Horizon Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Horizon Bank Bundle
Horizon Bank navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the bargaining power of customers, and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder seeking to grasp the bank's strategic positioning and future potential. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Horizon Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, empowering you with the knowledge to anticipate challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Depositors wield significant bargaining power over Horizon Bank, as they are the primary source of its funding. This power is amplified by their sensitivity to interest rates and the increasing availability of alternative investment options, such as money market funds and online savings accounts. In 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts across the US hovered around 0.46%, but competitive online banks were offering rates well over 4%, directly challenging traditional institutions like Horizon for customer deposits and impacting their cost of capital.
Technology and software vendors hold significant bargaining power over Horizon Bank, particularly those offering core banking systems, advanced cybersecurity, and AI-driven solutions. The uniqueness of their proprietary software and the substantial costs associated with switching platforms, often running into millions of dollars for a large institution, create high switching costs for Horizon. For example, the average cost of implementing a new core banking system can range from $50 million to over $200 million, depending on the bank's size and complexity.
The increasing digital transformation imperative in the banking sector, coupled with a growing reliance on sophisticated AI for fraud detection, customer service, and data analytics, further amplifies the leverage of these specialized suppliers. As banks like Horizon invest heavily in these areas, the demand for specialized, often proprietary, technological components increases, making it harder to find readily available substitutes and thus strengthening the vendors' negotiating position.
The bargaining power of suppliers within Horizon Bank's labor market is significant, particularly for skilled employees in areas like IT, risk management, and wealth management. A scarcity of qualified talent in these specialized fields means that employees can command higher salaries and better benefits, directly impacting the bank's operational costs. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals in the financial sector saw salary increases of up to 15% year-over-year, illustrating the leverage these workers possess.
Trends such as the widespread adoption of remote work further amplify this power. Employees now have broader options for employment, increasing competition among banks to attract and retain top performers. This necessitates competitive compensation packages and attractive work environments, as Horizon Bank must contend with other financial institutions vying for the same limited pool of highly skilled individuals.
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) and state banking authorities, wield considerable influence over Horizon Bank, acting as powerful de facto suppliers of its operational license and framework. Their power is evident in the imposition of capital requirements, which directly impact a bank's ability to lend and generate revenue. For instance, in 2024, the FDIC continued to emphasize robust capital adequacy ratios, requiring banks to maintain specific levels of equity relative to their risk-weighted assets. This necessitates Horizon Bank to allocate significant resources to capital reserves, thereby influencing its cost of doing business and strategic choices.
These entities dictate compliance standards and reporting obligations, adding to Horizon Bank's operational expenses. Meeting these requirements often involves substantial investments in technology, personnel, and internal controls. For example, ongoing cybersecurity regulations and data privacy mandates, which intensified in 2024, require continuous upgrades and adherence, directly increasing overhead. The threat of penalties for non-compliance further amplifies their bargaining power, forcing Horizon Bank to prioritize regulatory adherence over other potential investments.
Changes in the regulatory landscape, whether a move towards deregulation or increased oversight, directly affect Horizon Bank's operating costs and strategic flexibility. For instance, shifts in interest rate risk management guidelines or liquidity coverage ratios can necessitate adjustments to Horizon Bank's balance sheet composition. In 2024, discussions around potential adjustments to Basel III endgame rules continued, creating an environment of uncertainty that influenced banks' long-term planning and investment in compliance infrastructure.
- Capital Requirements: Regulatory bodies set minimum capital ratios, impacting Horizon Bank's lending capacity and profitability.
- Compliance Costs: Adherence to regulations for reporting, data security, and consumer protection adds significant operational expenses.
- Strategic Flexibility: Regulatory changes can force Horizon Bank to alter its business model, product offerings, or geographic expansion plans.
- Enforcement Actions: The potential for fines and penalties for non-compliance underscores the significant power of regulators.
Wholesale Funding Markets
The bargaining power of suppliers in wholesale funding markets for Horizon Bank is significant, primarily driven by institutional investors and interbank lenders. This power is directly linked to market liquidity, current interest rates, and Horizon Bank's own credit standing. For instance, during periods of economic uncertainty, the cost of borrowing in wholesale markets can surge. In early 2024, benchmark interest rates like the Federal Funds Rate remained elevated, impacting the cost of funds for banks relying on wholesale channels.
