternative learning pathways that offer speed, cost-effectiveness, and direct skill acquisition. These substitutes range from vocational training and corporate upskilling to online learning platforms and self-directed study resources.
In 2024, the demand for skilled trades continued to surge, with vocational programs providing a direct route to employment. For example, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected strong growth for electricians and HVAC technicians, jobs often accessible through these alternative educational routes.
Online learning platforms, including MOOCs and specialized bootcamps, also represent a growing substitute. The global online education market, valued at over $250 billion in 2023, highlights a significant shift towards flexible and skill-focused learning options that can bypass traditional public education structures.
| Substitute Type | Key Appeal | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Vocational Training | Faster workforce entry, practical skills | High demand for skilled trades, e.g., electricians |
| Online Learning Platforms (MOOCs, Bootcamps) | Accessibility, cost-effectiveness, specialization | Global online education market exceeding $250 billion (2023) |
| Corporate Upskilling Programs | Job-specific training, career advancement | Increased corporate L&D budgets, some exceeding $1,000/employee |
| Self-Learning Resources (OER, Tutorials) | Low cost, flexibility, self-paced learning | OER market valued at $2.1 billion (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in American public education is generally moderate to high. Online learning platforms and alternative educational providers can enter the market with relatively lower initial investment compared to establishing traditional brick-and-mortar schools, which often require significant capital for facilities and accreditation.
This lower barrier to entry, particularly in the digital space, allows for quicker market penetration. For instance, the rapid growth of online course providers and charter schools, which can be established more flexibly than traditional public school districts, demonstrates this trend. The increasing demand for flexible learning options further fuels this threat.
The threat of new entrants in American public education is generally low due to substantial barriers. These include the critical need for national and programmatic accreditation, a complex and lengthy undertaking for any new institution or program.
Meeting accreditation standards demands significant financial investment in robust quality assurance systems, continuous curriculum enhancement, and ensuring highly qualified faculty. For instance, the Council for Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA) oversees numerous recognized accrediting bodies, each with its own stringent requirements, making market entry a considerable challenge.
The threat of new entrants in American public education is moderate. Building a strong brand reputation and trust, especially in the online space, demands significant marketing investment and a proven history of student achievement. New players must contend with the established credibility of institutions like American Public Education, Inc. (APEI).
4
The threat of new entrants into American public education is generally moderate. Significant regulatory complexities, such as state authorization requirements and compliance with federal financial aid regulations like Title IV, create substantial barriers. For instance, navigating the labyrinth of state-specific approval processes and accreditations can be time-consuming and costly, deterring many potential new providers.
Furthermore, the evolving regulatory landscape, including potential shifts in federal and state policies regarding funding, accountability, and student privacy, adds a layer of complexity and risk for new institutions. This uncertainty can make long-term planning and investment more challenging. In 2024, the Department of Education continued to emphasize compliance and oversight, making it harder for unproven entities to gain traction.
However, certain niches within public education, particularly in specialized vocational training or online learning platforms, might see lower entry barriers. These areas can attract new players who leverage technology and innovative delivery models. Despite these opportunities, the overarching need for robust infrastructure, qualified faculty, and established reputation remains a significant hurdle for widespread new entry.
Key barriers for new entrants include:
- Stringent State Authorization: Each state has unique requirements for educational institutions to operate, often involving extensive documentation and fees.
- Federal Financial Aid Compliance: Adhering to complex federal regulations, such as those governing Title IV student aid programs, demands significant administrative and financial resources.
- Accreditation Hurdles: Gaining and maintaining accreditation from recognized bodies is a lengthy and rigorous process essential for legitimacy and financial aid eligibility.
- Capital Investment: Establishing the necessary physical or digital infrastructure, hiring qualified staff, and developing curriculum requires substantial upfront capital.
5
The threat of new entrants into American public education is moderate. While the barrier to entry isn't as high as in some industries, significant capital investment is still necessary. This includes funding for robust technology infrastructure, attracting and retaining skilled faculty, and establishing comprehensive student support systems. For instance, a new online public charter school might need millions to develop its learning platform and recruit qualified teachers, even without physical campuses.
New players also face the challenge of securing substantial funding for aggressive marketing campaigns. In a crowded educational landscape, attracting students requires significant outreach and brand building. Data from 2024 indicates that marketing budgets for educational institutions can easily reach hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of dollars annually to compete effectively for enrollment.
- Capital Investment: While lower than traditional brick-and-mortar institutions, significant investment is still required for technology, faculty, and student support.
- Marketing Costs: Aggressive marketing is essential to attract students in a competitive market, necessitating substantial financial outlay.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating state and federal regulations for public education can be complex and costly for new entrants.
- Brand Recognition: Established public school districts often benefit from existing brand recognition and community trust, making it harder for newcomers to gain traction.
The threat of new entrants in American public education is generally moderate. While online platforms can lower some entry barriers, significant hurdles remain, including stringent state authorization and federal financial aid compliance. For example, navigating Title IV regulations requires substantial administrative resources, a challenge for many new providers.
Accreditation is another major barrier, demanding rigorous quality assurance and faculty qualifications, as overseen by bodies like CHEA. Furthermore, building brand trust and securing adequate capital for marketing and infrastructure, estimated in the millions for new online schools in 2024, presents considerable challenges for newcomers aiming to compete with established institutions.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for American public education leverages data from government education statistics agencies, academic research databases, and reports from educational policy think tanks to assess competitive dynamics.