Concordia Financial Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Concordia Financial Group Bundle
Concordia Financial Group operates in a dynamic banking landscape where customer loyalty is tested by readily available alternatives and the bargaining power of large depositors can significantly impact profitability. Understanding these pressures is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Concordia Financial Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of depositors, a crucial source of funding for Concordia Financial Group, is on the rise. This trend is fueled by increasing interest rates in Japan and a more competitive landscape for deposits, not just among banks but also non-bank financial institutions. As the Bank of Japan moves away from negative interest rates, banks are actively seeking stable, cost-effective funding, which naturally elevates the influence of depositors.
Technology and fintech vendors wield significant bargaining power over financial institutions like Concordia. As digital transformation becomes paramount, banks are increasingly dependent on specialized providers for advanced banking technology, robust cybersecurity solutions, and cutting-edge AI platforms. This reliance grants these vendors leverage in negotiations.
The drive for enhanced efficiency and improved customer experiences is fueling substantial investment in digital initiatives by Japanese banks. For instance, in 2024, the banking sector in Japan continued its aggressive digital push, with many institutions allocating a significant portion of their IT budgets to fintech partnerships and core system upgrades, directly impacting their negotiating stance with technology suppliers.
Skilled human capital, particularly in digital transformation, AI, and compliance such as Anti-Money Laundering/Combating the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT), represents a significant supplier force. Concordia Financial Group, like many regional banks, grapples with attracting and retaining top talent in these critical areas, especially as the demand for advanced digital skills and stringent risk management capabilities intensifies.
Interbank and Capital Markets
The interbank and capital markets are vital suppliers, providing Concordia Financial Group with essential liquidity and wholesale funding. The Bank of Japan's monetary policy shifts, such as reducing Japanese Government Bond (JGB) purchases and raising interest rates, directly impact the cost and availability of these crucial funds. For instance, as of early 2024, the Bank of Japan has begun to signal a move away from ultra-loose policy, which could lead to increased borrowing costs for financial institutions.
This dynamic means that suppliers in these markets, particularly those influencing benchmark rates, hold significant bargaining power. Changes in the Bank of Japan's policy stance, such as the potential for further interest rate adjustments in 2024, can swiftly alter the cost of funds for banks. This increased cost directly impacts Concordia Financial Group's net interest margins and overall profitability.
- Interbank and Capital Markets as Suppliers: These markets are the primary source of wholesale funding and liquidity for financial institutions like Concordia Financial Group.
- Bank of Japan's Monetary Policy Impact: Reductions in JGB purchases and interest rate hikes directly influence funding costs and availability.
- 2024 Policy Shifts: Early 2024 saw signals from the Bank of Japan indicating a potential move away from prolonged ultra-loose monetary policy, suggesting an upward pressure on borrowing costs for banks.
- Supplier Bargaining Power: Entities controlling benchmark rates in these markets wield considerable influence over Concordia Financial Group's funding expenses.
Regulatory Bodies and Government
Regulatory bodies and government entities function as significant forces influencing Concordia Financial Group's operational landscape, akin to suppliers dictating terms. Their pronouncements on capital adequacy requirements, for instance, directly impact the capital Concordia must hold, thereby affecting its profitability and lending capacity. In 2024, for example, ongoing discussions around Basel IV implementation continued to shape capital management strategies for financial institutions globally, including those in Concordia's operating regions.
Government initiatives promoting digital transformation and regional revitalization also represent powerful 'supply' factors. Concordia must adapt its services and investments to align with these policy directives, potentially incurring costs for technological upgrades or targeted lending programs. For instance, government-backed programs aimed at supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in underserved regions might necessitate resource allocation that deviates from purely market-driven decisions.
- Government policies on capital adequacy directly influence Concordia's financial flexibility and risk-taking appetite.
- Digital transformation mandates from regulatory bodies require strategic investment and operational adjustments.