A bank's reliance on wholesale funding can elevate its cost of funds, especially when market liquidity tightens or credit conditions become more stringent. This was evident in late 2023 and early 2024, where increased volatility in certain financial sectors led some lenders to demand higher premiums for providing short-term funding. Horizon Bank's ability to secure favorable terms in these markets depends on its perceived financial health and the overall stability of the financial system.
- Market Liquidity: In 2024, the availability of liquidity in wholesale markets directly influences the bargaining power of lenders.
- Interest Rates: Prevailing interest rates, such as the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), dictate the cost of wholesale borrowing for Horizon Bank.
- Creditworthiness: Horizon Bank's credit ratings and financial performance are crucial factors that lenders assess when setting funding terms.
- Dependence on Wholesale Funding: A higher reliance on these markets increases the bank's vulnerability to supplier power, potentially raising its cost of funds.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Horizon Bank is multifaceted, encompassing depositors, technology vendors, skilled labor, regulatory bodies, and wholesale funding sources. Each group exerts influence through various mechanisms, impacting the bank's cost of capital, operational efficiency, and strategic flexibility.
Depositors hold significant power due to their control over funding, especially with competitive rates offered by online banks. In 2024, while average savings rates were low, some online institutions offered over 4%, directly challenging traditional banks for deposits. Technology vendors also wield considerable leverage, with high switching costs for core banking systems, potentially reaching $50 million to $200 million for implementation. This reliance on specialized, often proprietary, software for digital transformation and AI solutions strengthens their negotiating position.
Skilled labor, particularly in IT and risk management, commands higher wages due to talent scarcity. For example, cybersecurity professionals saw up to a 15% salary increase in 2024. Regulatory bodies like the FDIC act as powerful suppliers of operational licenses, imposing capital requirements and compliance standards that increase operational expenses. Wholesale funding markets also present supplier power, with lenders dictating terms based on liquidity and Horizon Bank's creditworthiness, as seen with elevated benchmark rates in early 2024.
| Supplier Group | Key Influence Factor | 2024 Data/Trend | Impact on Horizon Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Depositors | Interest rate sensitivity, alternative investments | Online banks offering >4% on savings vs. ~0.46% average | Increased cost of funds, competition for deposits |
| Technology Vendors | Proprietary software, high switching costs | Core system implementation cost: $50M-$200M+ | Dependency on vendors, significant IT investment |
| Skilled Labor | Talent scarcity, demand in specialized fields | Cybersecurity salaries up to 15% YoY | Higher labor costs, retention challenges |
| Regulatory Bodies | Capital requirements, compliance mandates | Continued emphasis on capital adequacy ratios | Increased operational expenses, reduced strategic flexibility |
| Wholesale Funding | Market liquidity, creditworthiness, interest rates | Elevated Federal Funds Rate impacting borrowing costs | Variable cost of funding, reliance on market conditions |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Horizon Bank, this analysis dissects the five competitive forces shaping its industry, revealing opportunities and threats.
Instantly understand competitive pressures with a clear, visual breakdown of Horizon Bank's Five Forces, enabling swift strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual depositors hold moderate bargaining power over Horizon Bank. This power stems from their ability to easily switch banks, especially with the rise of convenient digital banking options. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts across major US banks hovered around 0.46%, while high-yield online accounts offered significantly more, incentivizing customer movement.
Commercial and business clients, including municipalities, hold significant bargaining power with Horizon Bank. Their ability to negotiate favorable terms and fees is influenced by the scale of their financial requirements and the increasing availability of alternative financing options from private credit funds and non-bank lenders. In 2024, the competitive landscape for regional banks like Horizon Bank intensified as these non-bank institutions captured a larger share of the lending market, forcing traditional banks to adapt their strategies to retain business clients.
Borrowers, whether individuals or businesses seeking commercial, mortgage, or consumer loans, hold significant bargaining power. This power is amplified by the intensely competitive lending environment, where numerous banks, credit unions, and online lenders vie for their business, often competing on interest rates and loan terms.
As interest rates are projected to decline in 2024, demand for loans, especially mortgages, is expected to rise. This increased demand, coupled with a greater availability of credit options, naturally enhances borrowers' leverage in negotiating favorable loan conditions with institutions like Horizon Bank.
