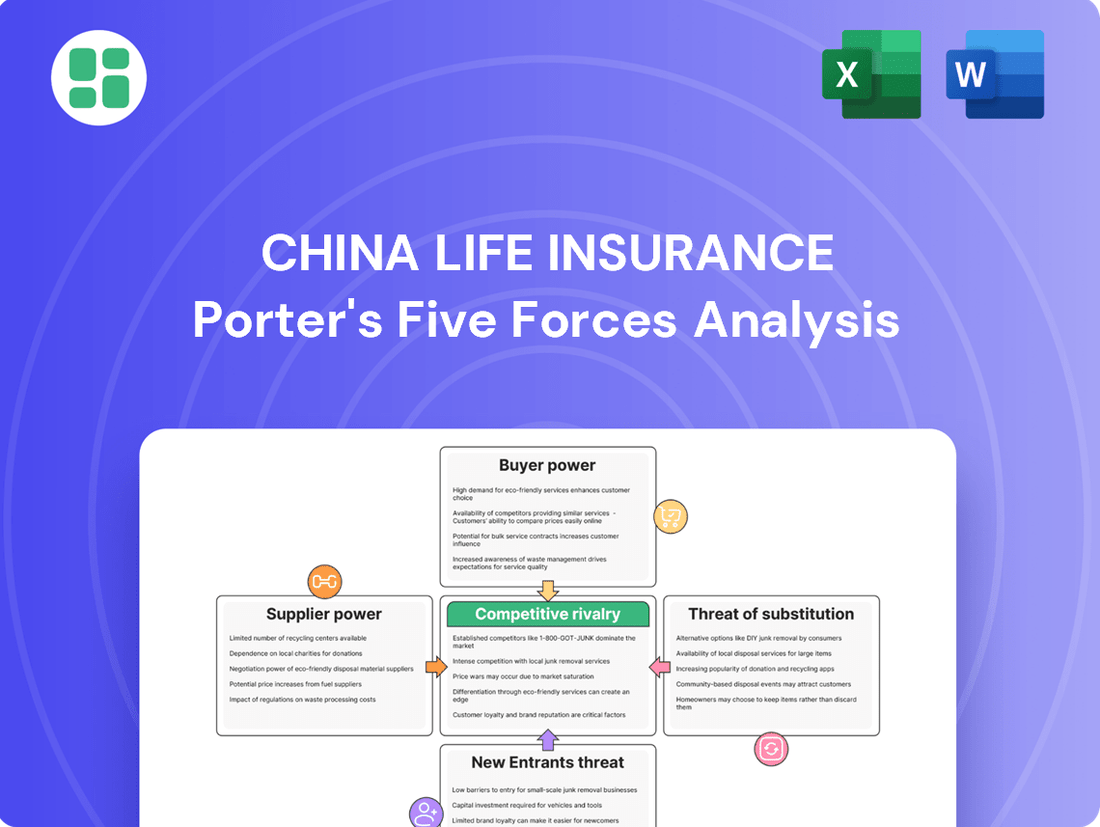
China Life Insurance Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Life Insurance Bundle
China Life Insurance operates in a dynamic market shaped by intense competition and evolving customer needs. Understanding the forces of buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, substitute products, and rivalry is crucial for navigating this landscape effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping China Life Insurance’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Reinsurers wield considerable influence over China Life due to the specialized and indispensable nature of their risk-transfer services. These services are vital for China Life to effectively manage its exposure to large-scale risks and to satisfy stringent regulatory capital requirements. The global reinsurance landscape, characterized by a concentration of a few dominant players, grants these entities significant leverage in negotiating pricing and contract terms.
As China Life Insurance pushes forward with its digital transformation, the companies supplying crucial technologies like artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and cloud computing are seeing their influence grow. China Life's capacity to innovate and improve customer interactions is increasingly tied to the advanced solutions these tech providers offer, creating a degree of reliance.
The intense focus on digital transformation across China's insurance industry between 2022 and 2025, with an estimated 30% of insurers investing heavily in AI and big data by 2024, directly amplifies the bargaining power of these technology suppliers. Their ability to deliver cutting-edge capabilities is essential for China Life to maintain its competitive edge in this evolving landscape.
China Life's asset management relies heavily on skilled investment professionals and potentially external managers. The sheer scale of managing trillions in assets means specialized talent and advanced platforms are crucial, which can grant significant bargaining power to top financial expertise and related service providers.
