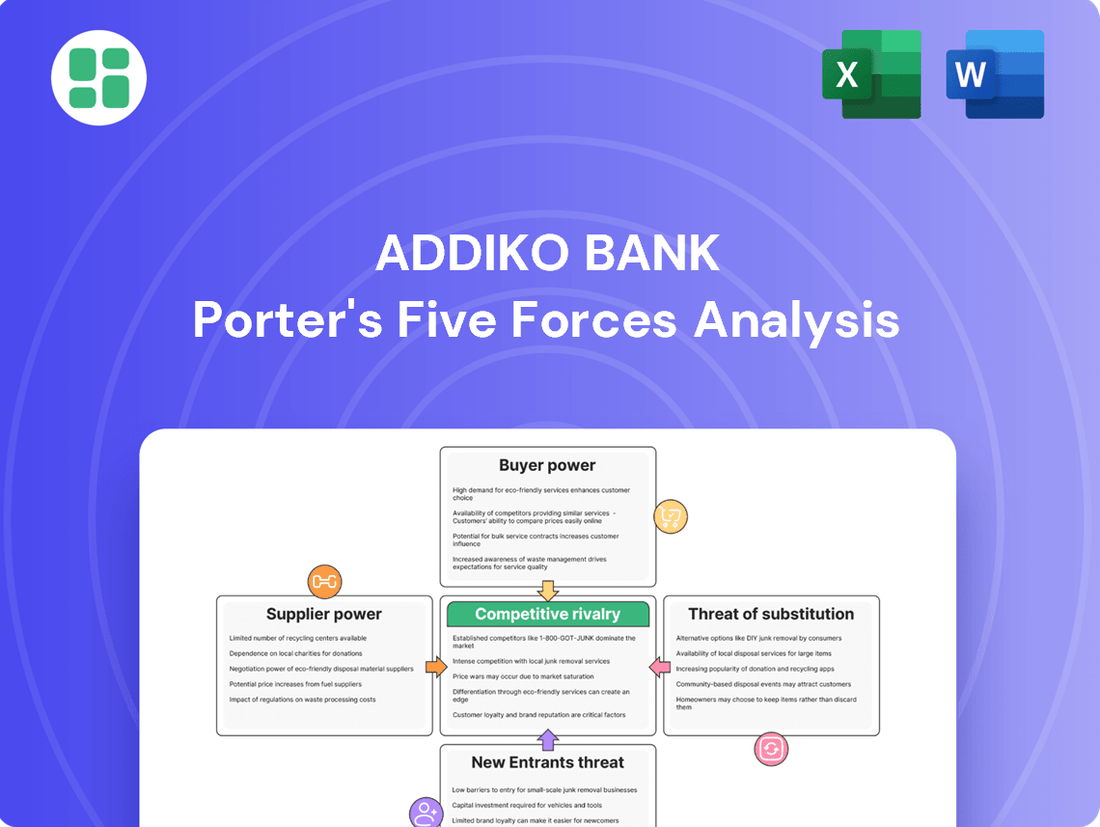
Addiko Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Addiko Bank Bundle
Addiko Bank faces significant competitive pressures, with the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers posing notable challenges. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the banking landscape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Addiko Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Addiko Bank's reliance on a wide retail depositor base provides a stable funding foundation. This broad distribution of funds generally limits the bargaining power of any single depositor. However, the competitive environment in Central and Eastern Europe means Addiko must offer competitive rates to secure and retain these crucial deposits, impacting its cost of funding.
Addiko Bank's strategic push into digital and mobile banking, exemplified by its 'Acceleration Program' and the planned 2025 digital consumer lending rollout, significantly elevates its dependence on technology and digital solution providers. This reliance grants these specialized suppliers, especially those in advanced AI and cybersecurity, considerable leverage.
The critical nature and intricate complexity of the solutions offered by these technology vendors are key drivers of their bargaining power. Their innovations are not just beneficial but essential for Addiko Bank's ability to execute its competitive strategy in the evolving financial landscape.