Wealth Management Clients
Wealth management clients at Horizon Bank wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial assets and the ease with which they can switch providers. This client base, often characterized by high net worth individuals, can readily move their portfolios to competing wealth management firms, sophisticated robo-advisors, or independent financial advisors. This dynamic forces Horizon Bank to deliver exceptional, personalized service and consistently competitive investment performance to retain these valuable clients.
The ability of these clients to easily compare and move their assets places considerable pressure on Horizon Bank's wealth management division. For instance, in 2024, the average assets under management for high-net-worth individuals globally continued to grow, with many actively seeking the best returns and service levels. This means Horizon Bank must not only match but often exceed the offerings of its rivals to maintain client loyalty and attract new business within this segment.
- Client Mobility: Wealth management clients can easily transfer assets, increasing their leverage.
- Demand for Personalization: High-net-worth individuals expect tailored financial advice and service.
- Competitive Landscape Pressure: Horizon Bank faces competition from traditional firms, fintech solutions, and independent advisors.
- Performance Sensitivity: Client retention is heavily tied to the bank's ability to deliver strong investment returns.
Access to Information and Digital Channels
Customers today have unprecedented access to financial information and banking services through digital channels. This ease of access significantly boosts their bargaining power. They can readily compare interest rates, fees, and the quality of services offered by various financial institutions online, making them more price-sensitive and demanding of superior digital experiences.
The widespread adoption of digital-first banking means customers expect to manage their entire financial lives, from checking accounts to loan applications, directly from their smartphones. This shift forces banks like Horizon Bank to compete not just on traditional metrics but also on the seamlessness and user-friendliness of their digital platforms. For instance, by mid-2024, a significant majority of retail banking transactions were conducted digitally, underscoring this trend.
- Increased Information Availability: Online comparison tools and financial aggregators allow customers to easily vet multiple banking options.
- Digital Channel Dominance: Mobile banking apps and online portals are now the primary interaction points for many consumers.
- Price Sensitivity: Easy comparison of rates and fees intensifies competition and drives down margins for banks.
- Demand for Seamless User Experience: Customers expect intuitive, efficient digital interfaces for all banking needs.
The bargaining power of customers for Horizon Bank is substantial, driven by increased access to information and the dominance of digital channels. Customers can easily compare rates and services, making them more price-sensitive and demanding of excellent digital experiences. This forces banks to prioritize user-friendly platforms.
By mid-2024, a significant majority of retail banking transactions were conducted digitally, highlighting the shift in customer interaction. This trend pressures banks like Horizon to compete on the seamlessness and efficiency of their online and mobile offerings, alongside traditional banking metrics.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Depositors | Moderate | Ease of switching, digital banking convenience, rate sensitivity |
| Commercial/Business Clients | Significant | Scale of needs, alternative financing options, competitive lending environment |
| Borrowers (All types) | Significant | Intense competition among lenders, availability of credit, declining interest rate environment (projected for 2024) |
