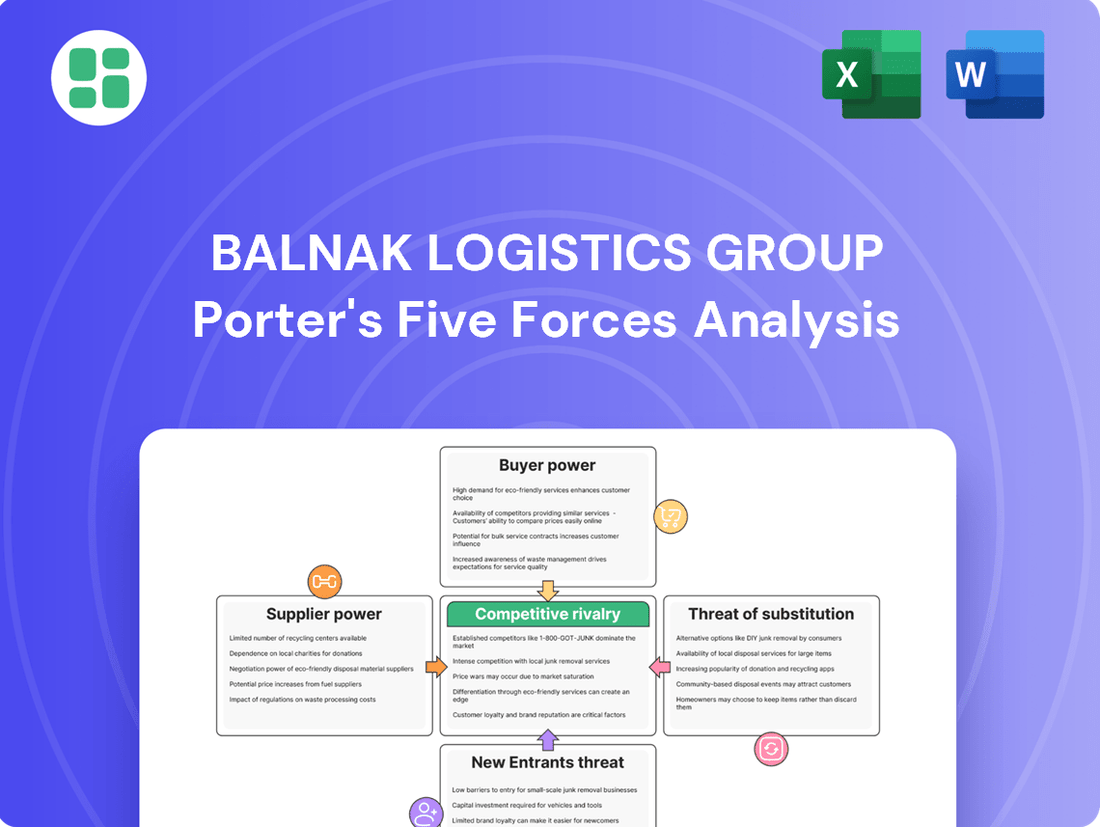
Balnak Logistics Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Balnak Logistics Group Bundle
Balnak Logistics Group navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry, moderate buyer power, and a significant threat from substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Balnak Logistics Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The cost of fuel is a major expense for Balnak Logistics Group, directly affecting their bottom line. In 2024, global oil prices experienced significant fluctuations, with Brent crude averaging around $83 per barrel for the year, impacting operational costs. This volatility grants fuel suppliers considerable leverage.
Geopolitical events and supply chain disruptions can lead to abrupt fuel price increases, further strengthening supplier bargaining power. For instance, events in the Middle East in early 2024 caused temporary spikes in oil prices, highlighting this vulnerability. Reliable fuel access is paramount, especially for operations in less accessible regions, making consistent supply a key factor in supplier negotiations.
Vehicle and equipment manufacturers wield considerable bargaining power over Balnak Logistics Group. The substantial capital outlay for specialized transport vehicles like heavy-duty trucks and the intricate warehousing machinery means Balnak is reliant on a select few suppliers who can meet these demanding specifications. This reliance is amplified when considering the specialized nature of components and the ongoing need for compatible maintenance and spare parts, creating a dependency that can tilt negotiations unfavorably.