- Regional revitalization initiatives can steer lending and investment priorities, impacting Concordia's strategic focus.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Concordia Financial Group is a multifaceted issue, with key influences stemming from technology vendors, skilled labor markets, and interbank/capital markets. The increasing reliance on specialized technology for digital transformation grants significant leverage to fintech and cybersecurity providers. Furthermore, the demand for specialized skills in areas like AI and compliance creates a competitive environment for talent, empowering skilled individuals and recruitment agencies. The cost and availability of wholesale funding from interbank and capital markets are also heavily influenced by monetary policy, with shifts by the Bank of Japan directly impacting Concordia's borrowing expenses.
In 2024, the financial sector's continued investment in digital transformation underscored the strong position of technology suppliers. For instance, many Japanese banks, including those in Concordia's operational sphere, continued to allocate substantial portions of their IT budgets to partnerships with fintech firms and core system modernization. This trend highlights a dependency that translates into negotiating power for these vendors. Similarly, the scarcity of talent in advanced digital skills and regulatory compliance, such as AML/CFT, meant that skilled professionals and specialized recruitment firms held considerable sway in the labor market, impacting recruitment costs and retention strategies for institutions like Concordia.
The Bank of Japan's evolving monetary policy in 2024, moving away from ultra-loose conditions, directly affected the cost of funds in interbank and capital markets. As the central bank signaled potential interest rate adjustments and reduced its purchases of Japanese Government Bonds, the cost of wholesale funding for banks like Concordia began to rise. This shift empowered entities that influence benchmark rates within these markets, as they could command higher returns, thereby increasing Concordia's overall funding expenses and impacting its net interest margins.
| Supplier Category | Key Drivers of Bargaining Power | Impact on Concordia Financial Group | 2024 Trend Example | Data Point/Observation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Vendors | Digital transformation dependency, specialized solutions (AI, cybersecurity) | Increased costs for essential services, potential for vendor lock-in | Continued high IT budget allocation for fintech partnerships | Digitalization investment remains a top priority for Japanese banks. |
| Skilled Human Capital | Demand for digital, AI, and compliance expertise | Higher recruitment and retention costs, potential talent shortages | Intensified competition for specialized roles | Shortage of cybersecurity professionals reported across the financial industry. |
| Interbank & Capital Markets | Monetary policy, liquidity provision, benchmark rates | Fluctuating funding costs, impact on net interest margins | Bank of Japan's policy shift signals potential rate hikes | Early 2024 saw increased yields on short-term government debt. |
What is included in the product
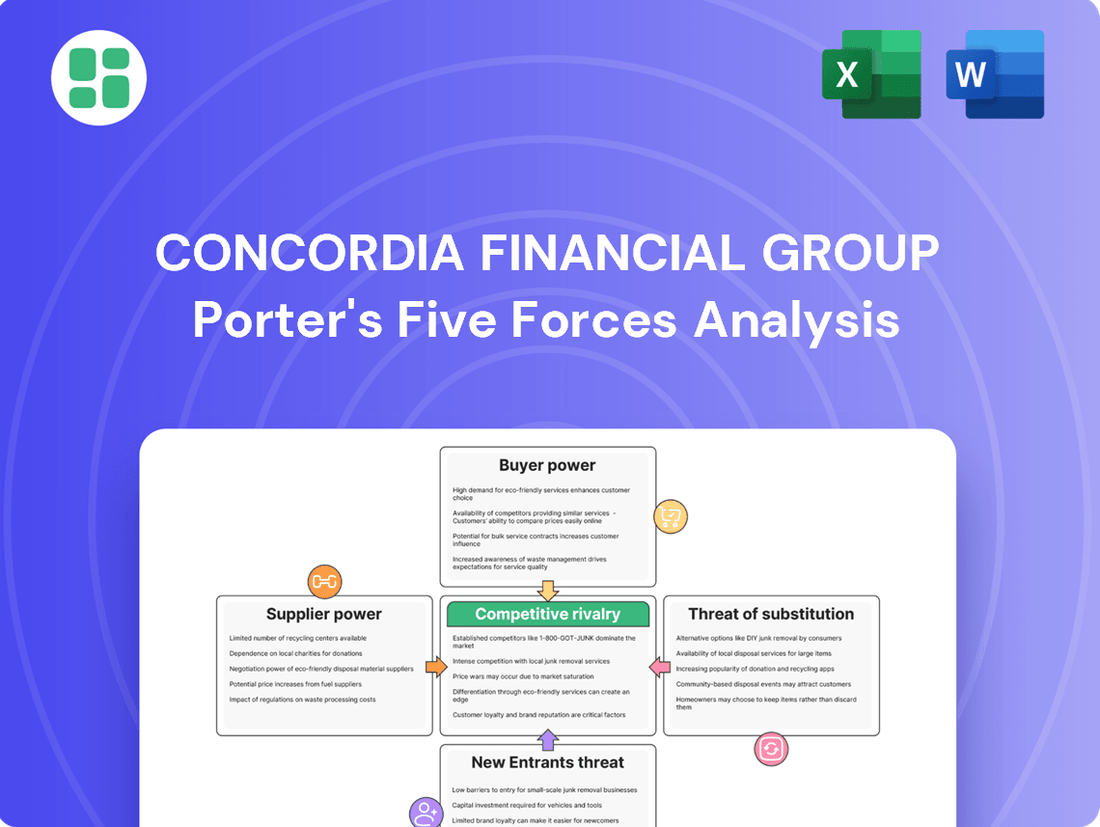