| Wealth Management Clients | Significant | High asset levels, ease of portfolio transfer, demand for personalization and performance |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
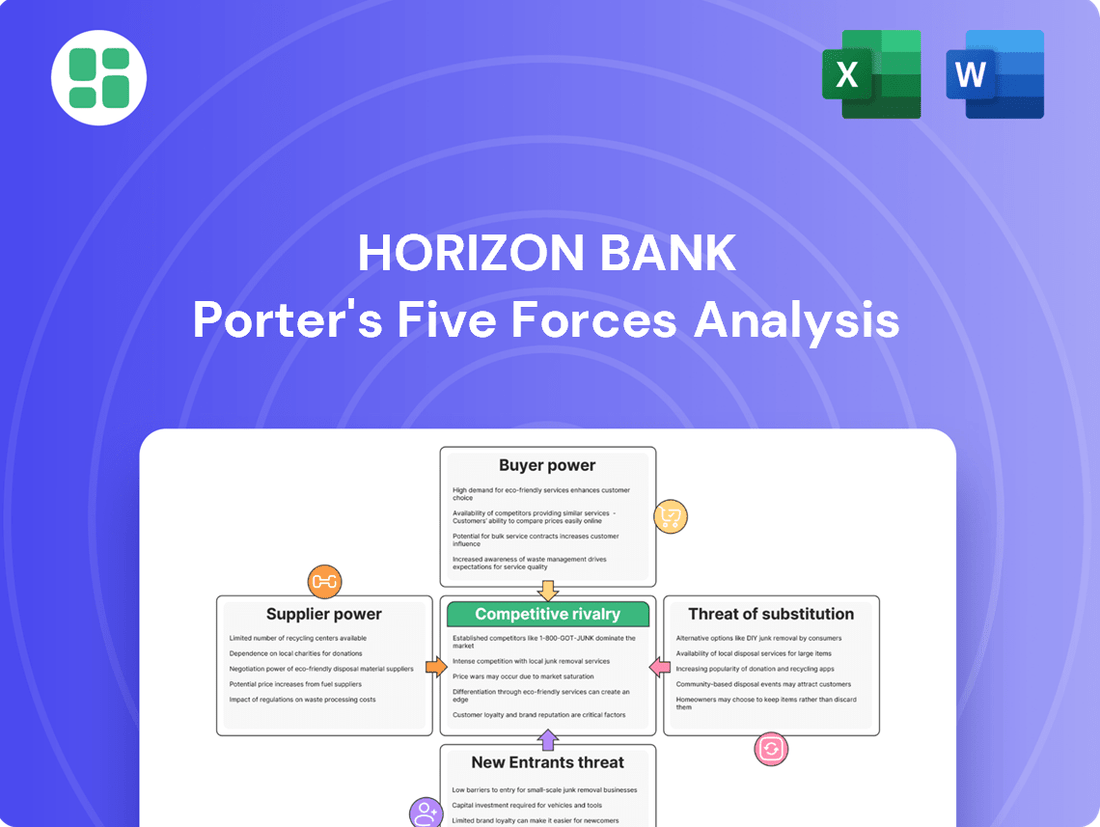
Horizon Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Horizon Bank meticulously details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Horizon Bank encounters significant competition from other regional and community banks within its core Midwestern operating areas, specifically Indiana and Michigan. This intense rivalry stems from the fact that many institutions offer comparable products and services, maintain a strong local presence, and actively compete for both deposits and loans.
For instance, in 2024, the banking landscape in Indiana saw numerous community banks actively pursuing market share. Many of these institutions, much like Horizon Bank, leverage their deep understanding of local economic conditions and customer relationships to differentiate themselves. This often translates into competitive pricing for loans and attractive rates for deposits, directly challenging Horizon Bank's customer acquisition and retention strategies.
Large national banks present a significant competitive force due to their vast resources, extensive branch networks, and advanced digital capabilities. These institutions, often with diversified revenue streams, can leverage economies of scale to offer competitive pricing and a wider array of products, directly challenging Horizon Bank's community-focused model.
Credit unions present a notable competitive force for Horizon Bank, often attracting customers with their member-centric approach and competitive pricing. Their non-profit structure allows them to pass savings onto members through lower loan rates and fewer fees, a significant draw for retail banking clients. For instance, in 2023, credit unions collectively held over $2.3 trillion in assets, demonstrating their substantial market presence and ability to compete effectively on price.
Online-Only Banks and Neobanks
The competitive rivalry from online-only banks and neobanks is intensifying, directly challenging traditional institutions like Horizon Bank. These digital disruptors, often with lower operating costs due to the absence of physical branches, are attracting customers with user-friendly interfaces, competitive fees, and innovative digital features. For instance, by the end of 2023, neobanks had captured a significant portion of the digital banking market, with some reporting millions of active users, demonstrating their growing appeal to tech-savvy demographics.
These fintech companies are fundamentally altering customer expectations by offering streamlined, often lower-cost, and highly convenient online banking services. They excel at attracting customers who prioritize digital solutions and may be less concerned with traditional branch networks. This trend is particularly evident among younger demographics, who are more likely to adopt digital-first financial tools. By the first half of 2024, reports indicated that a substantial percentage of new account openings at many institutions were initiated through mobile apps, underscoring the shift in customer behavior.
- Growing Market Share: Neobanks and digital-only banks are steadily increasing their market share, particularly among younger, digitally native consumers.
- Lower Cost Structures: Their operational models, free from extensive branch networks, allow for more competitive pricing on services and potentially higher interest rates on deposits.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Fintechs often lead with intuitive mobile apps and personalized digital services, setting a new benchmark for customer interaction in banking.
- Innovation in Services: These players are frequently at the forefront of offering specialized digital products, such as advanced budgeting tools, instant payment solutions, and integrated investment platforms.
