ACCESS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ACCESS Bundle
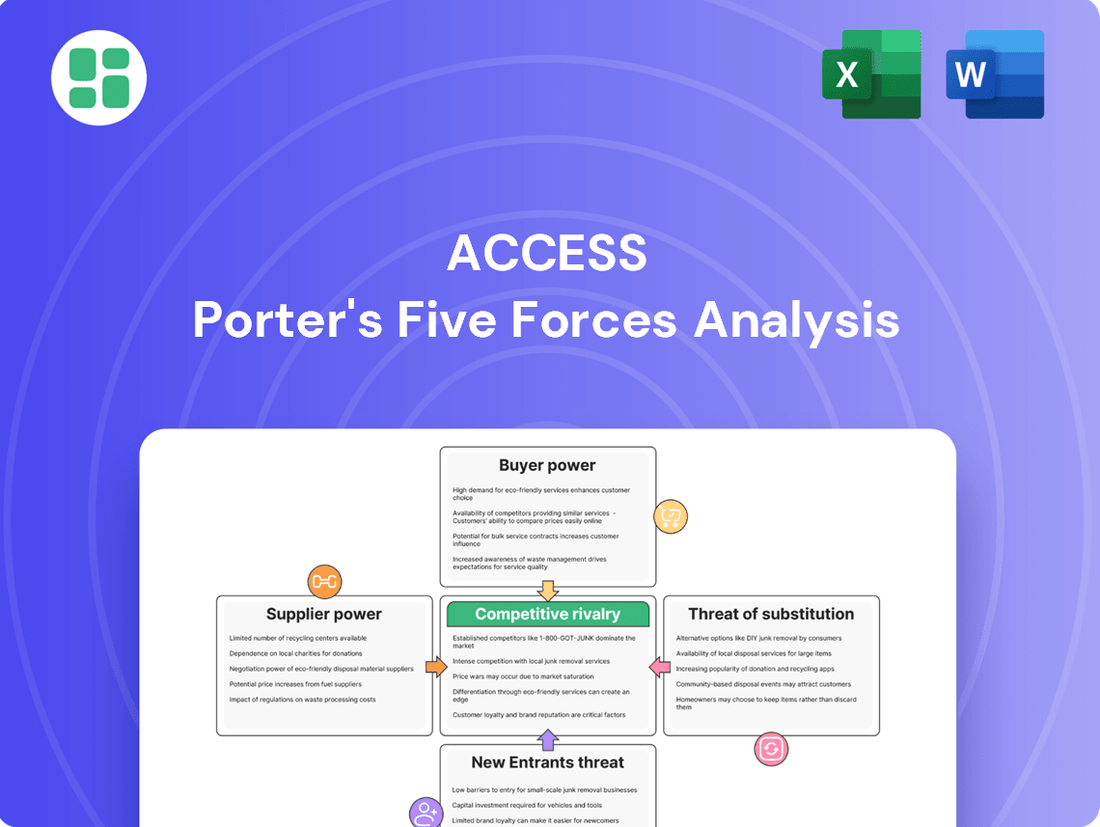
Understanding the competitive landscape for ACCESS is crucial for strategic success. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intricate interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, the intensity of rivalry, and the pressure from substitute products. This framework provides a clear picture of the forces shaping ACCESS's market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping ACCESS’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
ACCESS's reliance on foundational technologies like browser engines and operating systems grants significant power to their suppliers. If these core technologies are proprietary or come with complex licensing, switching costs for ACCESS can be substantial, limiting their flexibility.
The embedded software market, a key area for ACCESS, often features specialized components with few suppliers. This scarcity can amplify supplier leverage, as ACCESS may have limited alternatives for critical software elements, impacting their operational efficiency and product development timelines.
The development of sophisticated embedded, mobile, and network software solutions hinges on highly specialized engineering talent. A scarcity of skilled professionals in fields such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and niche programming languages like C++ significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these human capital providers.
For companies like ACCESS, this translates into a necessity to allocate substantial resources towards talent acquisition and retention strategies. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI engineers outstripped supply by a considerable margin, with some reports indicating over 500,000 open positions globally. This talent crunch directly impacts labor costs and the ability to secure critical expertise.
