Consumers National Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Consumers National Bank Bundle
Consumers National Bank navigates a landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and intense rivalry, with the threat of new entrants presenting a significant challenge. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Consumers National Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Technology providers, particularly those offering core banking software and specialized cybersecurity solutions, hold significant bargaining power over Consumers National Bank. The highly specialized nature of these services means few vendors can meet the bank's complex needs, increasing supplier leverage. For instance, switching core banking systems can cost millions and take years, with estimated costs for large banks ranging from $200 million to over $1 billion, creating substantial switching costs that lock banks into existing relationships.
The bargaining power of suppliers within Consumers National Bank's labor market is influenced by the availability of skilled financial professionals, IT specialists, and customer service representatives. A tight labor market, characterized by high demand and limited supply of these critical roles, can significantly amplify employee bargaining power, potentially driving up wages and benefits. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. unemployment rate hovered around 3.9%, indicating a relatively robust job market where skilled workers often have leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Consumers National Bank, particularly concerning regulatory compliance services, is considerable. Firms specializing in navigating complex financial regulations possess unique expertise that is critical for the bank's operations. For instance, the sheer volume of regulatory changes in 2024, impacting areas like data privacy and anti-money laundering, necessitates specialized external support.
Payment Network Processors
Payment network processors like Visa, Mastercard, and ACH networks hold significant bargaining power over banks such as Consumers National Bank. Their essential role in facilitating transactions means banks have few alternatives for processing card and electronic payments, a situation exacerbated by the limited number of dominant players in this market.
The indispensable nature of these networks, coupled with their concentrated market structure, allows them to dictate terms, including interchange fees and processing costs. For instance, in 2024, interchange fees continue to be a substantial operating expense for financial institutions, directly impacting profitability.
- Limited Alternatives: Banks rely heavily on a small number of major payment networks for transaction processing, restricting their ability to switch providers.
- Essential Service: These networks are critical infrastructure for any bank offering card-based or electronic payment services.
- Fee Structures: Processors can influence fee structures, directly impacting a bank's revenue and operational costs.
Marketing and Advertising Agencies
Marketing and advertising agencies can hold significant bargaining power over Consumers National Bank, particularly those with a proven track record in reaching specific local demographics. Their expertise in crafting targeted campaigns is crucial for customer acquisition, allowing them to command higher fees if their services are indispensable. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a local digital marketing campaign can range from $5,000 to $20,000 per month, depending on the scope and reach, demonstrating the potential financial leverage these agencies possess.
While not as fundamental as core banking technology, specialized agencies that excel in local market penetration can exert considerable influence. If Consumers National Bank heavily depends on these agencies to connect with its target audience, especially in competitive local markets, these suppliers can leverage this reliance. In 2024, banks are increasingly focusing on hyper-local marketing strategies, making agencies with deep community ties and demonstrable ROI even more valuable and thus, more powerful.
- Specialized Expertise: Agencies with unique insights into local consumer behavior and media consumption patterns offer a distinct advantage, making their services difficult to replicate in-house.
- Proven Local Reach: Agencies that can demonstrate a history of successfully engaging specific local customer segments for financial institutions have stronger negotiation positions.
- Dependence on Performance: The bank's reliance on these agencies for customer acquisition and brand visibility directly correlates to the agencies' bargaining power, especially when campaign performance is directly tied to agency compensation.
- Market Saturation: In markets with a high concentration of financial institutions vying for attention, the demand for effective advertising services increases, potentially empowering the agencies providing them.
Suppliers of critical technology, specialized regulatory services, and essential payment processing networks wield significant influence over Consumers National Bank. Their unique expertise and the high costs associated with switching providers create strong leverage, impacting the bank's operational costs and strategic flexibility.