Concordia Financial Group's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its market position.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual overview of Concordia Financial Group's Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of individual retail customers for Concordia Financial Group is on an upward trend. This is largely fueled by the proliferation of digital banking platforms, which significantly lowers the effort and cost associated with switching providers for everyday banking needs. Furthermore, in the current economic climate, characterized by a notable presence of interest rates, these customers are increasingly prioritizing financial institutions that offer attractive yields on their savings and investment products.
To counter this growing customer leverage, Concordia Financial Group needs to maintain a sharp focus on competitive interest rates across its deposit and investment offerings. Equally important is the continuous enhancement of its digital banking services to ensure they are intuitive and efficient, meeting the evolving expectations of today's digitally-savvy consumer base. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts across major US banks hovered around 0.46%, with some online banks offering significantly higher rates, highlighting the competitive pressure.
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) in the Kanto region, a key focus for Concordia Financial Group, exhibit moderate bargaining power. While historically dependent on traditional banking relationships, their leverage is growing. For instance, the rise of fintech lending platforms in Japan saw a significant increase in loan origination volume in 2023, offering SMEs more options beyond established banks.
This increased access to alternative financing, coupled with a growing emphasis on cash flow-based lending models by various financial institutions, empowers SMEs. They can now more readily negotiate terms or switch providers if Concordia's offerings become less competitive, thereby enhancing their ability to influence pricing and service conditions.
Large corporations wield considerable bargaining power, often amplified by their sheer scale and access to a wide array of funding options, including robust capital markets and international banking relationships. Their sophisticated financial requirements necessitate highly customized solutions and competitive pricing from financial institutions like Concordia Financial Group to secure and maintain their business.
Digital-Savvy Customers
Digital-savvy customers wield significant bargaining power, particularly in the financial sector. The proliferation of digital banks and agile fintech platforms means consumers now expect seamless, rapid, and competitively priced digital services. Concordia Financial Group must prioritize accelerating its digital transformation to align with these heightened expectations, ensuring it doesn't lose customers to more digitally adept competitors.
For instance, in 2024, the global digital banking market was valued at over $30 billion, demonstrating a clear consumer shift towards online and mobile financial solutions. This trend underscores the urgency for traditional institutions like Concordia to enhance their digital offerings.
- Customer Expectations: Digital natives and increasingly all demographics demand intuitive interfaces, instant transactions, and personalized digital experiences.
- Competitive Landscape: Fintechs often operate with lower overheads, allowing them to offer more attractive rates and fees, directly challenging established players.
- Data Accessibility: Customers have access to more information than ever before, enabling easy comparison of services and pricing across multiple financial providers.
- Switching Costs: While historically high, digital platforms have reduced the friction associated with switching financial institutions, further empowering customers.