Beyond customer deposits, Addiko Bank relies on interbank markets for short-term liquidity and capital markets for longer-term funding. The cost and availability of these wholesale funds are heavily influenced by macroeconomic conditions, central bank policies, and overall investor sentiment. For instance, in early 2024, central banks in regions where Addiko operates maintained relatively high interest rates, increasing the cost of borrowing for banks.
These external financial markets wield significant supplier power over Addiko Bank. When market liquidity tightens or investor confidence wanes, the cost of obtaining funds can surge, directly impacting Addiko's profitability and operational capacity. This dependence means Addiko must navigate these dynamic markets carefully to manage its funding costs effectively.
Human Capital (Skilled Talent)
The increasing demand for specialized skills in areas like IT, data analytics, and digital product development significantly boosts the bargaining power of skilled human capital. Addiko Bank, like many in the Central and Eastern European (CEE) region, faces a competitive landscape for this talent, which can translate into higher salary expectations and retention challenges.
- High demand for digital and data skills: Banks are investing heavily in technology, creating a premium for employees with expertise in AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing.
- Talent scarcity in CEE: The CEE region, while growing, may have a more limited pool of highly specialized talent compared to more mature markets, intensifying competition.
- Impact on wage costs: A tight labor market for skilled professionals can drive up recruitment and compensation costs for Addiko Bank.
Regulatory Bodies
Financial regulators, including the European Central Bank (ECB) and national authorities, exert significant influence as indirect suppliers by dictating operational frameworks. Their mandates on capital adequacy, such as the Basel III requirements, and evolving compliance standards, like the upcoming MREL requirements for 2025, directly impact Addiko Bank's strategic flexibility and impose substantial costs. These regulatory impositions effectively limit the bank's ability to pursue certain business strategies or allocate capital freely, akin to a supplier dictating terms.
The bargaining power of these regulatory bodies is substantial, as non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, reputational damage, and even operational restrictions. For instance, the ongoing focus on operational resilience, with new guidelines expected to be fully implemented by 2025, requires significant investment in technology and processes. This necessitates Addiko Bank to adapt its operations to meet these evolving demands, thereby increasing its operating costs and influencing its service offerings.
- Regulatory Imposition: Financial regulators set capital requirements and compliance standards, directly impacting Addiko Bank's operational costs and strategic choices.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to regulations like MREL and operational resilience guidelines (effective 2025) incurs significant investment, limiting financial flexibility.
- Strategic Constraint: Evolving regulatory landscapes, driven by bodies like the ECB, restrict Addiko Bank's operational freedom and ability to innovate without regulatory approval.
Addiko Bank's reliance on technology providers, particularly for digital transformation initiatives, grants these specialized suppliers significant bargaining power. The complexity and critical nature of solutions in areas like AI and cybersecurity mean these vendors can dictate terms, influencing Addiko's operational costs and strategic execution.
The bank's dependence on external financial markets for liquidity and capital also presents a supplier power dynamic. In early 2024, higher interest rates in CEE markets increased borrowing costs, directly impacting Addiko's funding expenses and profitability. This highlights the influence of market conditions and central bank policies on the bank's financial stability.
Skilled human capital, especially in digital and data analytics, is another area where suppliers hold considerable leverage. Addiko Bank faces intense competition for talent in the CEE region, leading to increased wage expectations and retention challenges, which can drive up operational costs.
Regulatory bodies, such as the ECB, act as powerful indirect suppliers by imposing capital adequacy and compliance standards. Requirements like MREL and operational resilience guidelines, with full implementation expected by 2025, necessitate significant investment, limiting Addiko's financial flexibility and strategic options.
| Supplier Type | Key Dependence | Impact on Addiko Bank | Example Data (Early 2024 CEE Rates) | Leverage Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers | Digital Transformation, AI, Cybersecurity | Higher costs for specialized solutions, potential delays | N/A (Specific vendor contracts not public) | High |
| Financial Markets | Liquidity, Wholesale Funding | Increased borrowing costs, reduced profitability | Average CEE policy rates around 4-6% | Medium to High |
| Skilled Human Capital | IT, Data Analytics, Digital Skills | Higher recruitment and retention costs, talent shortages | Estimated 10-15% salary increase for sought-after tech roles | High |
| Regulatory Bodies | Capital Adequacy, Compliance | Increased compliance costs, strategic constraints | MREL requirements for 2025 | Very High |
What is included in the product
This analysis provides a comprehensive assessment of the competitive forces impacting Addiko Bank, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the influence of substitute products.