Distribution Channel Commissions
Distribution channel commissions represent a key area where suppliers, in this case, individual agents and bancassurance partners, can exert bargaining power over China Life Insurance. While China Life leverages its vast proprietary agent network and bancassurance partnerships, shifts in commission structures and regulatory changes can alter these dynamics.
For instance, new regulations implemented in late 2024, which tightened rules around agent commissions, directly impacted the cost structure for insurers like China Life. This could lead to increased pressure from agents seeking higher compensation or more favorable commission terms, especially as the industry shifts focus from sheer agent recruitment to enhancing the professionalism and service quality of existing agents.
- Impact of Commission Regulations: New regulations in late 2024 aimed at controlling agent commissions could increase the bargaining power of agents by setting minimum compensation standards or limiting the insurer's flexibility in commission payouts.
- Shift in Agent Focus: A move towards professional services rather than just recruitment may empower agents to demand better commission structures reflecting their specialized skills and client management capabilities.
- Bancassurance Partnerships: Commissions paid to bancassurance partners also represent a significant cost, and these institutions, with their own client bases and distribution power, can negotiate terms that benefit them, especially in competitive markets.
Data and Analytics Service Providers
The bargaining power of data and analytics service providers for China Life Insurance is considerable. The growing need for tailored insurance products, particularly in health and critical illness segments, elevates the importance of sophisticated data analysis. This demand is a key driver of supplier power.
Specialized firms offering actuarial consulting and data services hold significant sway. Their unique expertise and proprietary data sets are vital for accurate pricing and effective risk modeling. For instance, in 2023, the global big data and business analytics market reached an estimated $271.8 billion, highlighting the value placed on these services.
- Crucial Expertise: Specialized data providers possess niche skills in actuarial science and risk assessment, making their services difficult to replicate internally.
- Proprietary Data: Access to unique or aggregated datasets provides a competitive edge and strengthens their negotiating position.
- Industry Trends: The push for unified health insurance data platforms further centralizes the importance and thus the power of these key suppliers.
- Market Value: The significant market size for data and analytics services indicates a strong demand that translates into supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for China Life Insurance is notably influenced by specialized technology providers and reinsurers. These entities offer indispensable services, with the global reinsurance market's concentration empowering key players in price negotiations. Furthermore, the increasing reliance on AI and big data solutions, a trend amplified by an estimated 30% of Chinese insurers investing heavily in these areas by 2024, significantly bolsters the leverage of technology suppliers.
| Supplier Type | Key Services | Bargaining Power Factors | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinsurers | Risk transfer, capital relief | Market concentration, specialized knowledge | Essential for meeting regulatory capital requirements |
| Technology Providers (AI, Big Data) | Advanced analytics, digital transformation tools | Critical for innovation and customer experience | 30% of insurers investing heavily in AI/Big Data by 2024 |
| Actuarial & Data Service Firms | Risk modeling, pricing accuracy, data analysis | Unique expertise, proprietary data sets | Global Big Data & Analytics market ~$271.8B in 2023 |
| Distribution Channels (Agents/Bancassurance) | Sales and client acquisition | Commission structures, client base leverage | Late 2024 regulations affecting commission payouts |
What is included in the product
This analysis scrutinizes the competitive landscape for China Life Insurance, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Navigate the complex competitive landscape of China Life Insurance with a streamlined Porter's Five Forces analysis, offering a clear, one-sheet summary for rapid strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual consumers in China's insurance market often exhibit high price sensitivity, particularly for straightforward, standardized products. This is amplified by the sheer number of competitors, making it easy for customers to shop around and compare prices. For instance, in 2023, the average premium for basic life insurance policies saw intense competition, with many providers offering discounts to attract new policyholders.
While price remains a significant factor, there's a growing trend towards valuing higher quality and more comprehensive coverage. This shift allows insurers like China Life to differentiate themselves beyond just cost, potentially reducing the absolute power of price as the sole determinant. The increasing demand for health and critical illness coverage reflects this move towards product features over pure price advantage.
The burgeoning online insurance sector further empowers customers by making price comparisons incredibly accessible. Platforms offering side-by-side policy analysis mean that insurers must remain competitive on price, as transparency is at an all-time high. This digital transformation has undeniably increased customer leverage in the market.