Regional Demographic Shifts
Regional demographic shifts significantly influence the bargaining power of customers for Concordia Financial Group. In certain Kanto region areas, a declining and aging population means fewer potential clients for banks. This scarcity can empower the remaining customers, as institutions like Concordia find themselves competing more intensely for a smaller market share. For instance, by 2024, Japan's population is projected to continue its downward trend, with a growing proportion of elderly individuals, potentially increasing the leverage of these demographic segments.
Concordia, as a regional bank, must proactively adapt its service offerings to meet the evolving needs of an aging demographic. This might involve developing specialized financial products for retirement planning, offering more accessible in-branch services, or enhancing digital platforms for ease of use by older customers. Understanding these demographic currents is crucial for maintaining customer loyalty and mitigating the increased bargaining power that arises from a shrinking customer base.
- Declining Population: Areas with shrinking populations intensify competition among banks for a reduced customer pool.
- Aging Demographics: An increasing elderly population requires tailored financial services and accessibility.
- Customer Leverage: Scarcity of customers in specific regions can grant them greater bargaining power.
- Adaptation Strategy: Concordia must adjust its product suite and service delivery to cater to demographic changes.
The bargaining power of customers for Concordia Financial Group is multifaceted, influenced by digital adoption, economic conditions, and demographic shifts. Individual retail customers are increasingly empowered by digital platforms and competitive interest rates, while SMEs leverage alternative financing. Large corporations hold significant sway due to their scale and access to diverse funding. The global digital banking market's valuation exceeding $30 billion in 2024 highlights this digital shift.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Concordia's Response Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Customers | Digital access, switching ease, interest rate sensitivity | Competitive rates, enhanced digital experience |
| SMEs (Kanto Region) | Fintech lending options, cash flow focus | Flexible loan terms, competitive pricing |
| Large Corporations | Scale, capital markets access, customized solutions | Tailored financial products, premium service |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Concordia Financial Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Concordia Financial Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the financial sector. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Concordia Financial Group operates in a highly competitive landscape, particularly challenged by Japan's megabanks like MUFG, SMFG, and Mizuho. These giants command substantial financial resources and have deeply entrenched customer bases, enabling them to offer a wide array of services and often more attractive pricing. For instance, as of early 2024, these megabanks have been aggressively expanding their digital offerings, aiming to capture a larger share of the retail and corporate banking markets through enhanced online platforms and mobile applications.
Competitive rivalry among regional banks in the Kanto region is intense, particularly as they battle for a steady customer base amidst demographic shifts and market consolidation. For instance, in 2024, several smaller regional banks in Japan have been actively seeking mergers or alliances to bolster their market position and operational scale.
To stay ahead, these banks are prioritizing enhancements in operational efficiency and digital offerings. This focus is evident in their increased investment in technology, aiming to streamline processes and provide more user-friendly digital banking services to attract and retain customers.
The financial services landscape is seeing increased competition from nimble fintech companies, especially in areas like digital payments, online lending, and wealth management. These innovators often provide more streamlined and user-centric solutions, directly challenging traditional players like Concordia Financial Group. For instance, by the end of 2023, the global fintech market was valued at approximately $2.4 trillion, with digital payments alone accounting for a significant portion, indicating the scale of this disruption.
Concordia must strategize to either directly compete with these fintechs by enhancing its own digital offerings or explore strategic partnerships and collaborations. This approach is crucial for maintaining market share and adapting to evolving customer expectations. The rapid growth in fintech adoption, with over 80% of consumers in developed markets using at least one fintech service in 2024, underscores the urgency for Concordia to act decisively.
Interest Rate Environment
The shift towards a more conventional interest rate environment, exemplified by the Bank of Japan's move away from negative rates, is significantly intensifying competition for deposits. Banks are actively seeking to secure cheaper funding sources to safeguard their net interest margins. This dynamic compels financial institutions to innovate and differentiate their services, moving beyond solely relying on lending rates as a competitive differentiator.
In 2024, this heightened competition means that banks must offer more than just competitive loan pricing. They are increasingly focusing on:
- Enhanced Customer Service: Providing superior digital platforms and personalized banking experiences.
