Bahnhof Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bahnhof Bundle
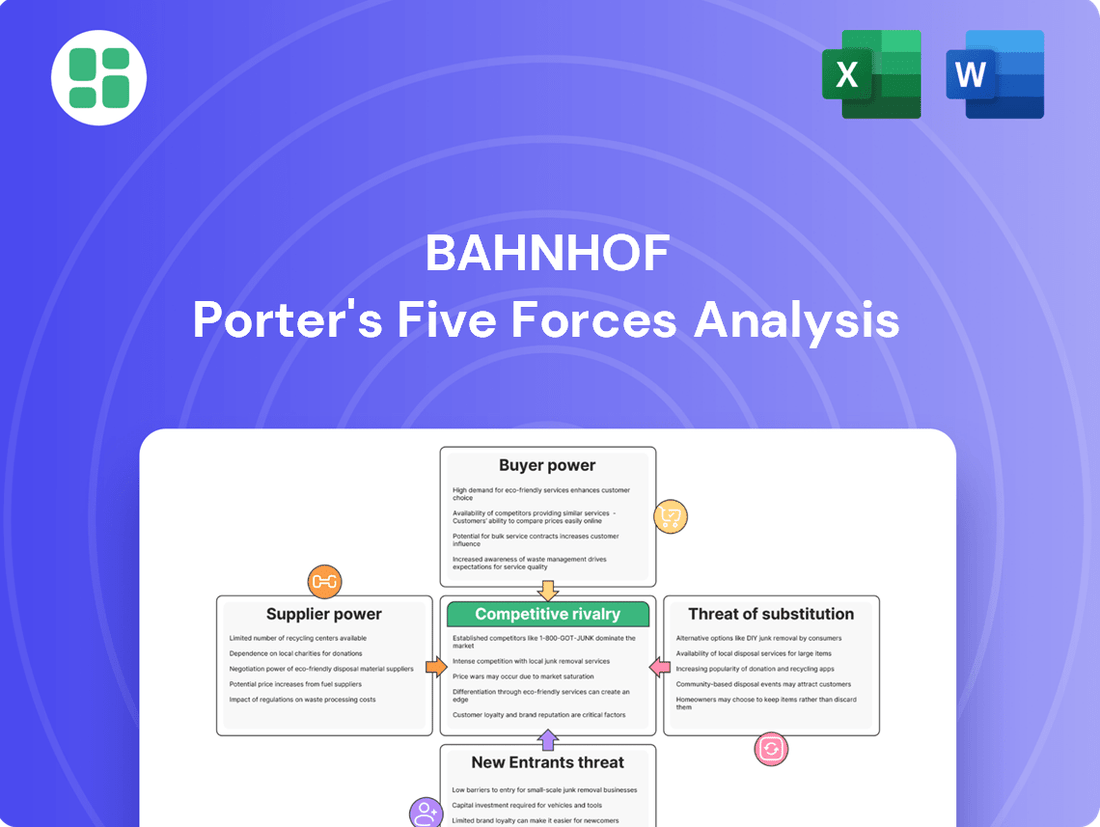
Bahnhof's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces: the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Understanding these forces is crucial for Bahnhof to identify its strategic advantages and potential vulnerabilities within the market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bahnhof’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bahnhof AB's supplier bargaining power is significantly shaped by the concentration of its key infrastructure and technology providers. A small number of vendors for specialized fiber optic equipment or advanced network hardware can grant these suppliers considerable leverage over Bahnhof. This is particularly true for critical, proprietary components where alternatives are scarce.
While Bahnhof's investment in its own network infrastructure helps to reduce reliance on external providers for some services, the procurement of core, high-capacity network hardware and specialized equipment remains a critical dependency. For example, in 2023, the global market for optical networking hardware saw continued consolidation, with a few major players dominating the supply of cutting-edge technology essential for high-speed internet services.
The availability of substitute inputs for a company like Bahnhof, an Internet Service Provider (ISP), is a key factor in understanding supplier power. For critical components like specialized fiber optic cables or advanced networking hardware, readily available substitutes are often limited. This is because the underlying technology standards are highly specific and require significant investment and expertise to replicate.