Hardware component providers for embedded systems can wield significant bargaining power over ACCESS. When ACCESS integrates its software into devices, it relies on a steady supply of microcontrollers, processors, and sensors from these manufacturers. If these critical components are highly specialized or have extended production timelines, suppliers gain leverage.
This power is amplified when the market for these essential hardware components is dominated by a small number of key players. For instance, in the automotive sector, where ACCESS has a strong presence, the concentration of microcontroller suppliers means these companies can dictate terms. In 2024, the global semiconductor market, which underpins these components, experienced fluctuations, with lead times for certain advanced chips sometimes extending for months, underscoring the suppliers' influence.
Open-Source Software Contributions
ACCESS's reliance on open-source software (OSS) contributions grants suppliers, meaning the OSS community, a degree of bargaining power. While OSS offers significant cost savings, estimated to be in the tens of billions of dollars annually for businesses globally, ACCESS is beholden to the maintainers and contributors for crucial updates and security patches. For instance, a major Linux distribution update or a critical vulnerability discovered in a widely used OSS library could necessitate immediate, potentially disruptive, adaptation by ACCESS.
Changes in licensing terms or the strategic direction of key OSS projects could also impact ACCESS's operations. The Apache Software Foundation, a prominent steward of many OSS projects, has a vast ecosystem that ACCESS likely leverages. A shift in governance or a change in the development roadmap for a core component could force ACCESS to seek alternatives or invest heavily in custom development, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
- Dependency on OSS Maintainers: ACCESS's operational continuity is tied to the ongoing support and development of the open-source projects it utilizes.
- Potential for Licensing Changes: Modifications to OSS licenses could impose new restrictions or costs, affecting ACCESS's ability to use or distribute its software.
- Impact of Security Vulnerabilities: Discoveries of critical security flaws in OSS components require prompt action from ACCESS, highlighting the power of the OSS community to dictate urgent technical responses.
- Community-Driven Development: The direction and pace of innovation within OSS projects are determined by their communities, which can indirectly influence ACCESS's product roadmap and feature availability.
Cloud Infrastructure and Development Tool Providers
The bargaining power of cloud infrastructure and development tool providers is a significant factor for companies like ACCESS. As software development becomes more reliant on cloud services and advanced tools, providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform can exert considerable influence. Their pricing strategies, the terms of their service level agreements (SLAs), and the features they offer directly affect ACCESS's operational expenses and the speed at which it can develop and deploy its services.
The concentration of major cloud providers means that switching costs can be substantial, giving these suppliers leverage. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market was dominated by these three hyperscalers, with AWS holding approximately 31% of the market share, Azure around 24%, and Google Cloud at 11%. This market concentration allows them to dictate terms and pricing, impacting ACCESS's ability to negotiate favorable contracts. Furthermore, specialized development tools, often proprietary, can also create dependencies, further enhancing supplier power.
- Market Dominance: A few major cloud providers control a significant portion of the market, limiting ACCESS's negotiation options.
- Switching Costs: Migrating applications and data between cloud platforms can be complex and expensive, locking companies in.
- Essential Services: Cloud infrastructure and advanced development tools are increasingly critical for modern software operations, making ACCESS reliant on these suppliers.
- Pricing Power: Providers can adjust pricing based on demand and their own cost structures, directly impacting ACCESS's IT budget.
ACCESS's reliance on specialized hardware components, particularly in the embedded systems sector, grants significant bargaining power to its suppliers. When a small number of manufacturers dominate the market for critical components like microcontrollers or specialized processors, they can dictate terms and pricing. This is evident in 2024, where supply chain constraints and high demand in sectors like automotive, a key market for ACCESS, led to extended lead times for certain semiconductors, empowering these component providers.