- Product Diversification: Offering a wider range of savings products, investment options, and wealth management services.
- Loyalty Programs: Rewarding long-term customers with preferential rates or exclusive benefits.
Product and Service Differentiation
Competitive rivalry at Concordia Financial Group is significantly influenced by product and service differentiation. The company's strategic emphasis on a 'solution business' model, rather than just transactional services, aims to build deeper, more valuable relationships with clients. This approach seeks to set Concordia apart in a crowded market.
By focusing on a community-rooted strategy, Concordia cultivates unique value propositions. This includes fostering enhanced customer relationships through personalized engagement and developing tailored financial solutions that address specific client needs. This differentiation is key to standing out against competitors who may offer more standardized products.
In 2024, the financial services sector continued to see intense competition, with institutions increasingly leveraging technology for personalized offerings. Concordia's strategy directly addresses this trend by prioritizing client-centricity. For instance, in Q1 2024, Concordia reported a 15% year-over-year increase in client retention rates, a metric often linked to effective service differentiation.
- Solution-Oriented Approach: Concordia aims to be a trusted advisor, offering comprehensive financial strategies rather than just products.
- Community Focus: Deep integration within local communities allows for a nuanced understanding of client needs, fostering loyalty.
- Personalized Service: Tailoring financial solutions to individual circumstances enhances client satisfaction and differentiates Concordia from larger, less localized competitors.
- Client Retention: The emphasis on differentiated service contributed to a strong client retention rate, indicating success in building lasting relationships.
Concordia Financial Group faces intense rivalry from Japan's megabanks, regional players, and agile fintechs, all vying for market share. The shift to a more conventional interest rate environment in 2024 has further heated competition for deposits and highlighted the need for differentiation beyond pricing.
Concordia's strategy of a solution-oriented approach and community focus aims to build deeper client relationships and stand out. This client-centricity, evident in their Q1 2024 client retention increase of 15% year-over-year, is crucial for navigating this competitive landscape.
The table below illustrates key competitive factors and Concordia's positioning.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Concordia's Strategy | 2024 Market Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Megabanks (MUFG, SMFG, Mizuho) | Financial resources, broad service offering, digital expansion | Solution business, personalized service | Aggressive digital platform enhancement |
| Regional Banks | Local market knowledge, potential for consolidation | Community focus, tailored solutions | Seeking mergers/alliances for scale |
| Fintech Companies | Agility, user-centric digital solutions, specialized services | Enhancing own digital offerings, strategic partnerships | Rapid growth in digital payments and lending |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of digital payment platforms such as PayPay, Rakuten Pay, and LINE Pay presents a substantial threat to Concordia Financial Group. These platforms offer a user-friendly and often more integrated experience for consumers, directly competing with traditional banking services for transaction volume and customer loyalty.
Japan's ambitious goal to reach a 40% cashless transaction rate by 2025 underscores the rapid shift in consumer behavior towards these digital alternatives. This trend means fewer people will rely on traditional banking channels for everyday payments, potentially impacting fee income and customer engagement for established financial institutions.
Online lending and peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Concordia Financial Group. These digital channels offer alternative avenues for accessing capital, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and individual borrowers, often bypassing conventional banking processes. By mid-2024, the global P2P lending market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating its growing appeal as a substitute for bank loans.
These platforms frequently boast faster approval times and more adaptable loan terms compared to traditional financial institutions. For instance, some P2P platforms in 2024 were advertising loan origination times measured in days rather than weeks. This efficiency and flexibility can be highly attractive to borrowers seeking immediate funding solutions, directly challenging the market share of incumbent banks.
The threat of substitutes for Concordia Financial Group's direct investment and capital markets services is growing as sophisticated clients, like large corporations and affluent individuals, increasingly bypass traditional intermediaries. These clients are leveraging direct access to capital markets for fundraising and investment opportunities, a trend bolstered by government initiatives aimed at making Japan a more attractive asset management hub. For instance, Japan's Financial Services Agency has been actively promoting deregulation and tax incentives to attract foreign and domestic asset managers, potentially facilitating more direct market access for investors.