The labor market also presents a dynamic where skilled professionals, particularly in IT and compliance, can command higher wages and benefits, especially in a tight job market as seen in 2024 with a 3.9% U.S. unemployment rate. Furthermore, marketing agencies with proven local reach can also exert considerable power, particularly as banks increasingly focus on hyper-local engagement strategies.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Example Impact on Consumers National Bank | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers (Core Banking, Cybersecurity) | High specialization, high switching costs | Increased costs for software licenses, maintenance, and upgrades; potential for vendor lock-in. | Switching core banking systems can cost $200 million to over $1 billion for large banks. |
| Payment Network Processors (Visa, Mastercard, ACH) | Essential service, limited alternatives, concentrated market | Dictation of interchange fees and processing costs, impacting profitability. | Interchange fees remain a substantial operating expense for financial institutions. |
| Skilled Labor (IT, Compliance, Finance) | Tight labor market, demand for specialized skills | Upward pressure on wages and benefits, increased recruitment costs. | U.S. unemployment rate around 3.9% in 2024 indicates a robust job market favoring skilled workers. |
| Regulatory Compliance Services | Unique expertise, critical for operations | Higher fees for specialized consulting and support services. | Increased volume of regulatory changes in 2024 necessitates specialized external support. |
| Specialized Marketing Agencies (Local Focus) | Proven local reach, specialized expertise in customer acquisition | Higher fees for targeted campaigns; dependence on agencies for local market penetration. | Average local digital marketing campaign costs range from $5,000 to $20,000 per month in 2024. |
What is included in the product
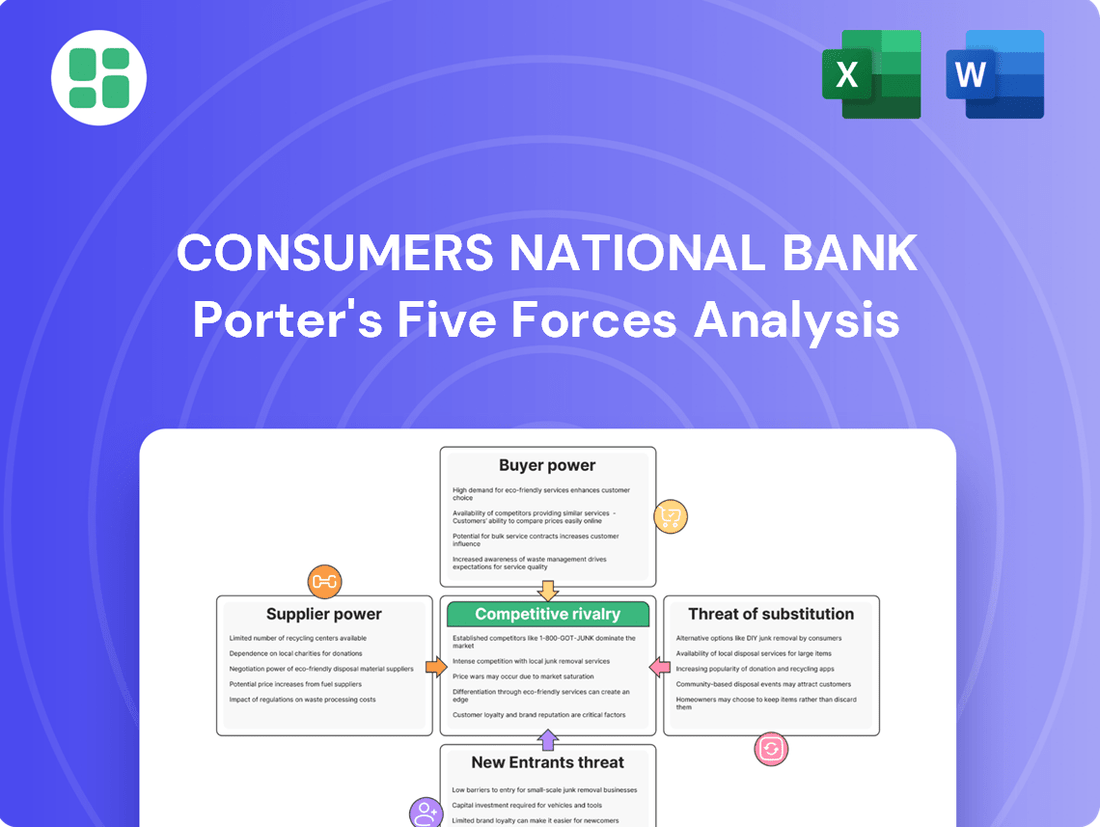
This Porter's Five Forces analysis unpacks the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and availability of substitutes impacting Consumers National Bank.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, empowering strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of individual deposit holders at Consumers National Bank is typically quite low. This is largely because basic checking and savings accounts are very similar across many financial institutions, making it easy for customers to switch banks if they find a slightly better offer. In 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts across major US banks hovered around 0.46%, highlighting the commoditized nature of these products.