As financial literacy in China surges, consumers are becoming more discerning about insurance. By 2024, a significant portion of the population demonstrates a greater understanding of health and pension benefits, leading them to demand more value and personalized offerings from providers like China Life. This trend is particularly evident in the growing interest in personal pension planning among younger Chinese citizens, who are actively seeking superior products and service experiences.
While switching costs for basic insurance products might be relatively low, for complex long-term products like pension plans or specialized health insurance, switching can involve higher costs and administrative hurdles. In 2024, China Life's extensive product portfolio, encompassing life, health, and pension insurance, creates a natural barrier for customers looking to move their accumulated benefits and policies to a competitor.
China Life's strategy to increase customer stickiness involves offering bundled solutions and personalized services across its integrated financial services platform. This approach, which often includes wealth management and investment products alongside insurance, makes it less convenient for customers to disentangle their financial lives and seek alternatives, thereby strengthening customer loyalty.
Digital Platforms and Accessibility
The widespread availability of digital insurance platforms and mobile apps has dramatically increased customer access to numerous insurance options. This digital shift allows consumers to easily compare policies, purchase coverage directly, and manage claims online, significantly reducing the effort and time previously required to navigate the insurance market.
This enhanced accessibility lowers search costs for customers, making it simpler than ever to find competitive pricing and favorable terms. As a result, customers are more empowered to switch providers if they find better deals, directly amplifying their bargaining power against insurers like China Life.
The growth trajectory of China's online insurance sector underscores this trend. For instance, the digital insurance market in China was estimated to reach approximately 2.2 trillion yuan in 2023, with continued strong growth anticipated. This digital penetration means more customers can readily leverage comparison tools and switch providers, exerting greater pressure on pricing and service offerings.
- Digital Platforms: Online insurance marketplaces and mobile applications provide consumers with unprecedented access to a broad spectrum of insurance products.
- Reduced Search Costs: Customers can efficiently compare policies, prices, and coverage from multiple providers, lowering the effort involved in finding the best options.
- Increased Switching: The ease of online transactions and information access empowers customers to switch insurers more readily, intensifying competition.
- Market Growth: China's digital insurance market, projected to continue its robust expansion, signifies a growing customer base that is increasingly digitally savvy and empowered.
Institutional Clients' Negotiating Power
Institutional clients, like large corporations purchasing group insurance or pension plans, wield significant negotiating power due to their substantial business volume and deep understanding of insurance requirements. These clients frequently seek tailored solutions, aggressive pricing, and extensive service offerings, allowing them to heavily influence terms with providers like China Life.
For instance, in 2024, large institutional contracts often involve multi-year commitments and significant premium volumes, giving these buyers leverage to negotiate lower rates and more favorable policy terms. Their ability to switch providers if unsatisfied further amplifies their bargaining strength.
- Volume Discounts: Institutional clients can demand volume discounts based on the size of their employee base or asset under management.
- Customization Demands: Their need for highly specific coverage, like tailored risk management or specialized pension fund structures, allows them to negotiate unique terms.
- Competitive Bidding: Large clients can solicit bids from multiple insurers, creating a competitive environment that drives down prices for China Life.
- Long-Term Relationships: While fostering loyalty, long-term contracts also give established institutional clients the power to renegotiate terms as their needs evolve or market conditions change.
Individual consumers in China's insurance market, especially for basic products, show high price sensitivity due to numerous competitors. By 2024, increased financial literacy means customers demand more value and personalized offerings, particularly in pension planning. While switching costs for complex products can be high, China Life's integrated services aim to boost customer loyalty.
What You See Is What You Get
China Life Insurance Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for China Life Insurance, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the industry. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, all presented in a professionally formatted report.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Chinese insurance sector is characterized by a high degree of concentration, with formidable state-owned enterprises such as China Life, Ping An, and PICC holding substantial market sway. This oligopolistic structure fuels aggressive competition, as these giants vie for dominance across various insurance lines, including life, property, and pensions.
China Life Insurance consistently demonstrates its leadership position, evidenced by its substantial gross written premiums and robust embedded value, underscoring its competitive strength within this intense market.
While China Life Insurance strives for product differentiation, the insurance market, particularly in established sectors, often sees products perceived as similar. This similarity naturally fuels price-based competition as companies vie for customer attention and loyalty.
This intensified price competition is further amplified by regulatory environments and market saturation in specific insurance categories. For instance, in 2023, the average premium growth for property and casualty insurance in China saw a modest increase, reflecting a competitive pricing landscape where insurers must offer attractive rates to gain market share.