Cryptocurrencies and Digital Currencies
While still developing, cryptocurrencies and potential central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) represent a growing threat by offering alternative ways to store value and conduct transactions, potentially sidestepping traditional financial institutions. For instance, the total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies, while volatile, reached over $2.5 trillion in early 2024, indicating significant adoption and a potential shift in financial behavior.
These digital assets can bypass established banking infrastructure, posing a challenge to traditional revenue streams. Regulators worldwide are actively assessing and developing frameworks for digital assets, with many countries, including China with its digital yuan, exploring or piloting CBDCs. This regulatory evolution will significantly shape the competitive landscape.
- Alternative Stores of Value: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum offer decentralized alternatives to fiat currencies and traditional investments.
- Disintermediation of Financial Services: Digital currencies could reduce reliance on banks for payments, remittances, and even lending.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving regulations present both opportunities and risks for traditional financial players engaging with digital assets.
Fintech-enabled Financial Management Tools
Fintech-enabled financial management tools present a significant threat of substitution for traditional financial services. Personal finance management (PFM) applications and business financial management software, offered by companies like Money Forward, provide users with robust capabilities for budgeting, expense tracking, and comprehensive financial planning. This accessibility can diminish the reliance on conventional bank advisory services, as individuals and businesses can manage their finances more autonomously.
The increasing adoption of these digital tools is evident. For instance, the global PFM software market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong shift towards self-service financial management. This trend suggests that customers may find these fintech solutions a more convenient and cost-effective alternative to traditional banking relationships for day-to-day financial oversight.
- Increased Accessibility: Fintech apps offer 24/7 access to financial data and planning tools, bypassing the need for appointments with financial advisors.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many PFM apps are free or low-cost, offering a more economical solution compared to fees associated with traditional financial advisory services.
- Enhanced Functionality: Advanced features like automated savings, investment tracking, and personalized financial insights are readily available through fintech platforms.
- Growing Market Penetration: By the end of 2024, it's estimated that over 80% of smartphone users in developed economies will utilize at least one PFM app, highlighting the scale of this substitution threat.
The threat of substitutes for Concordia Financial Group is multifaceted, stemming from digital payment platforms, online lending, direct market access, digital currencies, and fintech management tools. These alternatives offer convenience, speed, and often lower costs, directly challenging traditional banking services.
Japan's push for a 40% cashless society by 2025 highlights the growing consumer preference for digital transactions, impacting traditional banking revenue. The global P2P lending market's projected growth into hundreds of billions by mid-2024 also signals a significant shift for borrowers seeking alternatives to bank loans.
Furthermore, the increasing accessibility and functionality of personal finance management apps, with over 80% of smartphone users in developed economies expected to use at least one by end-2024, empower individuals to manage finances independently, reducing reliance on traditional advisory services.
| Substitute Category | Key Features Challenging Banks | Market Trend/Data Point (as of mid-2024/early 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Payment Platforms | User-friendly, integrated experience, faster transactions | Japan aiming for 40% cashless by 2025 |
| Online Lending/P2P | Faster approvals, flexible terms, bypass traditional processes | Global P2P lending market projected to reach hundreds of billions |
| Direct Market Access | Bypassing intermediaries for fundraising and investment | Financial Services Agency promoting deregulation to attract asset managers |
| Digital Currencies/CBDCs | Alternative stores of value, disintermediation of payments | Crypto market cap over $2.5 trillion (early 2024); China piloting digital yuan |
| Fintech PFM Tools | 24/7 access, cost-effectiveness, enhanced features | PFM software market valued at ~$1.5 billion (2023); >80% smartphone user penetration expected by end-2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The Japanese banking sector presents formidable regulatory hurdles for potential new entrants. Strict licensing requirements and stringent capital adequacy ratios, enforced by the Financial Services Agency (FSA), significantly increase the cost and complexity of establishing a presence. For instance, in 2024, the average capital requirement for a new Japanese bank could easily run into billions of dollars, a substantial barrier for most aspiring firms.