Small business borrowers, like those seeking commercial financing from Consumers National Bank, generally possess limited bargaining power. While the proliferation of alternative lenders and the emphasis on relationship banking offer some leverage, their smaller scale often restricts their ability to negotiate highly favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, the average commercial loan size for small businesses remained relatively modest, reflecting their ongoing need for accessible, albeit sometimes less negotiable, financing options.
Mortgage applicants wield considerable bargaining power. The widespread availability of online comparison tools in 2024 means borrowers can easily see and compare interest rates and fees from numerous lenders, fostering a highly competitive environment. This transparency directly translates into price sensitivity, as applicants can readily identify and secure the most favorable terms, putting pressure on banks like Consumers National Bank to offer competitive rates.
Large Commercial Clients
Large commercial clients, such as major local businesses or institutions requiring substantial commercial loans and treasury management services, wield significant bargaining power. Their ability to negotiate favorable terms stems from the sheer volume of business they bring and their sophisticated understanding of financial products. For instance, in 2024, large corporate clients often seek customized pricing and dedicated service models, leveraging their financial clout to secure competitive rates and specialized solutions from multiple banking partners.
These clients can effectively play banks against each other, demanding better interest rates on loans or lower fees for treasury services. Their financial sophistication means they understand the true cost of services and can articulate their needs precisely.
- Significant Loan Volumes: Clients seeking hundreds of millions in commercial loans can dictate terms.
- Treasury Management Needs: High transaction volumes in cash management and payments give clients leverage.
- Sophisticated Financial Understanding: Clients can analyze and compare complex fee structures and interest rate proposals.
- Alternative Banking Relationships: The ability to switch to another bank if terms are not met is a key bargaining chip.
Technology-Savvy Customers
Technology-savvy customers wield significant power, especially in the banking sector where digital experiences are paramount. These customers expect intuitive online platforms and mobile apps, readily switching to institutions that offer superior technology. In 2024, it's estimated that over 70% of banking transactions are conducted digitally, underscoring this shift.
- Digital Expectations: Customers increasingly demand seamless, user-friendly digital interfaces for all their banking needs, from account management to loan applications.
- Ease of Switching: The proliferation of digital banking options means customers can easily compare features and fees, and switch providers with minimal friction if their technological expectations aren't met.
- Influence on Innovation: This customer demand directly pressures banks to invest heavily in technology and innovation to remain competitive, influencing service delivery and the development of new digital products.
The bargaining power of customers at Consumers National Bank varies significantly depending on the customer segment. While individual deposit holders have minimal leverage due to the commoditized nature of basic banking products, large commercial clients can exert substantial influence. This is driven by the volume of business they bring and their ability to compare offers across multiple institutions.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Deposit Holders | Low | Commoditized products, low switching costs, minimal differentiation. |
| Small Business Borrowers | Limited | Smaller loan sizes, reliance on accessible financing, some leverage from alternative lenders. |
| Mortgage Applicants | High | Transparency in rates and fees, ease of comparison, price sensitivity. |
| Large Commercial Clients | Significant | High loan volumes, sophisticated financial needs, ability to negotiate terms and play banks against each other. |
| Technology-Savvy Customers | High | Expectation of seamless digital experiences, ease of switching, driving bank innovation. |
Full Version Awaits
Consumers National Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Consumers National Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the banking industry. You are looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing actionable insights into market dynamics and strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Local community banks intensely compete with Consumers National Bank within shared geographic areas. This rivalry often centers on offering highly personalized customer service, maintaining a strong physical presence, and actively participating in local community initiatives. For instance, in 2024, many community banks highlighted their commitment to local businesses through targeted lending programs, aiming to capture market share from institutions perceived as less community-focused.
Consumers National Bank faces significant competitive pressure from larger regional and national banks. These competitors often possess greater financial resources, allowing them to invest more heavily in technology and marketing. For instance, in 2024, major national banks continued to expand their digital offerings, providing customers with seamless mobile banking experiences and competitive interest rates that smaller institutions struggle to match.
The extensive branch networks of these larger players also present a challenge, offering greater accessibility to customers across wider geographic areas. This broad reach, coupled with a diverse range of financial products and services, from specialized business loans to wealth management, intensifies the rivalry. Many national banks have also been actively acquiring smaller banks, further consolidating market share and increasing competitive intensity.