Instantly identify and address competitive pressures with a clear, visual breakdown of Addiko Bank's industry landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in Central and Southeastern Europe enjoy a wealth of banking options, from established traditional institutions to nimble fintech startups and international digital banks. This competitive landscape, where over 60% of banking customers in the region are estimated to use at least one digital channel, means individuals and businesses can easily compare offerings and switch providers. This abundance of choice significantly amplifies customer bargaining power, as they can readily seek out better interest rates, lower fees, and superior service quality.
For basic banking needs, switching costs have dropped considerably. Digital onboarding makes it simple to open new accounts, and better system compatibility means customers can move their money and services more easily. This trend empowers customers by giving them more choices and flexibility.
While some small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may have more integrated banking services, making a switch a bit more complex, the general direction is clear: it's becoming easier for customers to change banks. This increased ease of transition directly boosts their bargaining power against financial institutions.
Digital platforms and financial aggregators have significantly boosted information transparency for consumers. Customers can now effortlessly compare loan rates, deposit yields, and service fees from various institutions. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of banking customers in the EU utilized online comparison tools before making financial decisions, driving a greater demand for competitive offerings.
This ease of access to comparative data empowers customers and directly impacts banks like Addiko. It compels them to offer more competitive pricing and higher service quality to attract and retain clients. In the consumer lending sector, where price sensitivity is high, this transparency ensures that banks must remain diligent in their pricing strategies to avoid losing business to rivals.
Rising Digital Expectations and Demand for Convenience
Modern customers, particularly younger generations, now expect constant, easy digital access to their banking needs, along with tailored financial advice and intuitive mobile apps. In 2023, for instance, the adoption of digital banking services continued its upward trend, with a significant portion of transactions occurring through mobile channels across the European banking sector. Addiko Bank's commitment to enhancing its digital platforms directly addresses this shift, recognizing that a failure to meet these elevated digital standards can push customers towards rivals who offer a more streamlined and convenient experience.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by these rising digital expectations and the relentless demand for convenience. Banks that fail to innovate and provide seamless digital journeys risk losing market share. For example, customer satisfaction scores are increasingly tied to the quality of a bank's digital interface and the speed of its online services.
- Digital Channel Dominance: By Q4 2023, over 70% of routine banking transactions for many European banks were conducted via digital channels, highlighting customer preference for self-service and 24/7 accessibility.
- Mobile App Engagement: The average monthly active users of leading banking mobile applications saw a 15% increase in 2023 compared to the previous year, indicating a strong reliance on these platforms for daily financial management.
- Personalization Demand: Surveys from late 2023 revealed that over 60% of banking customers expect personalized financial advice and product recommendations delivered through their digital banking platforms.
- Switching Behavior: A notable percentage of customers, often cited between 10-20% in recent studies, indicated a willingness to switch banks if their digital banking experience is perceived as subpar or inconvenient.
Price Sensitivity in Lending Segments
Even with Addiko Bank's strategy of premium pricing in consumer lending, customers, both individuals and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), remain keenly aware of interest rates, fees, and the total cost of borrowing. This price sensitivity means they will shop around for better deals.
The subdued demand observed in the SME loan market during 2024 is a clear indicator of this customer behavior. SMEs are actively looking for the most competitive pricing and favorable terms, which directly affects Addiko's ability to expand its presence in this segment.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers, including SMEs, are highly responsive to interest rates and fees in the lending market.
- Muted SME Demand (2024): This trend highlights customers' pursuit of better pricing and terms, impacting Addiko's growth.
- Competitive Landscape: Customers' willingness to seek out more affordable options puts pressure on Addiko to remain competitive.
Customers in Central and Southeastern Europe have numerous banking choices, leading to heightened bargaining power. The ease of comparing services and switching providers means banks must offer competitive rates and superior service to retain clients.