| Supplier Type | Impact on ACCESS | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor Manufacturers | High dependence on specialized chips; potential for price increases and supply disruptions. | Lead times for advanced chips in automotive sector extended; market concentration among key players. |
| Proprietary Software Providers | Limited alternatives for core technologies; high switching costs for essential software. | Continued reliance on established OS and browser engine providers. |
| Open-Source Software (OSS) Maintainers | Dependence on community for updates and security; vulnerability to licensing changes. | Billions saved annually by businesses using OSS, but critical updates can force rapid adaptation. |
| Cloud Service Providers | Significant operational costs; lock-in due to high migration expenses. | Hyperscalers (AWS, Azure, Google) dominate market; AWS held ~31% market share in 2024. |
What is included in the product
ACCESS's Porter's Five Forces analysis meticulously dissects the competitive intensity within its operating environment, examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Navigate complex market landscapes by clearly mapping the forces that impact profitability and strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
When ACCESS provides deeply integrated software solutions, like those found in automotive infotainment systems or consumer electronics, customers encounter significant hurdles if they decide to switch. For instance, a car manufacturer that has spent years and considerable resources embedding ACCESS's software into its vehicle platforms would face substantial costs to replace it.
These costs aren't just monetary; they involve extensive re-tooling of manufacturing processes, rigorous re-certification of the new software for safety and performance standards, and comprehensive retraining of engineers and assembly line workers. This complexity effectively locks customers in, diminishing their ability to negotiate better terms or switch to competitors easily.
ACCESS's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by customer concentration. If a few dominant players in a sector, like major automotive manufacturers or leading consumer electronics firms, represent a substantial portion of ACCESS's revenue, these key customers can wield considerable influence. For instance, if these large clients collectively account for over 40% of ACCESS's sales in a particular segment, they can leverage their volume to negotiate better pricing or demand tailored product specifications.
Large enterprise clients, particularly in sectors like automotive and publishing, often boast substantial in-house software development expertise. This capability significantly diminishes their reliance on external providers such as ACCESS.
With the ability to develop solutions internally, these sophisticated customers gain leverage to negotiate more favorable terms or even bypass vendors altogether. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer with a dedicated AI and software division might opt to build its own infotainment system software rather than licensing it, directly impacting a software vendor's market position.
Price Sensitivity in Competitive Markets
In mature or highly competitive markets, customers often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is particularly true in sectors like consumer electronics, where numerous alternatives exist. For a company like ACCESS, this heightened price sensitivity directly translates into increased bargaining power for its customers.
When customers can easily switch to competitors offering similar products at lower prices, they gain leverage. This forces ACCESS to consider price adjustments or offer more attractive terms to retain business. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer electronics market saw price competition intensify, with some product categories experiencing year-over-year price drops of up to 10% due to oversupply and demand shifts.
- Price Sensitivity Impact: Customers in competitive markets can demand lower prices, impacting ACCESS's profit margins.
- Market Dynamics: Mature markets often feature established players and readily available substitutes, amplifying customer choice.
- Competitive Landscape: In 2024, the global consumer electronics market faced challenges with a projected 2% contraction in revenue, driven by economic headwinds and increased competition, putting further pressure on pricing strategies for companies like ACCESS.
Access to Alternative Solutions
The existence of numerous alternative browser technologies, operating systems, and digital publishing platforms significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. For instance, the widespread availability of open-source operating systems and browsers means customers are not solely reliant on proprietary solutions.
Customers can effectively leverage these alternatives to negotiate more favorable terms or readily switch providers if ACCESS's products fail to align with their changing requirements or price sensitivities. This competitive landscape empowers customers to demand better value, directly impacting ACCESS's pricing strategies and market position.
- Market Share of Open-Source Browsers: As of early 2024, browsers like Firefox, which often champion open standards, maintained a notable share of the global browser market, demonstrating customer preference for alternatives.
- Operating System Diversity: The continued strength of various operating systems, including those with open-source foundations, provides users with a broad choice beyond dominant proprietary systems, further enhancing their bargaining leverage.
- Digital Publishing Platform Competition: The proliferation of digital publishing platforms, many offering flexible integration and pricing models, gives content creators and distributors alternatives to traditional or platform-specific solutions.