Credit unions present a significant competitive force for Consumers National Bank. As member-owned cooperatives, they often provide more favorable interest rates on savings and loans, alongside lower fees, directly appealing to cost-conscious consumers. In 2023, credit unions continued to grow their membership, with the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) reporting over 138 million members across the United States, indicating a substantial customer base that can divert business from traditional banks.
Online-Only Banks and Neobanks
The competitive rivalry from online-only banks and neobanks is a significant force for Consumers National Bank. These digital-first institutions are rapidly gaining market share by offering exceptionally competitive interest rates and minimal to no fees, directly challenging traditional banking models. For instance, by the end of 2023, neobanks in the US saw a substantial increase in customer acquisition, with some reporting year-over-year growth exceeding 20%.
These digital challengers, often backed by venture capital, invest heavily in user-friendly mobile applications and seamless digital experiences. They can attract a growing segment of consumers, particularly younger, tech-savvy demographics, who prioritize convenience, speed, and lower costs over the personalized, in-person service that Consumers National Bank typically provides. This trend is further amplified by the increasing comfort of consumers with managing their finances entirely through digital channels.
- Digital Competitors' Growth: Neobanks and online-only banks have experienced rapid customer growth, with some reporting over 20% year-over-year increases in 2023.
- Key Differentiators: These digital banks often compete on superior mobile banking features, lower fees, and higher interest rates compared to traditional banks.
- Customer Attraction: They appeal to tech-savvy individuals and those who value digital convenience and cost savings, posing a direct challenge to the local service model.
Non-Bank Financial Service Providers
The competitive rivalry from non-bank financial service providers is intensifying for traditional banks like Consumers National Bank. Fintech lenders, mortgage brokers, and specialized investment firms are adept at targeting and capturing lucrative segments of the financial services market. This can lead to pressure on incumbent banks as these specialized players often operate with lower overheads and more agile technological infrastructures.
These non-bank entities can cherry-pick profitable services, such as specific types of loans or investment products, thereby increasing competitive pressure on traditional banks. For instance, in 2024, the digital lending market continued its robust growth, with alternative lenders capturing a significant share of small business loans. This trend forces established banks to innovate and adapt their offerings to remain competitive.
- Fintech lenders are increasingly offering faster loan approvals and more personalized terms, attracting customers who might have previously relied on traditional bank loans.
- Mortgage brokers provide a competitive channel for home financing, often presenting a wider range of options from various lenders, including non-banks.
- Investment firms specializing in niche markets or offering direct-to-consumer investment platforms can attract assets that might otherwise be managed by bank wealth management divisions.
Consumers National Bank faces intense competition from a diverse range of financial institutions. Local community banks vie for market share through personalized service and community engagement, while larger regional and national banks leverage greater resources for technology and wider product offerings. In 2024, national banks continued to enhance their digital platforms and expand through acquisitions, intensifying rivalry.
Credit unions, as member-owned entities, offer attractive rates and lower fees, capturing a significant portion of the consumer base; by the end of 2023, over 138 million Americans were members of credit unions. Online-only banks and neobanks are rapidly growing by offering competitive rates and minimal fees, with some reporting over 20% year-over-year customer growth in 2023, appealing to tech-savvy demographics.
Non-bank financial service providers, including fintech lenders and specialized investment firms, also pose a significant threat by targeting lucrative market segments with agile operations and lower overheads. The digital lending market, for instance, saw continued robust growth in 2024, with alternative lenders capturing a larger share of small business loans.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Tactics | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Local Community Banks | Personalized service, community involvement | Targeted lending programs for local businesses |
| Regional/National Banks | Digital offerings, extensive branch networks, diverse products | Continued expansion of mobile banking, acquisitions |
| Credit Unions | Favorable rates, lower fees | Over 138 million members in the US (end of 2023) |
| Online-Only/Neobanks | High interest rates, low/no fees, user-friendly apps | Some reported >20% year-over-year customer growth (2023) |
| Non-Bank Financial Services | Specialized services, lower overheads, agile tech | Digital lending market growth, alternative lenders gaining share |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Online payment platforms like PayPal, Venmo, and Apple Pay present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. These platforms enable consumers to transfer funds and make payments directly, often bypassing the need to engage with a bank's core infrastructure for every transaction. This convenience and speed can lead to a reduced reliance on bank-issued checks or traditional direct deposit methods.