Digital platforms have increased transparency, allowing customers to easily compare offerings, which pressures banks to maintain competitive pricing, especially in price-sensitive areas like consumer lending. This transparency ensures banks must be diligent in their pricing strategies.
Rising digital expectations mean customers demand seamless online experiences and personalized services. Banks that fail to innovate in their digital offerings risk losing market share to competitors providing more convenient solutions. Customer satisfaction is increasingly linked to digital interface quality.
| Metric | 2023/2024 Data | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Transaction Share | Over 70% (Q4 2023) | Increases customer self-service and reduces reliance on traditional channels, facilitating easier switching. |
| Mobile App User Growth | 15% increase in monthly active users (2023) | Indicates strong customer preference for digital platforms, giving them more leverage to demand better digital experiences. |
| Demand for Personalization | Over 60% expect personalized advice (late 2023) | Customers can leverage this expectation to seek out banks offering tailored services, increasing their power. |
| Willingness to Switch Banks | 10-20% (recent studies) | A significant portion of customers are prepared to move for better digital experiences, directly empowering them. |
What You See Is What You Get
Addiko Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Addiko Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape including threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You'll receive this exact, professionally formatted analysis, providing actionable insights into Addiko Bank's strategic positioning and the external factors influencing its profitability.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The banking sector in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE) presents a dynamic competitive environment. It's a mosaic of local banks, established regional players, and international institutions, all vying for customers, creating a fragmented market. This fragmentation means a diverse range of offerings and pricing, but also a constant push for differentiation.
Despite the fragmentation, a significant trend towards consolidation is reshaping the CEE banking landscape. Mergers and acquisitions are becoming more common as banks aim to achieve greater economies of scale, enhance their technological capabilities, and solidify their market presence. For instance, in 2023, the CEE region saw several notable banking deals, reflecting this drive for consolidation and increased competitiveness.
Addiko Bank's strategic emphasis on consumer and SME lending means it faces significant competition. Many established banks and nimble fintech companies are also vying for these lucrative customer bases. This intense rivalry is particularly evident in consumer loans, driving pressure on pricing and the need for unique service offerings.
Digitalization and innovation are now the main arenas where banks compete. Addiko Bank, for instance, is actively investing in its digital platforms and mobile banking capabilities, mirroring a broader industry trend. This focus is crucial for enhancing customer experience and streamlining operations. In 2024, the European banking sector saw significant investment in fintech solutions, with digital transformation being a top priority for many institutions.
Profitability Pressures Amidst Interest Rate Changes
While Central and Eastern European banking markets have historically demonstrated robust profitability, recent shifts are creating new competitive dynamics. A key factor is the anticipated decline in net interest margins from their 2023 highs, coupled with persistent inflationary pressures on operating costs. This combination directly squeezes profitability, forcing banks like Addiko Bank to intensify efforts in operational optimization and strategic growth within their core markets to sustain financial performance.
The intensified pressure on profitability necessitates a sharp focus on efficiency and targeted growth initiatives. Banks are compelled to streamline their operations and explore new revenue streams in areas where they hold a competitive advantage. For instance, in 2024, many CEE banks are prioritizing digital transformation to reduce costs and improve customer experience, aiming to offset margin compression.
- Declining Net Interest Margins: Following peaks in 2023, net interest margins are expected to moderate, impacting a primary source of bank revenue.
- Inflationary Cost Pressures: Rising operational costs due to inflation require banks to enhance efficiency to protect profitability.
- Focus on Operational Optimization: Banks are investing in technology and process improvements to reduce cost-to-income ratios.
- Strategic Growth Areas: Identifying and capitalizing on growth opportunities in specific product lines or customer segments is crucial for maintaining competitive standing.
Impact of M&A Activity and Shareholder Changes
Recent takeover bids and shifts in Addiko Bank's shareholder structure highlight how mergers and acquisitions significantly impact competitive rivalry. For instance, in early 2024, reports indicated continued interest from potential acquirers, reflecting the ongoing consolidation trend in the European banking sector. These activities can swiftly reshape market dynamics, potentially leading to a more concentrated or fragmented competitive landscape depending on the deal's outcome.