For instance, in 2024, the global commercial vehicle market saw significant price increases driven by supply chain disruptions and rising raw material costs. Major truck manufacturers reported order backlogs extending well into 2025, a situation that inherently strengthens their position when negotiating with large fleet operators like Balnak. This market dynamic means Balnak may face less favorable terms on new fleet acquisitions or essential equipment upgrades, directly impacting operational costs.
Technology and software providers hold considerable sway over logistics companies like Balnak Logistics Group. Advanced operations depend on specialized software for everything from route planning to keeping track of inventory. Companies offering unique or widely adopted solutions can command higher prices for licenses and ongoing updates, impacting Balnak's operational costs.
Skilled Labor (Drivers, Logistics Experts)
The bargaining power of skilled labor, specifically drivers and logistics experts, is a significant factor for Balnak Logistics Group. A scarcity of qualified personnel directly impacts operational costs, as companies may need to offer higher wages and improved benefits to attract and retain talent. This can shift the leverage towards the labor force, increasing their ability to negotiate terms.
- Labor Shortages: In 2024, the trucking industry continued to grapple with driver shortages. For instance, the American Trucking Associations (ATA) projected a shortage of over 78,000 drivers in the U.S.
- Wage Inflation: To combat these shortages, many logistics companies, including those in Balnak's operational sphere, have seen increased wage demands. Average annual pay for experienced truck drivers in 2024 could range from $60,000 to over $90,000, depending on experience and routes.
- Impact on Costs: These rising labor costs directly affect Balnak's operational expenses, potentially squeezing profit margins if not managed effectively through efficiency gains or strategic pricing.
Infrastructure Access and Port Services
Access to critical infrastructure like ports, airports, and major road networks is fundamental for a logistics company like Balnak Logistics Group. The availability and cost of these services directly impact operational efficiency and profitability.
In 2024, global port congestion remained a significant factor, with average container dwell times at major hubs fluctuating. For instance, some European ports experienced average dwell times exceeding 72 hours during peak periods, increasing operational costs for logistics providers. Limited alternatives or the dominance of a few service providers in key transit points can give these infrastructure owners substantial bargaining power, influencing Balnak's costs and service delivery timelines.
- Port Fees: In 2024, average port handling fees for containerized cargo saw an increase of approximately 5-8% in key Asian and European trade lanes, reflecting rising operational and labor costs for port authorities.
- Airport Cargo Charges: Air cargo handling fees at major international airports, particularly for expedited services, can represent a substantial portion of air freight costs, with some airports increasing their rates by up to 6% year-on-year to fund infrastructure upgrades.
- Road Network Access: Tolls and access fees for major highway networks, especially in densely populated or economically vital regions, can add to the overall cost of land transportation, with some countries implementing new infrastructure charges in 2024.
- Limited Alternatives: In regions where only one or two major ports or airports are accessible, the bargaining power of those infrastructure providers is significantly amplified, potentially allowing them to dictate terms and pricing to logistics operators.
Suppliers of essential goods and services, such as fuel and vehicle manufacturers, hold significant bargaining power over Balnak Logistics Group. Fluctuations in global oil prices, averaging around $83 per barrel for Brent crude in 2024, directly impact operational costs, giving fuel suppliers leverage. Similarly, the reliance on specialized vehicle manufacturers, coupled with market-driven price increases and extended order backlogs in 2024 for commercial vehicles, strengthens their negotiating position.
Technology providers for critical logistics software and providers of essential infrastructure like ports also exert considerable influence. Companies offering unique or widely adopted solutions can command higher prices, while limited access to or dominance of key transit points by infrastructure owners can lead to increased fees and less favorable terms for logistics operators, as seen with rising port handling fees in 2024.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Suppliers | Volatility of oil prices, geopolitical events, reliable access | Brent crude averaged ~$83/barrel. Supply disruptions caused price spikes. |
| Vehicle & Equipment Manufacturers | Capital outlay for specialized assets, reliance on specific components, supply chain disruptions | Commercial vehicle prices increased; order backlogs extended into 2025. |
| Technology & Software Providers | Uniqueness or widespread adoption of solutions, need for specialized software | Increased demand for route optimization and inventory management software. |
| Skilled Labor (Drivers) | Labor shortages, wage inflation, demand for benefits | Projected U.S. driver shortage over 78,000; average annual pay $60k-$90k+. |
| Infrastructure Providers (Ports, Airports) | Availability and cost of services, limited alternatives, port congestion | Average port dwell times exceeded 72 hours in some hubs; port fees increased 5-8%. |
What is included in the product
This analysis tailors Porter's Five Forces to Balnak Logistics Group, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its market position.