Product and Service Differentiation
Horizon Bank faces intense rivalry in a market where differentiating core commercial and retail banking, wealth management, and lending services is challenging. In 2024, the banking industry continues to see competition primarily driven by interest rates, fees, customer service quality, and the sophistication of digital platforms. Banks like Horizon are compelled to innovate and tailor their services to stand out.
To address this, Horizon Bank is strategically investing in technology, particularly to improve its mortgage lending process. This focus on enhancing the customer experience through digital means is a key differentiator in a sector where many offerings are perceived as similar. For instance, by mid-2024, many banks reported significant increases in digital mortgage applications, highlighting the consumer demand for streamlined, tech-enabled services.
- Interest Rate Competition: Banks actively compete on the rates offered for savings accounts, loans, and mortgages, impacting customer acquisition and retention.
- Customer Service Excellence: Superior customer service, both in-person and through digital channels, remains a critical factor in differentiating banks.
- Digital Innovation: Investment in user-friendly mobile apps, online banking portals, and efficient digital processes, like Horizon's focus on mortgage lending, is crucial for attracting and keeping customers.
- Personalized Offerings: Tailoring financial products and advice to individual customer needs, moving beyond generic solutions, is an increasingly important differentiator.
Horizon Bank operates in a highly competitive banking environment, facing pressure from numerous regional, community, national, and digital-only banks, as well as credit unions. This intense rivalry is fueled by similar product offerings, a focus on customer relationships, and aggressive pricing strategies for both loans and deposits.
In 2024, the banking sector continued to see competition centered on interest rates, fees, service quality, and digital platform capabilities. Horizon Bank's investment in technology, particularly to streamline its mortgage lending, reflects a broader industry trend where digital innovation is key to attracting and retaining customers in a market where many services are perceived as commodities.
The rise of neobanks and online-only banks, which benefit from lower operating costs and offer user-friendly digital experiences, presents a significant challenge. By the end of 2023, these digital disruptors had captured a substantial portion of the market, demonstrating their growing appeal, especially among younger, tech-savvy consumers.
| Competitor Type | Key Differentiators | Impact on Horizon Bank | Example Data (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional/Community Banks | Local market knowledge, customer relationships, competitive pricing | Direct competition for deposits and loans in core markets | Numerous community banks actively seeking market share in Indiana and Michigan in 2024. |
| National Banks | Vast resources, extensive networks, advanced digital capabilities, economies of scale | Ability to offer broader product ranges and competitive pricing | National banks leverage diversified revenue streams to challenge community-focused models. |
| Credit Unions | Member-centric approach, lower rates, fewer fees (non-profit status) | Attract retail banking clients seeking cost savings | Credit unions held over $2.3 trillion in assets collectively in 2023, indicating significant market presence. |
| Online-Only/Neobanks | Lower operating costs, user-friendly interfaces, innovative digital features | Attracting digitally native consumers, setting new customer experience benchmarks | Significant portion of digital banking market captured by neobanks by end of 2023, with millions of active users reported by some. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech lending platforms pose a significant threat by offering alternative financing. These non-bank lenders and peer-to-peer platforms bypass traditional banking channels, providing faster approvals and more flexible terms that appeal to borrowers dissatisfied with conventional credit policies.
In 2024, the fintech lending sector continued its robust growth, with digital lenders originating an estimated $200 billion in loans, capturing a larger share of the consumer and small business credit markets. This trend directly challenges traditional banks like Horizon Bank by siphoning off potential loan customers.
The threat of substitutes for Horizon Bank is significant, largely driven by the proliferation of payment service providers. Companies like PayPal, Venmo, and various mobile payment apps enable direct peer-to-peer and business-to-consumer transactions, bypassing traditional banking channels for many everyday uses.
This trend is amplified by embedded finance, where non-financial companies integrate payment solutions directly into their platforms, further reducing reliance on banks. For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at over $8 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift towards alternative payment methods.
The rise of direct investment and brokerage platforms poses a significant threat to traditional banking services. These platforms, such as Robinhood and Schwab, allow individuals to bypass banks and invest directly in stocks, bonds, and other assets, diverting funds that might otherwise be held in deposit accounts. This trend is accelerating, with retail trading volume remaining elevated in 2024 compared to pre-pandemic levels, indicating a sustained shift in consumer behavior.