These changes in ownership can directly influence how Addiko Bank competes. A new majority shareholder might bring a different strategic vision, potentially leading to aggressive pricing, new product offerings, or a focus on different customer segments. This dynamism creates both uncertainty for existing players and opportunities for strategic repositioning within the market.
- Shareholder Activism: Increased shareholder activism can pressure management to prioritize short-term gains, potentially affecting long-term competitive strategies.
- M&A Impact: A successful acquisition of Addiko Bank by a larger entity could lead to significant operational efficiencies and a stronger competitive position against rivals.
- Market Consolidation: The ongoing trend of M&A in the banking sector means that Addiko Bank must constantly adapt to a changing competitive environment where larger, more integrated players may emerge.
- Strategic Alliances: In the absence of a takeover, Addiko Bank might pursue strategic alliances or partnerships to bolster its competitive standing, especially in areas like digital banking or specialized financial services.
Addiko Bank faces intense competition from a mix of local banks, regional powerhouses, and international financial institutions across Central and Eastern Europe. This rivalry is particularly sharp in consumer and SME lending, pushing banks to innovate in digital services and pricing strategies. The ongoing trend of consolidation, with several significant deals in 2023 and continued M&A interest in early 2024, further intensifies this competitive landscape.
The pressure on net interest margins, expected to decline from 2023 peaks, coupled with rising operational costs due to inflation, forces banks like Addiko to prioritize efficiency. In 2024, European banks are channeling significant investment into fintech and digital transformation to cut costs and enhance customer experience, directly impacting competitive dynamics.
| Metric | 2023 (Est.) | 2024 (Proj.) | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Interest Margin (CEE Avg.) | ~3.0% | ~2.7% | Increased pressure on revenue, driving efficiency focus. |
| Digital Banking Adoption | ~60% | ~65% | Key differentiator; banks investing heavily in platforms. |
| Cost-to-Income Ratio (CEE Avg.) | ~55% | ~53% | Efficiency gains are crucial for maintaining profitability. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech lending platforms present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Addiko Bank. These platforms, including peer-to-peer (P2P) lenders and direct digital lenders, offer streamlined and often faster loan application and approval processes for both consumers and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). For instance, by mid-2024, the global P2P lending market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating a substantial shift in borrowing behavior away from traditional institutions.
The convenience and speed offered by fintech alternatives directly challenge the established banking model. Many of these digital lenders can approve loans within minutes, a stark contrast to the days or weeks often required by traditional banks. This efficiency, coupled with potentially competitive interest rates, makes them an attractive substitute for customers seeking quick access to capital, thereby eroding market share for incumbent banks.
The rise of non-bank digital payment service providers (PSPs) and digital wallet solutions presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. These platforms, such as PayPal, Stripe, and Apple Pay, offer streamlined, often cheaper, and more convenient transaction experiences, particularly for online and mobile payments.
While not directly replacing all banking functions, these PSPs can effectively disintermediate Addiko Bank from crucial customer touchpoints and revenue generation, especially within the retail sector. For instance, in 2024, the global digital payments market continued its robust expansion, with transaction volumes projected to reach trillions of dollars, indicating a substantial shift in consumer behavior away from traditional payment methods.
The proliferation of embedded finance solutions presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. These integrated financial offerings, such as 'Buy Now, Pay Later' at online retailers or in-app lending, allow consumers to access credit and manage payments without directly engaging with a bank. For instance, the global embedded finance market was projected to reach $7.2 trillion by 2030, indicating a substantial shift in how consumers access financial products.
Direct Capital Market Access for Larger Businesses
Larger or rapidly growing small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that Addiko Bank serves may increasingly bypass traditional banking channels by accessing capital markets directly. This trend means they could issue corporate bonds or seek private equity funding, thereby reducing their reliance on bank loans for significant expansion initiatives. For instance, in 2024, the global market for corporate bond issuance saw continued activity, with companies across various sectors leveraging this avenue for substantial capital raising.