In 2024, the adoption of these alternative payment methods continues to grow. For instance, Venmo reported over $270 billion in total payment volume in 2023, showcasing a substantial shift in consumer behavior away from traditional banking channels for peer-to-peer and smaller merchant transactions. This trend directly challenges banks by siphoning off transaction-based revenue and reducing customer touchpoints.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms present a notable threat by directly connecting borrowers with investors, circumventing traditional banking channels. For many personal and small business loans, P2P options can offer quicker approvals and sometimes more favorable terms. For instance, in 2023, the P2P lending market continued its growth, with platforms facilitating billions in loans, demonstrating their increasing viability as an alternative to bank financing.
Fintech investment apps pose a significant threat by offering automated, low-cost alternatives to traditional banking services. Robo-advisors, for instance, allow individuals to manage investments without human advisors. In 2024, the global robo-advisor market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift towards these digital solutions.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Solutions
The emerging threat from cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology presents a long-term challenge to traditional banking. These decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions aim to replace core banking functions such as payments, lending, and asset custody, potentially offering an alternative financial infrastructure.
While mainstream adoption is still developing, the underlying technology offers a glimpse into future financial ecosystems. For instance, the total value locked in DeFi protocols reached over $200 billion in late 2021, indicating significant growth and interest, though this figure fluctuates. By mid-2024, while the DeFi landscape continues to evolve, the total value locked in DeFi protocols remained substantial, with estimates varying but generally in the tens of billions of dollars, demonstrating continued, albeit more volatile, investor participation. This growth signals a potential shift in how financial services are accessed and managed.
- Decentralized Payments: Cryptocurrencies offer peer-to-peer transaction capabilities, bypassing traditional intermediaries.
- Alternative Lending: DeFi platforms facilitate lending and borrowing without traditional banks.
- Digital Asset Storage: Blockchain technology provides secure, digital methods for storing and transferring assets.
- Growing Market Share: While still niche, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization has seen peaks in the trillions of dollars, indicating a growing alternative financial space.
Alternative Lending Solutions
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking services, particularly in lending, is significant and growing. Specialized non-bank lenders are increasingly offering tailored solutions that can bypass conventional bank loan processes.
For instance, invoice financing firms provide capital against outstanding invoices, a direct substitute for working capital loans. In 2024, the global invoice financing market was projected to reach over $3 trillion, demonstrating substantial adoption.
Point-of-sale (POS) financing, often offered by fintech companies, allows consumers to pay for purchases in installments, substituting for credit cards or personal loans. The U.S. POS lending market alone saw significant growth in 2024, with transaction volumes expected to climb.
- Invoice Financing: Companies like Kabbage (now American Express) and BlueVine offer rapid invoice financing, often with faster approval than traditional banks.
- Point-of-Sale Financing: Affirm and Klarna provide buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) options, directly competing with credit card offerings for consumer purchases.
- Payday and Short-Term Lenders: While often criticized, these lenders offer immediate, albeit expensive, access to funds, substituting for emergency personal loans from banks.
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking services is multifaceted, encompassing digital payment platforms, peer-to-peer lending, fintech investment apps, cryptocurrencies, and specialized non-bank lenders.
These substitutes offer convenience, speed, tailored solutions, and sometimes lower costs, directly challenging banks by siphoning off transaction revenue and reducing customer engagement.
The continued growth and adoption of these alternatives, as evidenced by billions in transaction volumes and market valuations, highlight their increasing viability and impact on the banking sector.
Consumers National Bank must actively monitor and adapt to these evolving substitute offerings to maintain its competitive position.
| Substitute Type | Key Players/Examples | 2023/2024 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Payment Platforms | PayPal, Venmo, Apple Pay | Venmo: Over $270 billion in total payment volume (2023) |
| P2P Lending Platforms | LendingClub, Prosper | Billions facilitated in loans (2023), offering faster approvals |
| Fintech Investment Apps (Robo-advisors) | Betterment, Wealthfront | Global robo-advisor market valued ~ $2.5 billion (2024 projection), growing substantially |
| Cryptocurrencies & DeFi | Bitcoin, Ethereum, various DeFi protocols | Total value locked in DeFi protocols substantial in tens of billions (mid-2024), though volatile |
| Specialized Non-Bank Lenders | Invoice financing firms, BNPL providers | Invoice financing market projected over $3 trillion (2024); BNPL competes with credit cards |
Entrants Threaten
Agile fintech startups pose a significant threat by leveraging cutting-edge technology to offer specialized banking services, often at more competitive prices or with enhanced user experiences. These nimble players can carve out profitable niches, like mobile-first checking accounts or streamlined payment solutions, bypassing the overhead associated with traditional banking infrastructure.