Balnak Logistics Group's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces, perfect for quick decision-making and alleviating the pain of complex market assessments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Balnak Logistics Group's customers, spread across diverse sectors, wield influence through their purchasing volume and market concentration. Major clients, or those whose business constitutes a substantial percentage of Balnak's income, can leverage this position to negotiate better pricing, request tailored services, or seek preferential treatment, thereby limiting Balnak's ability to set terms freely. For instance, if a single client accounted for 15% of Balnak's 2023 revenue, their ability to demand concessions would be significant.
Switching logistics providers for Balnak Logistics Group's customers can involve administrative tasks and integrating new systems, but these hurdles are often manageable, particularly for routine shipping and warehousing. For instance, a study in early 2024 indicated that the average time to onboard a new logistics partner for small to medium-sized enterprises was around two weeks, with associated costs typically below 1% of annual logistics spend.
When these switching costs are perceived as low, customers naturally gain more leverage. They can more readily explore alternative providers if they are unsatisfied with Balnak's pricing or service quality, knowing the transition won't be overly burdensome or expensive.
The Turkish logistics market is quite crowded, with many companies, both local and international, providing similar services. This means customers aren't limited to just one or two options; they have a good selection to choose from.
Having many alternative logistics providers available gives customers more leverage. They can easily switch to a competitor if they feel Balnak Logistics Group isn't meeting their price or service expectations, which puts pressure on Balnak to stay competitive.
For instance, in 2023, the Turkish logistics sector saw significant growth, with the number of registered logistics firms increasing by 8%. This expansion directly contributes to the abundance of choices available to customers, thereby amplifying their bargaining power against any single provider like Balnak.
Price Sensitivity of Logistics Services
The price sensitivity of logistics services significantly impacts the bargaining power of customers for Balnak Logistics Group. For many businesses, logistics expenses represent a substantial portion of their total operational costs, making them highly attuned to pricing. This means customers often push for lower rates, forcing Balnak to remain competitive to secure business.
This intense focus on price can put pressure on Balnak's profit margins. To counter this, the company must either offer exceptional service that justifies a premium or achieve superior operational efficiency to maintain profitability at competitive price points. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of freight transportation in the US saw fluctuations, with trucking rates, a major component for many logistics providers, experiencing a general downward trend compared to earlier years, reflecting this customer price sensitivity.
- High Logistics Costs: For many companies, logistics can account for 10-15% of their total revenue, making them acutely aware of every dollar spent on shipping and warehousing.
- Customer Demand for Lower Prices: This cost consciousness translates directly into customer pressure on logistics providers like Balnak to offer the lowest possible rates.
- Profit Margin Erosion: Without a strong differentiator or cost advantage, meeting customer price demands can directly reduce Balnak's profitability per service.
- Focus on Efficiency and Value-Added Services: To combat price sensitivity, Balnak must emphasize operational efficiency and unique service offerings that customers value beyond just the price tag.
Customization and Specialized Service Demands
Balnak Logistics Group's commitment to delivering customized solutions across diverse sectors, including automotive and pharmaceuticals, means clients often present unique and intricate logistical challenges. This specialization, while fostering strong customer relationships, can also empower clients with significant demands. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer requiring highly specific just-in-time delivery schedules for critical components might possess considerable bargaining power due to the volume and complexity of their needs.
Customers with high-value or particularly specialized service requirements can exert considerable influence. This leverage allows them to negotiate for bespoke terms, potentially impacting Balnak's operational costs and service delivery models. For example, a pharmaceutical company needing temperature-controlled, end-to-end supply chain management for sensitive biologics may demand stringent service level agreements and preferential pricing, reflecting the specialized nature of the service and the potential disruption if those needs aren't met.
- Customization Drives Leverage: Balnak's tailored solutions for industries like e-commerce fulfillment, where specific packaging and delivery windows are paramount, can give large clients more negotiating power.
- High-Value Demands: Clients requiring specialized handling for oversized or hazardous materials, common in the oil and gas sector, often have fewer alternative providers, but their critical needs grant them leverage.