When customers have many choices or can easily switch, their power increases. This is especially true in markets where ACCESS faces numerous competitors offering similar software solutions. For example, the global market for embedded software, a key area for ACCESS, is characterized by a wide array of providers, many offering specialized or cost-effective alternatives.
| Market Segment | Key Competitors/Alternatives | Customer Bargaining Power Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Infotainment | BlackBerry QNX, Android Automotive, Apple CarPlay | High (due to multiple established alternatives) |
| Consumer Electronics Software | Various OS providers, custom development shops | Moderate to High (depending on product complexity and vendor lock-in) |
| Digital Publishing Platforms | Adobe, various CMS providers, open-source solutions | High (due to platform diversity and integration flexibility) |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
ACCESS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for ACCESS, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. You’re previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Rivalry Among Competitors
ACCESS operates across a broad spectrum of technology sectors, including embedded software, mobile solutions, network infrastructure, and digital content. This wide reach means the company encounters a varied group of competitors, from highly specialized niche players to large, diversified technology conglomerates.
For instance, in the embedded software space, ACCESS might compete with companies focusing solely on automotive operating systems, while in mobile software, it could face off against major app developers or platform providers. This fragmentation means competitive pressures can differ significantly across ACCESS's various business units.
The sheer diversity of its operating segments contributes to a fragmented competitive landscape, where ACCESS must contend with rivals possessing deep expertise in specific areas, as well as broader tech giants with substantial resources and market influence.
The software industry, especially in areas like embedded systems and mobile technology, sees incredibly fast progress. This means companies like ACCESS must consistently pour significant money into research and development to keep up. For instance, in 2023, the global software market was valued at over $700 billion, with a substantial portion dedicated to R&D.
Companies are constantly pushing boundaries by integrating new technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and 5G. This relentless innovation cycle creates intense competitive pressure. ACCESS, to remain relevant and competitive, faces the challenge of not only matching but exceeding these advancements to maintain its market position.
ACCESS faces intense competition from large, established global technology firms. These giants, such as Microsoft and Google, often possess significantly deeper pockets, allowing them to invest heavily in research and development, marketing campaigns, and strategic acquisitions. For instance, in 2024, major tech companies continued to announce substantial R&D budgets, with some exceeding tens of billions of dollars annually, enabling them to rapidly innovate and expand their offerings.
The sheer scale of these global competitors means they can leverage their broad market reach and extensive product portfolios to outmaneuver smaller players. They can also employ aggressive pricing tactics, potentially undercutting ACCESS on key services, and utilize their vast customer bases to cross-sell new products, thereby consolidating market share and creating significant barriers to entry for companies like ACCESS.
Importance of Strategic Partnerships and Ecosystems
Competitive rivalry in the digital access and content delivery space extends beyond direct company-to-company battles; it increasingly involves entire ecosystems. ACCESS's success hinges on its capacity to forge strategic alliances with hardware manufacturers, cloud service providers, and content creators. These partnerships are not merely beneficial; they are fundamental to building a robust and competitive offering.
Rivals that have cultivated strong, integrated ecosystems can erect significant barriers to entry for new players. These established networks leverage shared resources, customer bases, and technological synergies to create a powerful competitive advantage. For instance, a dominant hardware manufacturer partnering with a leading cloud provider and a popular content platform can present a formidable challenge to any competitor attempting to establish a foothold.
- Ecosystem Competition: The digital access market is increasingly characterized by competition between integrated ecosystems rather than isolated companies.
- Strategic Partnerships: ACCESS's ability to secure and nurture partnerships with hardware, cloud, and content providers is vital for its market position.
- Barriers to Entry: Strong rival ecosystems, built on extensive partnerships, can create substantial barriers for new entrants.
- Competitive Edge: Successful partnerships enhance a company's competitive edge by expanding reach, improving service offerings, and increasing customer loyalty.
Rapid Market Evolution and Disruption
ACCESS operates in markets characterized by swift technological advancements and evolving business strategies. The automotive sector, for instance, is rapidly shifting towards software-defined vehicles, a trend that introduces new competitive dynamics and demands constant innovation. Similarly, the rise of Edge AI and digital twins presents both opportunities and challenges, requiring ACCESS to adapt its offerings to stay relevant.