Wealth management services are also under pressure as these platforms offer increasingly sophisticated tools and lower fees. For instance, many robo-advisors integrated into these platforms provide automated portfolio management, directly competing with human financial advisors. In 2024, the assets under management for robo-advisors are projected to reach over $2 trillion globally, highlighting the growing appeal of these alternatives.
Furthermore, the increasing acceptance of alternative investments by financial planners, driven by market uncertainty and a desire for diversification, further erodes the reliance on traditional bank products. As of early 2024, a significant percentage of financial advisors reported incorporating alternative investments like private equity and hedge funds into client portfolios, seeking higher potential returns and reduced correlation with traditional markets.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology
The burgeoning threat from cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology presents a novel challenge to traditional banking. These decentralized systems offer alternative avenues for transactions, lending, and asset management, potentially bypassing established financial intermediaries. As of early 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization hovered around $1.6 trillion, indicating significant adoption and growing influence.
While still in its formative stages, blockchain's capacity to disrupt core banking functions is undeniable. Regulators are increasingly acknowledging this shift, with some jurisdictions authorizing banks to engage in crypto-related services. For instance, by mid-2024, several major financial institutions were exploring or offering custody services for digital assets.
- Growing Mainstream Acceptance: Major financial players are increasingly involved in the digital asset space, signaling a move beyond niche adoption.
- Regulatory Evolution: As regulators adapt, the pathway for traditional institutions to integrate or compete with crypto services is becoming clearer.
- Technological Maturation: Blockchain advancements continue to enhance efficiency and security, making these alternatives more viable for a wider range of financial activities.
Alternative Wealth Management Solutions
The threat of substitutes in wealth management is significant, as clients have numerous options beyond traditional banks. Independent financial advisors, for instance, offer personalized service and can often be more agile than large institutions. In 2024, the independent advisor channel continued to grow, with many firms reporting increased assets under management.
Robo-advisors represent another potent substitute, providing low-cost, algorithm-driven investment management. These platforms saw substantial inflows in 2023 and are projected to continue their expansion. Their accessibility and ease of use appeal to a broad range of investors, particularly younger demographics.
Furthermore, a variety of non-bank entities, including fintech startups and specialized investment firms, are increasingly offering comprehensive wealth management and financial planning services. These alternatives often leverage technology to provide innovative solutions and competitive pricing, directly challenging the market share of traditional bank wealth divisions.
- Independent Financial Advisors: Continued growth in AUM for independent firms in 2024.
- Robo-Advisors: Significant asset inflows in 2023 and strong projected growth.
- Fintech Startups: Offering specialized, tech-driven wealth management solutions.
- Non-Bank Entities: Diversification of services challenging traditional banking models.
The threat of substitutes for Horizon Bank is substantial, driven by evolving customer preferences and technological advancements. Fintech lending platforms, payment service providers, direct investment platforms, and even cryptocurrencies offer compelling alternatives that bypass traditional banking channels. These substitutes often provide greater convenience, speed, and lower costs, directly impacting Horizon Bank's customer base and revenue streams.
| Substitute Area | 2024 Data Point | Impact on Traditional Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech Lending | Estimated $200 billion in loans originated by digital lenders. | Siphons off potential loan customers, particularly from small businesses and consumers seeking faster approvals. |
| Digital Payments | Global digital payments market valued over $8 trillion in 2023. | Reduces reliance on bank-issued cards and traditional transaction processing for everyday purchases. |
| Direct Investment Platforms | Retail trading volume remained elevated in 2024 compared to pre-pandemic levels. | Diverts funds from traditional deposit accounts as individuals invest directly in securities. |
| Robo-Advisors | Projected global assets under management over $2 trillion by 2024. | Competes with bank-offered wealth management services by providing low-cost, automated portfolio management. |
| Cryptocurrencies | Global market capitalization around $1.6 trillion as of early 2024. | Offers alternative avenues for transactions, lending, and asset management, potentially bypassing intermediaries. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat from new digital-only banks, or neobanks, is significant for traditional institutions like Horizon Bank. These challengers, often operating with considerably lower overhead due to their lack of physical branches, are rapidly capturing market share. For instance, by the end of 2023, neobanks in the US had attracted millions of customers, demonstrating their ability to scale quickly. Their digital-first approach, coupled with user-friendly mobile applications and competitive fee structures, appeals strongly to younger, tech-savvy demographics.