This shift presents a threat as it directly siphons off potentially lucrative financing business from banks like Addiko. As businesses mature and their funding needs grow, the allure of potentially more flexible terms or lower costs available through capital markets can become substantial. This is particularly relevant as companies gain the scale and creditworthiness to be attractive to institutional investors.
- Direct Capital Market Access: Larger SMEs can issue bonds or seek private equity, reducing bank dependence.
- Reduced Loan Demand: This trend directly impacts the demand for traditional bank financing.
- Market Trends: Corporate bond issuance remained a significant capital-raising tool for businesses in 2024.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Finance
The rise of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology poses a potential, albeit nascent, threat of substitution for traditional banking services in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE). While widespread adoption for mainstream banking is still developing, these technologies offer alternative avenues for payments, lending, and investments.
As regulatory landscapes around digital assets continue to mature, particularly in 2024 and looking towards 2025, new platforms may emerge that bypass conventional banking infrastructure. For instance, decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols are already enabling peer-to-peer lending and borrowing, potentially reducing reliance on banks for these functions. By mid-2024, the total value locked in DeFi protocols globally had surpassed $100 billion, indicating significant user engagement and capital flow outside traditional financial institutions.
- Emerging Alternative: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain offer new payment rails and investment vehicles.
- DeFi Growth: Decentralized finance platforms provide alternatives for lending and borrowing.
- Regulatory Evolution: Evolving regulations in 2024 and 2025 will shape the competitive landscape for these technologies.
- Potential Disruption: These innovations could facilitate financial activities outside traditional banking channels.
The threat of substitutes for Addiko Bank is substantial, stemming from a range of financial technology innovations and alternative capital sources. Fintech lending platforms, digital payment providers, embedded finance solutions, direct access to capital markets for SMEs, and the evolving landscape of cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance all present viable alternatives to traditional banking services.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Addiko Bank | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Lending | Speed, convenience, streamlined processes | Erodes market share in consumer and SME loans | Global P2P lending market projected in hundreds of billions |
| Digital Payments | Efficiency, lower costs, enhanced user experience | Disintermediates bank from customer transactions | Global digital payments market transaction volumes in trillions |
| Embedded Finance | Seamless integration into non-financial platforms | Reduces direct engagement with banks for credit | Global embedded finance market projected to reach $7.2T by 2030 |
| Capital Markets Access | Direct funding for larger SMEs via bonds/PE | Siphons off lucrative financing business | Continued significant corporate bond issuance activity in 2024 |
| Crypto/DeFi | Alternative payment rails, P2P lending | Potential for disintermediation as regulations mature | DeFi total value locked surpassed $100B mid-2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector faces formidable regulatory and capital hurdles, significantly limiting the threat of new entrants. For instance, in 2024, the European Banking Authority continued to emphasize robust capital adequacy ratios, with many banks maintaining Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratios well above the minimum regulatory requirements, often exceeding 15%.
These stringent requirements, including those mandated by Basel III and the upcoming DORA regulations, necessitate massive initial capital outlays and ongoing compliance investments, creating a substantial barrier that deters potential new competitors from establishing themselves as full-service banks.
The financial services sector, particularly banking, hinges on deep-seated brand trust and a loyal customer base, which are incredibly difficult and costly for new entrants to cultivate. For instance, acquiring a new customer in banking can cost significantly more than retaining an existing one, with estimates often ranging from five to twenty-five times higher. Addiko Bank, like other incumbent institutions, benefits from years of operational history and established relationships, creating a formidable barrier for newcomers aiming to attract and retain sensitive financial dealings like deposits and loans.
Incumbent banks like Addiko Bank enjoy substantial economies of scale in their technology infrastructure, extensive branch networks, and streamlined operational processes. For instance, in 2024, major European banks continued to invest billions in digital transformation, creating a high barrier for new players to replicate this technological advantage and achieve comparable cost efficiencies.
New entrants must overcome the significant hurdle of building out comprehensive operational capabilities, which demands massive initial capital outlay and considerable time. This operational complexity, coupled with the need to establish trust and regulatory compliance, acts as a strong deterrent, limiting the immediate threat of widespread new competition.