- Service Complexity: The more intricate a customer's logistical requirements, such as multi-modal transport with real-time tracking and reporting for a global retail chain, the greater their potential to negotiate favorable terms.
- Industry Benchmarks: In 2024, the logistics industry saw increased pressure on pricing due to overcapacity in certain segments, potentially amplifying customer bargaining power for standard services.
Balnak Logistics Group's customers possess significant bargaining power, primarily driven by the availability of numerous alternative providers in the competitive Turkish logistics market. This abundance of choice, evidenced by an 8% increase in registered logistics firms in 2023, allows clients to easily switch if Balnak's pricing or service quality falls short, pressuring Balnak to maintain competitive offerings.
The price sensitivity of logistics services further amplifies customer leverage. With logistics often representing 10-15% of a company's revenue, clients actively seek lower rates, potentially eroding Balnak's profit margins unless the company emphasizes efficiency or unique value-added services. For instance, fluctuating US trucking rates in 2024 indicated this downward price pressure.
Furthermore, customers requiring highly customized or specialized solutions, such as just-in-time delivery for automotive components or temperature-controlled transport for pharmaceuticals, gain considerable influence. The complexity and critical nature of these demands can lead to stringent service level agreements and preferential pricing negotiations, as clients with unique needs often have fewer suitable alternatives.
| Factor | Impact on Balnak | Customer Leverage | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider Availability | Increased competition for business | High | 8% growth in Turkish logistics firms (2023) |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on profit margins | High | Logistics costs can be 10-15% of revenue |
| Service Customization Needs | Operational complexity, potential for premium pricing | Moderate to High | US trucking rates saw downward trends (2024) |
Preview Before You Purchase
Balnak Logistics Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Balnak Logistics Group details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. You'll gain actionable insights into the strategic positioning and potential challenges facing Balnak Logistics Group.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Turkish logistics landscape is highly competitive, characterized by a significant number of both domestic and international companies vying for market share. Balnak Logistics Group contends with a broad spectrum of providers, many offering comprehensive, integrated services that mirror Balnak's own offerings, from freight forwarding and warehousing to customs brokerage.
In 2024, the Turkish logistics market is estimated to be worth over $100 billion, with the sector experiencing robust growth driven by e-commerce and international trade. This expansion attracts new entrants and intensifies competition among established players like Balnak, who must continually innovate and optimize their operations to stay ahead in this dynamic environment.
The Turkish logistics market, while promising due to its geographical advantage, can experience intensified competition when growth slows or certain segments become saturated. For instance, in 2023, while overall logistics demand remained robust, specific areas like e-commerce fulfillment faced increased pressure as more players entered the space, leading to heightened rivalry.
This intensified competition often manifests as price wars as companies vie for market share, impacting profitability. Market saturation can force businesses to differentiate through service quality or innovation rather than solely relying on pricing strategies to stand out in a crowded field.
Balnak Logistics Group distinguishes itself through highly customized logistics solutions and a significant investment in advanced tracking and management technology. This focus on tailored services aims to create a competitive edge beyond standard offerings.
However, the intensity of competitive rivalry is heightened if competitors can readily adopt similar technological advancements or develop comparable specialized service packages. For instance, if key rivals in the European logistics market, which saw a 5.2% growth in 2023, begin offering similar bespoke freight optimization or real-time inventory visibility, Balnak's differentiation advantage could diminish, forcing a greater reliance on price competition for basic transport services.
Exit Barriers and Fixed Costs
The logistics sector, including companies like Balnak Logistics Group, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These investments in fleets, advanced warehousing, sophisticated IT systems, and extensive operational networks are significant. For instance, a new, modern warehouse facility can easily cost tens of millions of dollars, and a fleet of commercial trucks represents millions more in capital outlay.
These high initial and ongoing expenditures create considerable exit barriers. Companies are often reluctant to divest assets that have lost value or are difficult to sell quickly, leading them to remain active in the market even when profitability is low. This persistence naturally fuels a more intense and sustained competitive rivalry among existing players.
- High Capital Investment: The logistics industry demands significant upfront capital for assets like trucks, trailers, and warehouse infrastructure, often running into millions for a single operational unit.
- Network Maintenance Costs: Maintaining an extensive network of depots, technology platforms, and skilled personnel is a continuous and substantial expense for logistics providers.