While China Life's traditional life insurance segments are mature, the emerging health and pension insurance markets are experiencing fierce competition. This intense rivalry is driven by the significant growth potential in these areas. For instance, in 2023, the health insurance market in China saw a substantial expansion, with premiums reaching new heights, attracting numerous domestic and international players eager to capture market share.
Insurers are actively developing innovative and customized health and pension products to appeal to a growing demand for comprehensive coverage and retirement planning. Companies are also investing heavily in digital transformation, utilizing advanced analytics and online platforms to reach new customer segments and enhance service delivery. This strategic push for differentiation and digital engagement is intensifying the competitive landscape in these high-growth sectors.
Regulatory Influence on Competition
Regulatory shifts, like updated solvency standards and caps on bancassurance acquisition expenses and agent commissions, profoundly influence competitive landscapes. For instance, China's National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) has been actively refining rules to bolster insurer stability.
While some regulatory adjustments are designed to assist smaller insurance entities, established giants such as China Life Insurance leverage their considerable economies of scale and extensive distribution networks. This creates substantial hurdles for emerging or smaller competitors seeking to gain market traction.
In 2024, China Life Insurance's robust financial standing, evidenced by its consistent profitability and market share, allows it to absorb regulatory compliance costs more readily than smaller rivals. This disparity reinforces its competitive advantage.
- Regulatory changes Revised solvency requirements and controls on bancassurance acquisition costs and agent commissions are key drivers of competitive dynamics.
- Economies of scale Larger insurers like China Life benefit from cost efficiencies not available to smaller players.
- Distribution channels Established networks provide China Life with a significant advantage in reaching customers.
- Barriers to entry These factors collectively erect significant barriers for new or smaller insurance companies.
Digitalization and Innovation Race
Insurers are locked in a fierce competition, pouring significant resources into digital transformation and technological innovation. This race is fundamentally reshaping customer engagement, streamlining operations, and accelerating product development. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global InsurTech market was valued at approximately $26.5 billion, demonstrating the scale of investment in this area.
The drive to adopt advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and various fintech solutions fuels this intense rivalry. Companies are vying to deliver superior digital customer experiences and highly personalized insurance products. China Life, a major player, has been actively investing in digital platforms, aiming to enhance user experience and operational efficiency; by 2024, its digital transformation initiatives are expected to yield significant improvements in customer acquisition and retention.
- Digital Investment: Insurers globally are increasing R&D spending on AI and data analytics, with projections indicating continued growth through 2025.
- Customer Experience Focus: Companies are prioritizing seamless digital onboarding and personalized policy management to attract and retain policyholders.
- Fintech Integration: The adoption of fintech solutions is key to offering innovative products and improving claims processing efficiency.
- Competitive Differentiation: Success in the digitalization race is becoming a primary differentiator, impacting market share and profitability.
Competitive rivalry within China's insurance sector is intense, driven by a few dominant state-owned enterprises like China Life, Ping An, and PICC. These giants compete aggressively across all insurance lines, with China Life consistently demonstrating its market leadership through strong financial metrics. While product differentiation is a goal, many offerings are perceived as similar, leading to price-based competition, especially in mature markets like property and casualty insurance, where average premium growth remained modest in 2023.
The health and pension insurance markets are particularly competitive due to their high growth potential, attracting numerous players. Insurers are investing heavily in digital transformation and innovative product development to capture market share. For instance, the global InsurTech market was valued at approximately $26.5 billion by the end of 2023, highlighting the significant investment in technology to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
| Metric | China Life (2023 Data) | Industry Trend (2023-2024) | Key Competitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Written Premiums (GWPs) | Significant Growth | Steady growth, especially in health and pension | Ping An, PICC |
| Digital Investment | High | Increasing R&D in AI and data analytics | All major players |
| Market Share (Life Insurance) | Dominant | Stable, with slight shifts in niche segments | Ping An, CPIC |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Government social security programs in China, such as the basic pension and medical insurance schemes, offer a foundational level of protection that acts as a substitute for private insurance. By 2023, China's basic pension insurance covered over 1.07 billion people, and its basic medical insurance covered more than 1.3 billion individuals, demonstrating the broad reach of these public services.
While these government programs provide essential coverage, private insurance like that offered by China Life often steps in to offer supplementary benefits, higher payout limits, and specialized coverage not found in public plans. For instance, China Life's 2023 annual report showed significant growth in its life insurance business, indicating a demand for enhanced protection beyond the basic social safety net.