For instance, in 2024, fintechs continued to disrupt traditional banking models. Digital-only banks and payment processors reported substantial user growth, with some achieving millions of active customers. This rapid adoption highlights the appeal of their often lower fee structures and more intuitive digital interfaces, directly challenging incumbent banks like Consumers National Bank.
Large technology companies, often referred to as Big Tech, pose a significant threat of new entrants to the banking sector. Giants like Apple, Google, and Amazon possess vast customer bases, substantial financial reserves, and proven expertise in data analytics and user experience. For instance, Apple's credit card, Apple Card, launched in 2019, has already garnered millions of users, demonstrating their ability to rapidly acquire customers in financial services. In 2023, Google Pay processed billions of transactions, showcasing their existing infrastructure for financial interactions.
The expansion of non-bank financial institutions into traditional banking services poses a significant threat. These entities, like major investment firms and insurance companies, already have established financial expertise and extensive customer bases, allowing them to leverage existing relationships and capabilities. For instance, in 2024, many large asset managers continued to broaden their product suites to include deposit-taking and lending, directly competing with incumbent banks.
Neobanks and Digital-Only Banks
The rise of neobanks and digital-only banks presents a significant threat to traditional institutions like Consumers National Bank. These agile, tech-first players, such as Chime and Revolut, operate with substantially lower overheads by eschewing physical branches. This cost advantage allows them to offer highly attractive interest rates and innovative digital features, directly appealing to a growing customer base that values digital convenience and competitive pricing over traditional banking experiences.
For instance, in 2023, neobanks continued to gain market share, with some reporting substantial user growth. Chime, a prominent US neobank, announced reaching over 15 million customers by early 2024, demonstrating their ability to attract and retain users. Their success is largely driven by user-friendly mobile apps, fee-free checking accounts, and early direct deposit features, all of which challenge the established fee structures and service models of incumbent banks.
- Lower Overhead Costs: Digital-only banks avoid the significant expenses associated with maintaining a physical branch network, leading to more competitive pricing.
- Innovative Digital Features: They often lead in offering advanced mobile banking functionalities, personalized financial management tools, and seamless user experiences.
- Customer Acquisition: Their focus on digital channels and competitive offerings allows for rapid customer acquisition, particularly among younger, tech-savvy demographics.
- Regulatory Landscape: While facing evolving regulations, their digital-native structure can sometimes allow for quicker adaptation to new fintech-friendly policies.
Regulatory Changes Lowering Barriers
Potential regulatory shifts could significantly ease entry into the banking sector. For instance, if capital requirements are lowered from current levels, which in 2024 still represent substantial hurdles for many, new firms might find it more feasible to establish operations.
Streamlined licensing procedures, a topic of ongoing discussion in financial policy circles, could also reduce the time and resources needed to become a licensed bank. This could attract fintech companies or even large tech firms looking to offer banking services, increasing competitive intensity for established players like Consumers National Bank.
- Lowered Capital Requirements: A reduction in the minimum capital a new bank must hold could attract non-traditional players.
- Simplified Licensing: Faster and less burdensome approval processes for new banking charters would lower the barrier to entry.
- Increased Competition: These changes could lead to a more crowded market, forcing existing banks to innovate and improve efficiency.
The threat of new entrants remains a significant concern for Consumers National Bank, driven by agile fintech startups and Big Tech companies. These new players often leverage lower overheads and advanced digital capabilities to attract customers. For example, in 2024, fintechs continued to report substantial user growth, with some digital-only banks reaching millions of active customers, often due to lower fees and intuitive interfaces.
| Competitor Type | Key Advantages | 2024/2025 Trend Example |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech Startups | Lower overhead, specialized services, enhanced UX | Rapid user acquisition for digital-only banks |
| Big Tech Companies | Vast customer bases, financial reserves, data expertise | Expansion into credit and payment services |
| Non-bank Financial Institutions | Established expertise, existing customer relationships | Broadening product suites into deposit and lending |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Consumers National Bank is built upon a foundation of reliable data, including the bank's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from sources like IBISWorld and S&P Global Market Intelligence. We also incorporate macroeconomic data from government agencies and financial news outlets to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.