- Asset Specificity: Specialized logistics equipment and facilities are not easily repurposed, making it costly and time-consuming for companies to exit the market.
- Sustained Competition: Due to these high exit barriers, companies are incentivized to continue operating and competing, even in less favorable economic conditions, thereby intensifying rivalry.
Price Competition and Aggressive Marketing
In the logistics sector, particularly for standardized services, price competition is fierce. This intensity means that companies often resort to aggressive pricing tactics and extensive marketing campaigns to win and keep customers. This constant pressure directly impacts profit margins for all players, including Balnak Logistics Group.
For instance, in 2024, the global freight forwarding market saw significant price fluctuations. Major carriers in the ocean freight sector, like Maersk and MSC, engaged in rate wars, especially on key Asia-Europe routes, to capture market share. This dynamic forces logistics providers to either match these lower prices, squeezing their own profitability, or risk losing volume.
- Intense Price Wars: The commoditization of certain logistics services, such as standard container shipping and less-than-truckload (LTL) freight, makes price a primary competitive differentiator.
- Aggressive Marketing Spend: Companies are investing heavily in digital marketing, targeted advertising, and promotional offers to stand out in a crowded marketplace. In 2024, marketing budgets for top logistics firms saw an average increase of 8-10%.
- Margin Erosion: The constant need to offer competitive pricing can lead to reduced profit margins for logistics providers if they cannot offset lower rates with increased efficiency or value-added services.
- Customer Retention Challenges: In a price-sensitive environment, customer loyalty can be fragile, as clients may switch to competitors offering slightly better rates, necessitating continuous efforts to retain business.
Competitive rivalry within the Turkish logistics sector is exceptionally high, with numerous domestic and international players offering similar integrated services. This intense competition, fueled by a market valued over $100 billion in 2024 and robust growth, pressures companies like Balnak Logistics Group to constantly innovate and optimize.
The sector's substantial fixed costs and high exit barriers, such as millions invested in fleets and warehousing, keep companies competing even when margins are thin. This persistence, combined with aggressive pricing tactics and marketing spend, which saw an average 8-10% increase in 2024 for top firms, leads to significant margin erosion.
Price wars are common, particularly for standardized services, with major global carriers engaging in rate battles on key routes. This necessitates differentiation through custom solutions and technology, as Balnak does, to avoid being solely reliant on price competition.
| Key Competitor Actions | Impact on Rivalry | Balnak's Response |
| Aggressive pricing on standard services | Increased price pressure, margin erosion | Focus on value-added services, customization |
| Investment in advanced technology | Potential commoditization of differentiation | Continued investment in proprietary tech, service integration |
| Market expansion into new segments | Increased competition in niche areas | Strengthening core competencies, strategic partnerships |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers developing in-house logistics capabilities represent a significant threat of substitutes for Balnak Logistics Group. Large enterprises, particularly those with substantial and predictable shipping volumes, might find it economically viable and strategically advantageous to build their own logistics networks. This can include investing in fleets, warehousing, and technology, thereby bypassing the need for third-party logistics (3PL) providers.
For instance, a major e-commerce player with millions of daily shipments could potentially achieve greater efficiency and cost control by managing its own last-mile delivery operations. In 2023, reports indicated that several large retail and manufacturing firms were indeed expanding their internal logistics arms, driven by a desire for end-to-end visibility and reduced reliance on external partners. This trend directly competes with Balnak's service offerings.
Customers may choose transportation modes that Balnak Logistics Group doesn't fully offer or integrate, impacting demand for their multi-modal services. For instance, a growing preference for rail or maritime transport for bulk cargo, driven by cost or environmental concerns, could divert business from Balnak's road-centric solutions. The global freight market saw significant shifts in 2024, with rail freight volumes in North America increasing by an estimated 3.5% year-over-year, signaling a potential substitute for long-haul trucking.
Digital freight platforms and aggregators represent a growing substitute threat to traditional logistics providers like Balnak Logistics Group. These online marketplaces directly connect shippers with carriers, often cutting out intermediaries. For instance, by mid-2024, platforms like Uber Freight and Convoy had significantly expanded their networks, offering shippers more direct access to capacity and potentially lower costs.
These digital solutions can offer enhanced transparency in pricing and transit times, along with streamlined booking and tracking capabilities, which traditional methods may lack. This ease of use and potential for cost savings makes them an attractive alternative for many businesses looking to move goods efficiently.