Niche Entry by Fintechs and Digital-Only Banks
The threat of new entrants for Addiko Bank is amplified by nimble fintechs and digital-only banks. While establishing a full banking license remains a hurdle, these disruptors often carve out niches, focusing on specific services like digital consumer lending or specialized small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) financing. Their technological prowess and streamlined operations allow them to offer attractive alternatives to underserved segments of the market.
These new players are not just targeting small gaps; they are actively expanding their portfolios. For instance, by 2024, the European fintech sector saw significant growth, with digital payment providers and challenger banks capturing a larger share of transactions. This gradual expansion of services means that what starts as a niche offering can evolve into a broader competitive challenge, forcing incumbents like Addiko Bank to adapt their strategies to retain customer loyalty and market share.
- Niche Focus: Fintechs and neo-banks often enter by targeting specific, underserved niches, such as digital-only consumer lending or specialized SME financing.
- Agility and Technology: They leverage agility and advanced technology to offer streamlined, user-friendly solutions.
- Service Expansion: These new entrants are progressively broadening their service offerings, moving beyond initial niche markets.
- Market Share Growth: By 2024, digital-only banking services continued to gain traction across Europe, indicating a growing competitive pressure on traditional banks.
Access to Stable Funding and Skilled Talent
New entrants to the banking sector, like Addiko Bank's competitors, face significant challenges in securing the substantial initial capital required. Beyond just seed money, they need reliable and stable funding sources, such as a robust and diversified deposit base, which is difficult to build quickly. For instance, in 2024, traditional banks continued to rely heavily on customer deposits, which formed a significant portion of their funding structure, a hurdle for newcomers aiming to compete on lending capacity.
Access to skilled talent is another major barrier. The modern banking landscape demands expertise not only in traditional financial operations but also in rapidly evolving digital technologies, cybersecurity, and data analytics. Attracting and retaining top talent in these competitive fields is crucial for any new entrant aiming to offer innovative services and compete effectively with established players like Addiko Bank.
- Capital Requirements: New entrants need substantial capital for licensing, technology, and operational setup.
- Funding Sources: Establishing a stable, diversified deposit base is critical for long-term viability.
- Talent Acquisition: Banks require skilled professionals in both traditional finance and digital innovation.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex banking regulations adds to the cost and time for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Addiko Bank is generally considered moderate, primarily due to high barriers to entry. These include significant capital requirements and stringent regulatory compliance, which necessitate substantial upfront investment and ongoing operational costs. For example, in 2024, European banking regulations continued to enforce robust capital adequacy, with many established banks maintaining CET1 ratios well above 15%, a benchmark difficult for newcomers to match immediately.
While traditional full-service banks face these high barriers, nimble fintechs and digital-only banks pose a more dynamic threat by targeting specific market niches with advanced technology. These players are increasingly expanding their service portfolios, as seen in the 2024 growth of digital payment providers and challenger banks capturing more European transactions, forcing incumbents like Addiko Bank to remain competitive through innovation and customer retention.
New entrants must also contend with the challenge of building brand trust and customer loyalty, which takes considerable time and resources. Acquiring a new banking customer can cost significantly more than retaining an existing one, often ranging from five to twenty-five times higher. Addiko Bank benefits from its established history and relationships, creating a substantial hurdle for new players seeking to attract and retain customers for core financial services.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Substantial initial investment for licensing, technology, and operations. | High deterrent for full-service banking. | Maintaining CET1 ratios above 15% for regulatory compliance. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating complex and evolving financial regulations. | Increases cost, time, and complexity. | Adapting to new data protection and digital operational resilience regulations. |
| Brand Trust & Loyalty | Building a reputation and customer base in a trust-sensitive industry. | Difficult and costly to acquire customers. | Customer acquisition costs can be 5-25x higher than retention costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Leveraging existing infrastructure, technology, and networks. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies. | Billions invested by major European banks in digital transformation. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Addiko Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of reliable data, including the bank's official annual reports, publicly available financial statements, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate data from reputable financial news outlets and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.