For instance, while there are numerous hardware manufacturers, the actual components that form the backbone of a high-speed internet network often rely on proprietary technologies or specific interoperability standards. This scarcity of alternative, equally functional inputs means that suppliers of these essential elements can wield considerable influence over pricing and terms. In 2024, the global market for optical fiber cable, a critical input for ISPs, saw continued consolidation among key manufacturers, further concentrating supply and potentially increasing supplier leverage.
Switching costs for Bahnhof are substantial, especially when it comes to core network infrastructure and data center services. For instance, migrating a complex routing platform from one provider to another requires significant investment in new hardware, software, and extensive reconfiguration. This complexity and the associated capital expenditure directly increase Bahnhof’s reliance on existing suppliers, thereby enhancing their bargaining power.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into the retail internet service provider (ISP) market is generally low. Companies that supply essential hardware or backbone network capacity, like fiber optic cable manufacturers or large telecommunications infrastructure firms, typically operate on different business models and face distinct regulatory hurdles compared to consumer-facing ISPs. For instance, a backbone provider's focus is on wholesale capacity and network management, not customer acquisition and service delivery.
While direct forward integration by traditional suppliers is uncommon, a nuanced form of this threat emerges from large cloud service providers. These entities are increasingly offering direct connectivity solutions, effectively bypassing traditional ISP retail channels for enterprise clients. This indirect forward integration by giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, which leverage their vast infrastructure to provide dedicated network access, can be seen as a competitive pressure, particularly for business-oriented ISP services.
In 2024, the ISP sector continues to see consolidation and strategic partnerships rather than direct supplier forward integration. For example, while a hardware supplier might partner with an ISP for bundled offerings, they are unlikely to launch their own competing retail internet service. The capital expenditure and operational complexity of running a nationwide ISP network remain significant deterrents for most hardware or infrastructure providers.
- Low Direct Integration: Traditional hardware manufacturers and backbone providers rarely enter the retail ISP space due to disparate business models and regulatory environments.
- Indirect Integration Threat: Major cloud providers offering direct connectivity solutions represent a form of indirect forward integration, impacting enterprise-focused ISPs.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the ISP market prioritizes partnerships and consolidation over direct forward integration by suppliers.
Impact of Input on Bahnhof's Cost or Differentiation
The bargaining power of suppliers significantly impacts Bahnhof's cost structure and its ability to differentiate. Critical inputs like high-quality, secure network equipment, reliable power for its data centers, and robust backbone connectivity are essential for delivering core services and upholding its reputation for privacy and data security.
Any price hikes or quality dips from these suppliers directly translate into increased operational costs for Bahnhof, potentially eroding profit margins. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor shortage continued to affect the availability and cost of advanced networking hardware, a key component for Bahnhof's infrastructure. This can force Bahnhof to absorb these costs or pass them on to customers, impacting its competitive edge.
- Network Equipment: Dependence on a few specialized vendors for high-performance routers and switches can give those suppliers leverage.
- Power Providers: Reliable and competitively priced electricity is paramount for data center operations; disruptions or significant price increases from energy suppliers can be detrimental.
- Fiber Optic Providers: Access to high-capacity fiber optic networks, often controlled by a limited number of wholesale providers, is crucial for backbone connectivity.
Bahnhof's supplier bargaining power is amplified by the limited number of providers for specialized network hardware and critical infrastructure components. The high costs associated with switching these essential inputs, such as advanced routing equipment or proprietary fiber optic technology, further solidify supplier leverage. This concentration means suppliers can exert significant influence over pricing and terms, directly impacting Bahnhof's operational expenses and service delivery capabilities.