The competitive pressure from these platforms is expected to intensify as they continue to invest in technology and expand their service offerings, potentially impacting Balnak Logistics Group's market share and pricing power in the freight forwarding sector.
Improvements in Supply Chain Efficiency
Advances in supply chain management technologies are a significant threat of substitutes for traditional logistics services. For instance, innovations like real-time tracking and predictive analytics allow companies to optimize inventory levels, reducing the reliance on extensive warehousing. In 2024, the global supply chain management market was valued at approximately $30 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of over 10% through 2030, indicating a strong trend towards greater efficiency.
Highly optimized production schedules and just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems further diminish the need for certain logistics functions, such as large-scale warehousing and long-haul transportation. Companies adopting these leaner models can reduce their operational footprint and associated logistics costs. For example, manufacturers implementing JIT have reported inventory holding cost reductions of up to 25%.
- Technological Advancements: Real-time tracking and predictive analytics reduce warehousing needs.
- Lean Manufacturing: Just-in-time inventory lowers demand for traditional logistics.
- Efficiency Gains: Optimized production schedules minimize the requirement for extensive transportation.
- Market Trends: The growing supply chain management market highlights a shift towards greater efficiency.
Customers Opting for Less Complex Shipping Solutions
Customers needing simpler, smaller-scale shipping might choose postal services or express couriers, bypassing Balnak's integrated solutions. This trend is evident as e-commerce platforms increasingly offer direct-to-consumer shipping options, bypassing traditional logistics providers for less complex shipments.
For instance, the global parcel delivery market, excluding freight, is projected to grow significantly, with a substantial portion driven by smaller shipments that could be handled by alternative providers. In 2024, the express delivery market alone was valued in the hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating a strong demand for services that Balnak may not directly compete with for very basic shipping needs.
- Postal Services: Offer basic, cost-effective shipping for smaller parcels, often utilized by individuals and small businesses.
- Express Couriers: Provide faster delivery for time-sensitive packages, competing on speed rather than comprehensive logistics.
- Direct-to-Consumer Models: Brands managing their own shipping bypass third-party logistics for certain customer segments.
- Market Share Erosion: For less complex shipping needs, these alternatives represent a viable substitution, potentially impacting Balnak's market share in those specific segments.
The threat of substitutes for Balnak Logistics Group is multifaceted, encompassing customers developing in-house capabilities, alternative transportation modes, digital freight platforms, and technological advancements. Customers opting for self-sufficiency in logistics, especially large enterprises, can bypass third-party providers. For instance, a significant trend in 2023 saw major retail firms expanding their internal logistics operations to gain better control and visibility.
Furthermore, shifts towards modes like rail freight, driven by cost or environmental factors, present a substitution for Balnak's road-centric services. In 2024, North American rail freight volumes saw an estimated 3.5% year-over-year increase, indicating a growing preference for this alternative for bulk cargo.
Digital freight platforms, such as Uber Freight and Convoy, are also gaining traction by directly connecting shippers with carriers, often offering enhanced transparency and potentially lower costs. By mid-2024, these platforms had considerably expanded their reach, providing a more streamlined alternative to traditional logistics models.
Technological advancements in supply chain management, including real-time tracking and predictive analytics, are reducing the need for extensive warehousing and traditional logistics functions. The global supply chain management market, valued around $30 billion in 2024, reflects this shift towards greater efficiency and optimization, which can diminish reliance on comprehensive logistics providers.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Balnak | 2024 Data Point |
| In-house Logistics | Customers building their own logistics networks | Reduced demand for 3PL services | Expansion of internal logistics arms by large retail firms in 2023 |
| Alternative Transport Modes | Preference for rail or maritime over road | Diversion of freight from Balnak's road solutions | 3.5% YoY increase in North American rail freight volumes in 2024 |
| Digital Freight Platforms | Online marketplaces connecting shippers and carriers | Increased competition, potential price pressure | Significant network expansion by platforms like Uber Freight and Convoy by mid-2024 |
| Supply Chain Technology | Optimized production, JIT inventory, real-time tracking | Reduced need for warehousing and extensive transportation | Global SCM market valued at ~$30 billion in 2024, growing at >10% CAGR |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the integrated logistics sector demands significant upfront capital. This includes acquiring or leasing a substantial fleet of trucks and other transport vehicles, setting up and maintaining warehousing and distribution centers, and investing heavily in sophisticated IT systems for tracking, management, and customer service. For example, a new entrant might need to budget upwards of $50 million just to establish a basic operational capacity in a major market.