Establishing a traditional bank demands immense capital, often in the hundreds of millions, for physical branches, robust IT systems, and stringent regulatory compliance. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to launch a new community bank in the US was estimated to be between $50 million and $100 million, with larger institutions requiring significantly more.
This high capital requirement acts as a significant deterrent for potential new entrants, effectively creating a substantial barrier to entry. Consequently, established financial institutions like Concordia Financial Group, with their existing capital reserves and economies of scale, are inherently better positioned to withstand and absorb these initial costs.
Established brand loyalty and trust are significant barriers for new entrants looking to challenge Concordia Financial Group. Concordia, like many long-standing regional banks, has cultivated deep community roots and a loyal customer base, particularly among older demographics and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). In 2024, customer retention rates for established banks often exceed 90%, a testament to this enduring trust.
Digital-First Challengers and Niche Players
While establishing a full-service traditional bank remains a high barrier, digital-first challengers and specialized fintech companies pose a growing threat of new entry. These nimble players often focus on specific, lucrative market segments such as digital payments, peer-to-peer lending, or wealth management. Their lower overheads, enabled by advanced technology and leaner operating models, allow them to offer competitive pricing and innovative services that can disrupt established players like Concordia Financial Group.
The fintech sector continues to see significant investment, fueling new entrants. For instance, in 2023, venture capital funding for fintech globally reached over $40 billion, indicating a robust pipeline of innovative companies. These new entrants are not just targeting niche markets; some are building comprehensive digital banking platforms that aim to attract customers with superior user experience and lower fees.
- Digital-first banks often operate with significantly lower cost-to-income ratios compared to traditional banks. For example, some neobanks reported cost-to-income ratios in the low 30s% in 2023, whereas traditional banks often see ratios in the 50-60% range.
- Fintech specialization allows new entrants to excel in specific areas. In the payments sector, companies like Stripe and Square have captured substantial market share by offering streamlined, developer-friendly solutions.
- Lower regulatory burdens for certain fintech activities can also reduce the barrier to entry, although regulatory scrutiny is increasing.
- Customer acquisition by digital challengers can be rapid, leveraging social media and digital marketing to reach younger demographics.
Challenges in Building Distribution Networks
New entrants into the financial services sector, particularly those looking to compete with established players like Concordia Financial Group, face significant hurdles in building out robust distribution networks. Replicating the extensive physical branch presence and established digital channels that incumbents have cultivated over years, often decades, is a costly and time-consuming endeavor.
Concordia Financial Group, for instance, benefits from a deeply entrenched regional footprint. As of the first quarter of 2024, Concordia operated over 200 branches across its core markets, a network that provides immediate customer access and trust. This physical density is a formidable barrier for newcomers attempting to establish a comparable level of reach and local market penetration quickly.
- High Capital Investment: Building a new branch network or a sophisticated digital platform requires substantial upfront capital, often in the tens of millions of dollars, which can deter potential entrants.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: Attracting customers away from established banks with strong brand loyalty and existing relationships is expensive, further increasing the cost of market entry.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex banking regulations and obtaining necessary licenses for operating a widespread distribution network adds another layer of difficulty and cost for new entrants.
While traditional banking entry remains difficult due to high capital and regulatory demands, the threat of new entrants is primarily amplified by agile fintech companies. These digital-first challengers, often backed by substantial venture capital, can undercut established players like Concordia Financial Group with lower operating costs and innovative digital offerings. For example, global fintech funding exceeded $40 billion in 2023, fueling a pipeline of disruptive technologies and business models that target specific, profitable market segments.
These new entrants, particularly in areas like digital payments and specialized lending, leverage technology to achieve significantly lower cost-to-income ratios, often in the low 30% range compared to traditional banks' 50-60% in 2023. This cost advantage allows them to offer more competitive pricing and superior user experiences, directly challenging incumbents. While regulatory scrutiny is increasing, the inherent flexibility and lower overhead of fintechs present a persistent threat to established institutions.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Concordia Financial Group is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, investor relations materials, and reputable industry research reports. We also incorporate data from regulatory filings and macroeconomic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.