For investment-linked life insurance and pension products, direct investments in financial markets like stocks and bonds, as well as alternative wealth management products from banks and asset managers, pose a significant threat. These alternatives can attract customers seeking higher returns, especially in periods of low interest rates, directly competing with insurance companies' investment offerings.
For large institutional clients and financially robust individuals, self-insurance or retaining risks presents a viable substitute to traditional insurance. This is particularly true for predictable or lower-severity risks where internal risk management is strong. For example, a large corporation might choose to self-insure its property damage deductibles, saving on premium costs.
Fintech Solutions and Alternative Lending
The threat of substitutes for China Life Insurance is intensifying due to the rapid growth of fintech. These platforms are increasingly offering alternative lending, peer-to-peer insurance, and micro-insurance products. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global insurtech market size was valued at approximately USD 11.4 billion, with projections indicating significant expansion. This indicates a growing consumer appetite for digital-first, flexible insurance solutions that can bypass traditional channels.
These new models directly challenge established insurance distribution and product structures. Tech-savvy consumers, particularly younger demographics, are drawn to the convenience and customization offered by fintech. In 2024, digital insurance sales are expected to continue their upward trajectory, potentially capturing a larger share of the market previously dominated by traditional insurers like China Life.
The key substitutes include:
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) insurance platforms: Allowing individuals to pool risk and share premiums, often with lower overheads than traditional insurers.
- Micro-insurance products: Offering coverage for specific, often low-cost, risks, making insurance accessible to a broader population segment.
- Embedded insurance: Integrating insurance seamlessly into other purchases or services, such as travel bookings or e-commerce transactions.
- Digital-only insurers (Insurtechs): Focusing on online distribution and automated processes to offer competitive pricing and agile product development.
Preventative Healthcare and Wellness Programs
The growing focus on preventative healthcare and wellness programs presents a potential threat of substitutes for traditional health insurance. As individuals increasingly adopt healthier lifestyles and utilize health management technologies, the likelihood of incurring significant medical expenses may decrease.
This shift could reduce the perceived value of comprehensive health insurance for some consumers. For instance, by 2024, the global digital health market is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating a significant investment in technologies that promote wellness and potentially reduce the need for reactive medical care.
- Reduced Incidence of Claims: Effective wellness programs can lower the frequency and severity of health issues, directly impacting the claims made against insurance policies.
- Empowered Consumers: Health-conscious individuals may opt for more tailored or less comprehensive insurance plans if they feel their proactive health management sufficiently mitigates risk.
- Technological Advancements: Wearable devices and health apps offer continuous monitoring and personalized advice, acting as a form of self-insurance against common ailments.
Government social security programs, covering over 1.07 billion people for pensions and 1.3 billion for medical insurance by 2023, offer a baseline protection. However, private insurance like China Life's, which saw significant life insurance growth in 2023, provides enhanced benefits and specialized coverage.
Fintech innovations, including P2P insurance and micro-insurance, are rapidly gaining traction, with the global insurtech market valued at approximately USD 11.4 billion by the end of 2023. These digital platforms offer convenience and customization, appealing particularly to younger, tech-savvy consumers, with digital insurance sales projected for continued growth in 2024.
Direct investments in financial markets and wealth management products also serve as substitutes, attracting customers seeking higher returns. Furthermore, self-insurance by large corporations for predictable risks represents another competitive alternative.
The rise of preventative healthcare and wellness technologies, with the global digital health market projected for substantial growth in 2024, could reduce the perceived need for traditional health insurance by lowering the incidence of claims.
Entrants Threaten
The insurance sector, particularly in China, presents formidable barriers to entry due to stringent regulations and substantial capital demands. Operating an insurance company requires significant financial reserves to ensure solvency and meet ongoing obligations.
The minimum registered capital for an insurance firm in China stands at CNY200 million, a substantial figure that deters many potential new players. Furthermore, the implementation of China Risk Oriented Solvency System (C-ROSS) Phase II has escalated these capital requirements, making it even more challenging for newcomers to establish a foothold.
Regulatory oversight from bodies like the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) imposes rigorous market entry criteria, including licensing, operational standards, and risk management frameworks. These combined factors create a high-stakes environment that significantly limits the threat of new entrants into China's insurance market.