The logistics sector faces substantial barriers to entry, particularly concerning regulatory compliance. For instance, obtaining necessary operating licenses and adhering to customs regulations, especially for international freight forwarding, demands significant investment in time and resources. In 2024, the Global Logistics Index highlighted that navigating these complex legal frameworks is a primary deterrent for nascent players aiming to compete with established firms like Balnak Logistics Group.
Established players like Balnak Logistics Group leverage strong brand reputations and deep-rooted customer relationships, built over years of reliable service. For instance, in 2024, logistics companies with a proven track record often command higher pricing power due to this trust.
Newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and demonstrate exceptional service to even begin chipping away at this loyalty. The cost and time required to build comparable brand equity present a significant barrier, as customers often prioritize dependability in a sector where disruptions can be costly.
Network Density and Operational Complexity
The significant capital and time required to establish a comprehensive domestic and international logistics network, encompassing routes, partnerships, and operational hubs, presents a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. Balnak Logistics Group, for instance, has invested heavily over decades to build its extensive global reach.
The intricate nature of managing a diverse array of logistics operations across multiple transportation modes and varied geographical regions adds another layer of complexity, deterring newcomers. This operational intricacy, coupled with regulatory compliance across different jurisdictions, requires specialized expertise and robust systems that are difficult to replicate quickly.
- Network Investment: Building a global logistics network can cost billions of dollars. For example, major players often have fleets of thousands of vehicles and operate hundreds of facilities worldwide.
- Operational Complexity: Managing a fleet of over 10,000 vehicles, as some large logistics firms do, involves sophisticated route optimization, maintenance scheduling, and driver management, creating high entry barriers.
- Partnership Reliance: New entrants often struggle to secure the same level of advantageous partnerships with airlines, shipping lines, and other carriers that established companies like Balnak Logistics Group have cultivated over years, impacting cost and service efficiency.
Access to Skilled Labor and Specialized Technology
The need for a highly skilled workforce, including experienced drivers, customs specialists, and IT professionals, presents a significant barrier for new entrants. Acquiring and retaining such talent can be both time-consuming and expensive, especially in a competitive labor market. For instance, in 2024, the demand for certified commercial truck drivers remained high, with the American Trucking Associations reporting a shortage of over 78,000 drivers.
Furthermore, access to cutting-edge logistics technologies, such as advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), AI-powered route optimization, and automation solutions, is crucial for efficiency and competitiveness. New companies often struggle to afford the substantial investment required for these technologies, giving established players with existing infrastructure and technological capabilities a distinct advantage.
- Skilled Labor Shortages: Ongoing shortages in key logistics roles, like truck drivers, increase recruitment costs and lead times for new entrants.
- Technology Investment Costs: High capital expenditure for advanced logistics software and automation equipment creates a significant entry hurdle.
- Training and Development: The necessity for specialized training in customs regulations, international shipping, and new technologies adds to the operational burden for newcomers.
- Established Workforce Expertise: Incumbent firms benefit from teams already proficient in complex logistics operations and technology integration.
The threat of new entrants into the integrated logistics sector is generally low due to substantial barriers. Significant capital investment is required for fleets, warehousing, and IT systems, with initial capacity potentially costing upwards of $50 million. Regulatory compliance, including licenses and customs, adds complexity and cost, as highlighted by the 2024 Global Logistics Index, which noted these frameworks deter new players.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Acquiring vehicles, facilities, and technology | $50M+ for basic operational capacity |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating licenses and international customs | Complex frameworks deterring nascent players (Global Logistics Index) |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Established trust and long-term customer ties | Higher pricing power for incumbents |
| Network & Partnerships | Extensive global routes and carrier agreements | Billions invested in global networks (thousands of vehicles, hundreds of facilities) |
| Skilled Workforce & Technology | Access to drivers, specialists, and advanced systems | 78,000+ truck driver shortage (American Trucking Associations) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Balnak Logistics Group is built upon a foundation of industry-specific market research reports, financial disclosures from publicly traded logistics companies, and economic data from reputable sources to ensure a comprehensive assessment of competitive pressures.