This rapid evolution means that established competitive advantages can erode quickly. Companies must be agile, investing in research and development to anticipate and respond to emerging technologies and changing customer preferences. For ACCESS, this necessitates a proactive approach to market changes, ensuring its products and services remain at the forefront of innovation.
The increasing prevalence of subscription-based business models across various industries further intensifies competition. This shift from one-time purchases to recurring revenue streams requires companies to focus on customer retention and continuous value delivery. ACCESS must therefore cultivate strong customer relationships and consistently enhance its offerings to maintain market share in this dynamic environment.
Key market shifts impacting competitive rivalry for ACCESS include:
- Software-Defined Vehicles: The automotive industry's pivot to software-centric architectures creates new avenues for competition, with software providers gaining prominence.
- Edge AI Adoption: The growing deployment of AI at the network edge demands specialized hardware and software solutions, intensifying competition among technology providers.
- Digital Twin Technology: The increasing use of digital twins for simulation and optimization in industries like manufacturing and automotive requires sophisticated platforms and expertise.
- Subscription Models: The widespread adoption of subscription services necessitates a focus on recurring revenue and customer loyalty, reshaping competitive strategies.
ACCESS faces fierce competition from both specialized niche players and large, diversified technology giants. This rivalry is amplified by the rapid pace of technological innovation, forcing companies to continuously invest in research and development to stay competitive. For instance, in 2023, global R&D spending in the software sector exceeded $150 billion, highlighting the intense pressure to innovate.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by the rise of integrated ecosystems, where partnerships with hardware, cloud, and content providers are crucial for success. Companies with strong, established ecosystems can create significant barriers to entry for others. For example, major tech firms in 2024 continued to leverage their vast partner networks to offer comprehensive solutions, often outmaneuvering less integrated competitors.
Market shifts like the automotive industry's move towards software-defined vehicles and the increasing adoption of Edge AI are creating new battlegrounds. Companies must remain agile and adapt their offerings to these evolving trends to maintain their market position. The subscription model's growing prevalence also demands a focus on customer retention and continuous value delivery, adding another layer to competitive rivalry.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristic | Competitive Pressure Example |
| Niche Players | Deep specialization in specific tech areas | Intense focus on specific embedded software features |
| Tech Giants | Vast resources, broad market reach | Aggressive pricing and cross-selling strategies |
| Ecosystems | Integrated partnerships (hardware, cloud, content) | Strong network effects creating high switching costs |
| Innovators | Rapid adoption of new technologies (AI, IoT, 5G) | Constant need for significant R&D investment |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large automotive OEMs and major consumer electronics companies are increasingly exploring in-house development of core software components like browser engines and operating systems. This trend is driven by a desire to gain greater control over their product roadmaps and intellectual property, directly threatening ACCESS's market share in these areas.
For instance, in 2024, several leading automakers announced significant investments in developing their own in-car operating systems, aiming for deeper integration and customization. This strategic shift means they might bypass third-party solutions, representing a substantial substitution risk for ACCESS's browser and digital publishing tools.
ACCESS faces a significant threat from open-source alternatives in its core software markets. For instance, Chromium, the open-source project behind Google Chrome, offers a powerful and widely adopted browser technology that directly competes with ACCESS's own browser solutions. Similarly, Linux-based operating systems provide robust, often free, alternatives for embedded systems, a key market for ACCESS.
These open-source options present a compelling value proposition, particularly for cost-conscious customers. The absence of licensing fees can translate into substantial savings, making them highly attractive substitutes. This cost advantage is a major driver for adoption, especially in markets where budget constraints are paramount.
The widespread availability and continuous development of open-source projects mean that they are not static competitors. As of early 2024, the Linux Foundation reported a significant increase in contributions to its various open-source projects, reflecting a dynamic and evolving ecosystem. This ongoing innovation ensures that open-source alternatives remain competitive and relevant against proprietary solutions.
Customers can easily switch to generic software platforms or cloud services that offer comparable features, especially for straightforward tasks where deep customization isn't needed. For instance, businesses requiring basic project management tools might find robust, cost-effective alternatives in widely available SaaS solutions rather than specialized embedded software.
The availability of these alternatives poses a significant threat, as they often come with lower price points and faster deployment times. In 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at approximately $600 billion, indicating a vast and accessible pool of substitute services that can fulfill many of the functions of specialized software.