Tech giants like Apple, Google, and Amazon are increasingly encroaching on traditional financial services. These companies possess massive customer bases and advanced technological infrastructure, allowing them to offer competitive payment solutions, lending platforms, and even investment tools. For instance, Apple Pay has seen significant adoption, and Google Pay continues to expand its reach, demonstrating the potential for these tech players to disrupt established financial institutions.
Changes in banking regulations, especially any moves towards deregulation, could significantly lower the hurdles for new financial service providers to enter the market. For instance, if capital requirements were reduced, it would make it easier for startups to establish themselves. While the banking sector is inherently robustly regulated, a more relaxed approach could invite new entrants or enable existing non-bank firms to broaden their financial service offerings, potentially increasing competition for Horizon Bank.
Specialized Fintech Startups
Specialized fintech startups pose a significant threat to traditional banks like Horizon Bank. These agile companies often target specific, profitable niches within financial services, such as peer-to-peer lending, international money transfers, or personalized budgeting apps. Their focused approach allows them to develop highly efficient and user-friendly solutions that can directly compete with or even surpass the offerings of larger, more diversified institutions.
The rapid growth and adoption of fintech solutions underscore this threat. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at approximately $2.5 trillion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $3.5 trillion by 2024, demonstrating substantial market penetration and customer acceptance. These startups leverage advanced technology and lean operational models to offer competitive pricing and superior customer experiences, effectively chipping away at established banks' market share.
- Niche Specialization: Fintech startups excel by focusing on specific areas like digital payments, wealth management, or business lending, offering tailored solutions.
- Agility and Innovation: Their lean structures enable rapid product development and adaptation to evolving customer needs, often outpacing larger banks.
- Customer Experience: Many fintechs prioritize seamless digital interfaces and personalized services, attracting customers seeking convenience and efficiency.
- Market Share Erosion: By capturing specific customer segments with specialized offerings, fintechs can gradually reduce the overall market share of incumbent banks.
Capital Requirements and Licensing
The traditional banking sector faces significant threats from new entrants due to high capital requirements and the intricate licensing procedures. For instance, establishing a new bank in the United States typically necessitates meeting stringent capital adequacy ratios, often in the tens of millions of dollars, and navigating a complex regulatory approval process involving federal and state authorities. This acts as a considerable deterrent for many aspiring competitors.
However, the rise of financial technology (fintech) presents a nuanced challenge. Many fintech firms can enter the market with lower initial capital outlays and often operate under lighter regulatory frameworks, especially when focusing on specific services like payments or digital lending. For example, some neobanks, which operate entirely online, can launch with a fraction of the capital needed for a brick-and-mortar institution, allowing them to target underserved market segments more readily.
- Capital Requirements: Traditional banks often need hundreds of millions to billions in capital, while some fintechs can start with millions or less, particularly for niche services.
- Licensing Complexity: Obtaining a full banking charter is a lengthy and costly process, whereas fintechs may leverage existing licenses or operate under less restrictive payment regulations.
- Fintech Entry: Companies like Revolut and Chime have entered the market with digital-first models, demonstrating that lower overhead and regulatory arbitrage can facilitate entry.
- Regulatory Evolution: While regulators are adapting, the pace of innovation by fintechs often outstrips the speed of regulatory change, creating temporary windows of opportunity for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Horizon Bank is amplified by the evolving regulatory landscape and the agility of fintech innovators. While traditional banking requires substantial capital and complex licensing, fintech startups can often enter with less, especially in specialized areas. This allows them to capture market share by offering streamlined digital experiences and competitive pricing, as evidenced by the rapid growth of neobanks and payment platforms.
| Competitor Type | Key Advantage | Impact on Horizon Bank | Example (2023-2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neobanks | Lower overhead, digital-first experience | Customer acquisition, particularly among younger demographics | Chime reported over 15 million customers by early 2024. |
| Fintech Startups (Niche) | Specialized services, rapid innovation | Erosion of specific profitable segments (e.g., payments, lending) | Global fintech market projected to exceed $3.5 trillion in 2024. |
| Tech Giants | Large customer base, advanced tech | Disruption of payment systems and potential expansion into lending | Apple Pay adoption continued to grow, reaching hundreds of millions of users globally. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Horizon Bank is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the bank's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific research from reputable sources like IBISWorld and S&P Global Market Intelligence. This blend of internal and external data provides a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.