Established brand loyalty and trust pose a significant barrier for new entrants in China's insurance market. Large state-owned insurers, such as China Life, leverage decades of operation, resulting in deep-rooted brand recognition and public confidence. For instance, China Life, as of the first half of 2024, reported total assets exceeding 6.5 trillion RMB, a testament to its scale and established market position.
China Life Insurance boasts an incredibly extensive distribution network, a significant barrier for potential new entrants. This network includes a massive sales force, with over 1.1 million agents as of the end of 2023, alongside strategic bancassurance partnerships and increasingly robust digital channels.
Replicating this reach and efficiency demands substantial capital investment and considerable time, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively. For instance, building a comparable agent network would require years of recruitment, training, and management, a hurdle few new companies can easily overcome.
Economies of Scale and Cost Advantages
Existing large insurers, like China Life, benefit from substantial economies of scale. This means they can spread their fixed costs over a larger volume of business, leading to lower per-unit costs in areas such as underwriting, claims processing, and investment management.
New entrants, on the other hand, would likely start with smaller operations. This lack of scale would translate into higher per-unit costs, creating a significant hurdle for them to compete effectively on price or achieve profitability in the short to medium term.
For instance, in 2023, China Life Insurance reported total assets of over 7.1 trillion RMB. A new entrant would struggle to match this asset base and the associated cost efficiencies derived from managing such a large portfolio.
- Economies of Scale: Large insurers possess significant cost advantages due to their size, impacting underwriting, claims, and investment management.
- Higher Per-Unit Costs for New Entrants: Start-ups face increased operational expenses per policy compared to established players.
- Profitability Challenges: The cost disadvantage makes it difficult for new entrants to achieve profitability quickly, especially when competing on price.
- China Life's Asset Base: With over 7.1 trillion RMB in assets as of 2023, China Life demonstrates the scale new entrants must overcome.
Access to Data and Talent
The insurance industry, particularly for a company like China Life Insurance, is fundamentally built on data. Accurate risk assessment, pricing, and the development of new products all hinge on access to extensive historical customer and claims data. New companies entering the market would face a significant hurdle in amassing a comparable data repository, a process that takes years and substantial investment.
Beyond data, the talent pool presents another formidable barrier. The insurance sector requires highly specialized professionals, including actuaries who perform complex statistical analyses and underwriters who assess risk. Attracting and retaining these skilled individuals is challenging, as demand often outstrips supply, and established players like China Life have built strong relationships with top talent.
- Data Acquisition Costs: New entrants would need to invest heavily in data infrastructure and potentially acquire smaller datasets, which is far less efficient than leveraging existing, comprehensive databases.
- Talent Scarcity: The global shortage of qualified actuaries, for instance, means that competition for these professionals is fierce, favoring established companies with competitive compensation and career development programs.
- Regulatory Hurdles: While not directly data or talent, navigating data privacy regulations (like China's PIPL) adds complexity and cost for new entrants seeking to build their data capabilities.
The threat of new entrants in China's insurance market, particularly for a giant like China Life, is significantly low. This is primarily due to the immense capital requirements, with minimum registered capital at CNY200 million, further amplified by C-ROSS Phase II regulations.
Established brand loyalty and China Life's extensive distribution network, boasting over 1.1 million agents as of late 2023, create substantial hurdles. Newcomers also face challenges in replicating the economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents, evidenced by China Life's 2023 asset base exceeding 7.1 trillion RMB.
Furthermore, the critical need for vast amounts of historical data for risk assessment and the scarcity of specialized talent like actuaries present further barriers. Navigating complex data privacy laws like China's PIPL also adds to the cost and complexity for new entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | China Life's Advantage (as of 2023/H1 2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High minimum registered capital (CNY200M) and C-ROSS Phase II | Deters new players, requires significant upfront investment | Established financial strength, ability to meet evolving capital standards |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Decades of operation, state-owned backing | Difficult for new brands to gain customer confidence | Deep-rooted recognition and public trust |
| Distribution Network | Vast sales force, bancassurance, digital channels | Costly and time-consuming to replicate reach | Over 1.1 million agents (end of 2023), extensive partnerships |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large volume | Higher operational costs for smaller new entrants | Total assets exceeding 7.1 trillion RMB (2023) |
| Data & Talent | Need for historical data, scarcity of actuaries | Significant investment in data infrastructure and talent acquisition | Existing comprehensive data repositories and established talent relationships |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for China Life Insurance is built upon a foundation of publicly available data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry research firms and financial news outlets to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.