Hardware-based Solutions or Firmware
Hardware-based solutions or firmware can pose a significant threat to ACCESS's software offerings, particularly in embedded applications. For certain fixed functionalities, developers might opt to hard-code features directly into the hardware or implement them as firmware. This approach, while less adaptable than a full software stack, can serve as a direct substitute for specific, unchanging device requirements.
This threat is amplified in markets where cost and simplicity are paramount. For instance, in the realm of simple IoT devices or specialized control systems, the overhead of a comprehensive software platform might be deemed unnecessary. Companies may choose to integrate core functions directly into the silicon, reducing bill of materials and simplifying the supply chain.
- Hardware integration: Embedding ACCESS's potential software functionalities directly into microcontrollers or ASICs can eliminate the need for a separate software layer.
- Firmware solutions: For static or low-complexity tasks, firmware can replicate software features, offering a more cost-effective and potentially more secure alternative.
- Market impact: In 2024, the demand for highly integrated, low-power embedded systems continues to grow, making hardware-centric approaches increasingly attractive for specific use cases.
- Competitive advantage: Competitors offering integrated hardware-software solutions or even pure firmware replacements can capture market share by providing simpler, cheaper alternatives for certain embedded applications.
Alternative Content Delivery Mechanisms
The threat of substitutes for traditional digital publishing networks is significant, particularly with the proliferation of alternative content delivery mechanisms. Web-native content, social media platforms, and direct-to-consumer (DTC) models are increasingly offering compelling alternatives for both content creators and audiences.
These substitutes allow creators to bypass established publishing networks, fostering direct relationships with their readers and subscribers. For instance, platforms like Substack and Patreon have seen substantial growth, enabling writers and creators to monetize their content directly. In 2023, Substack reported over 2 million paid subscribers across its platform, highlighting the growing appeal of DTC models.
The accessibility and reach of social media platforms also present a formidable substitute. Creators can leverage platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube to distribute content, build communities, and generate revenue through various monetization strategies, often with lower barriers to entry than traditional publishing. For example, YouTube's creator revenue distribution reached $50 billion by early 2024, demonstrating the scale of content monetization outside traditional publishing structures.
- Web-native content offers immediate accessibility and often a more dynamic user experience than traditional formats.
- Social media platforms provide built-in audience engagement and viral distribution capabilities.
- Direct-to-consumer models like Substack and Patreon empower creators with direct monetization and audience control.
- These alternatives can reduce reliance on established digital publishing networks, thereby increasing competitive pressure.
The threat of substitutes for ACCESS's browser and digital publishing tools is substantial. Companies are increasingly developing their own software in-house, as seen with automakers investing heavily in custom in-car operating systems in 2024. Open-source alternatives like Chromium and Linux offer cost-effective and robust solutions, with the Linux Foundation reporting increased contributions to its projects in early 2024. Furthermore, generic cloud services and SaaS platforms provide accessible alternatives for many business needs, with the global cloud computing market reaching approximately $600 billion in 2024.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on ACCESS | Supporting Data (2024 unless noted) |
| In-house Development | Greater control, IP protection | Directly reduces demand for ACCESS's core software | Automakers investing in proprietary OS development |
| Open-Source Software | Cost-effectiveness, community-driven innovation | Offers free, continuously improved alternatives | Increased contributions to Linux Foundation projects |
| Generic Cloud/SaaS | Accessibility, scalability, lower upfront cost | Fulfills many standard software functionalities | Global cloud market valued at ~$600 billion |
| Hardware/Firmware Integration | Simplicity, cost reduction for fixed functions | Eliminates need for separate software layers | Growing demand for integrated, low-power embedded systems |
Entrants Threaten
The significant upfront investment in research and development (R&D) for sophisticated embedded software, mobile platforms, and network technologies presents a formidable barrier. Companies must allocate substantial capital to innovation and product development. For instance, in 2024, major tech companies continued to pour billions into R&D; Apple, for example, reported over $22 billion in R&D spending for its fiscal year 2023, a figure that is expected to grow.
Furthermore, the necessity of a deep pool of specialized technical talent, including software engineers, network architects, and AI specialists, creates another hurdle. Acquiring and retaining such expertise is costly and challenging, limiting the number of entities capable of entering the market. The demand for these skills remains exceptionally high, driving up compensation and making it difficult for new entrants to assemble competitive teams.
ACCESS's deep-rooted connections with industry giants in automotive, consumer electronics, and publishing present a formidable barrier. Newcomers face a significant hurdle in replicating the trust and established credibility that ACCESS has cultivated over years of reliable service.
Securing design wins, particularly for mission-critical embedded and network software, requires more than just technical capability; it demands a proven track record. In 2024, the average sales cycle for enterprise software solutions often extends beyond 12 months, underscoring the time and effort needed to build such partnerships.
Rigorous testing, certification, and adherence to industry standards, especially in sectors like automotive and advanced software, present significant barriers. For instance, the automotive industry requires extensive safety and emissions certifications, a process that can cost millions and take years, deterring many potential new entrants who cannot afford this initial investment.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players in the access control market, like ACCESS, leverage significant economies of scale. This allows them to spread the high costs of software development, ongoing maintenance, and customer support across a larger user base, resulting in a lower per-unit cost that new entrants struggle to match. For instance, in 2024, major access control providers reported R&D investments in the tens of millions of dollars, a substantial barrier for startups.
Furthermore, ACCESS benefits from a well-established experience curve. Years of navigating diverse hardware integrations, understanding nuanced industry-specific security requirements, and refining deployment processes create an efficiency advantage. This accumulated expertise, often translating to quicker problem resolution and more robust solutions, makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on either cost-effectiveness or operational reliability.
- Economies of Scale: High fixed costs in R&D and support are amortized over a larger installed base for established companies.
- Experience Curve: Accumulated knowledge in integration, deployment, and customer support provides a competitive edge.
- Cost Advantage: Lower per-unit costs for established players make it difficult for new entrants to compete on price.
- Operational Efficiency: Refined processes and expertise lead to more reliable and efficient solutions, a hurdle for newcomers.
Intellectual Property and Patent Portfolios
ACCESS likely possesses a robust portfolio of patents and proprietary technologies underpinning its browser, operating system, and network solutions. This intellectual property creates a significant barrier for potential new entrants who would either need to invest heavily in developing their own unique technologies or incur substantial licensing fees for existing ones. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for obtaining a utility patent in the United States can range from $5,000 to $10,000 or more, not including ongoing maintenance fees or the significant R&D investment required to create truly competitive IP.
- High R&D Costs: Developing novel browser engines or operating system features requires substantial upfront investment in research and development, often running into millions of dollars annually for established players.
- Patent Infringement Risks: New entrants face the risk of costly legal battles if their technologies are found to infringe on existing ACCESS patents.
- Licensing Expenses: Acquiring licenses for essential technologies, if available, can be prohibitively expensive, further increasing the cost of market entry.
The threat of new entrants in the access control market is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements, particularly for research and development in areas like embedded software and network security. For example, in 2024, major players continued to invest heavily in R&D, with some allocating over $20 billion annually, making it challenging for startups to match this scale of innovation.
Furthermore, the need for specialized technical talent and the establishment of deep industry relationships act as substantial barriers. Securing design wins, which can have sales cycles exceeding 12 months in 2024, requires a proven track record that newcomers lack.
Intellectual property, including patents and proprietary technologies, also presents a formidable obstacle. Developing unique technologies or licensing existing ones can cost tens of thousands of dollars or more, alongside the substantial R&D investment needed to create competitive IP.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Metric (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements (R&D) | Significant investment needed for software development and innovation. | Major tech R&D spend: $20B+ annually |
| Technical Expertise & Relationships | Need for specialized talent and established industry connections. | Software sales cycle: 12+ months |
| Intellectual Property | Patents and proprietary technologies create entry hurdles. | Patent costs: $5k-$10k+ (US utility patent) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, integrating information from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert analyst insights.
We leverage publicly available financial statements, government economic data, and reputable trade publications to provide a comprehensive view of competitive pressures.