| Supplier Category | Key Components | Supplier Power Factors | Impact on Bahnhof | 2024 Market Trend Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network Hardware | Routers, Switches, Servers | Proprietary technology, limited vendors, high switching costs | Increased procurement costs, potential supply chain delays | Continued consolidation among major networking equipment manufacturers |
| Fiber Optic Infrastructure | High-capacity fiber optic cables, network access points | Concentrated market, specialized manufacturing, significant infrastructure investment | Higher wholesale bandwidth costs, dependence on provider availability | Limited new entrants in wholesale fiber deployment, maintaining supplier concentration |
| Data Center Services | Power, Cooling, Physical Security | Reliable energy supply, specialized facilities, long-term contracts | Operational cost volatility, risk of service disruption | Increased demand for energy-efficient data centers, potential for higher power costs |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Bahnhof's market, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threats from new entrants and substitutes, and ultimately, Bahnhof's strategic positioning.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Effortlessly adapt analysis to new market entrants or shifting supplier power with customizable templates.
Customers Bargaining Power
Bahnhof's customer base, comprising both individuals and businesses, displays a spectrum of price sensitivity. For many private users, competitive pricing is a significant factor when choosing broadband services.
However, Bahnhof's corporate clients and those who value its strong emphasis on privacy and security often exhibit lower price sensitivity. These customers tend to prioritize service quality, reliability, and the unique data protection features Bahnhof offers, which can justify a premium price point.
The Swedish Internet Service Provider (ISP) market is quite mature and sees a lot of competition. Major companies like Telia, Tele2, and others are all offering broadband services. This means customers have plenty of options to choose from when looking for an internet provider.
This wide availability of choices really boosts the bargaining power of customers. If they aren't happy with their current ISP, they can switch to another provider without much hassle. For instance, in 2023, Sweden had a broadband penetration rate of over 90%, indicating a highly accessible and competitive market where customer switching is common.
Switching costs for customers in the Swedish broadband market are not a significant hurdle. While some minor inconveniences like technical setup or existing contract terms might exist, regulatory bodies and the competitive landscape are actively working to minimize these barriers. For instance, in 2024, Sweden continued its focus on consumer protection within the telecommunications sector, aiming to simplify the process of changing providers.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers in Sweden benefit from a high degree of transparency regarding internet service provider (ISP) offerings, including speeds and pricing. This is significantly influenced by regulatory mandates for clear information disclosure and the availability of independent comparison websites. For instance, in 2024, several Swedish consumer advocacy groups actively published detailed comparisons of broadband plans, highlighting price-to-performance ratios.
This readily available information empowers customers to effectively compare Bahnhof's services against those of its competitors. They can easily ascertain whether Bahnhof offers competitive pricing and performance metrics, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations or their willingness to switch providers if perceived value is lacking. This transparency directly translates into enhanced bargaining power for the end consumer.
- Informed Decision-Making: Swedish consumers have access to extensive data on ISP services, facilitating informed choices.
- Competitive Landscape Clarity: Comparison tools and regulatory transparency make it simple to evaluate Bahnhof against rivals.
- Price Sensitivity: Transparency on pricing allows customers to readily identify and act on price discrepancies, increasing their bargaining power.
Customer Ability to Bundle Services
Customers, especially larger corporate clients, often prefer to consolidate their IT infrastructure and connectivity needs through bundled service offerings. Bahnhof's comprehensive portfolio, encompassing high-speed broadband, secure colocation facilities, and scalable cloud services, directly addresses this preference.
By offering integrated solutions, Bahnhof can potentially reduce a customer's motivation to engage with multiple vendors for disparate services. However, this very ability to provide a one-stop shop also amplifies the customer's bargaining power. When a client consolidates multiple services with a single provider like Bahnhof, they gain significant leverage to negotiate more favorable terms and pricing for the entire package.
- Bundled Service Demand: Corporate clients increasingly seek integrated solutions for broadband, colocation, and cloud services.
- Bahnhof's Portfolio Strength: Bahnhof's diverse service range allows it to meet these bundled demands effectively.
- Customer Leverage: The ability to bundle services with a single provider enhances customer negotiation power for comprehensive packages.
The bargaining power of Bahnhof's customers is significant due to the competitive and transparent nature of the Swedish internet market. With over 90% broadband penetration in 2023, customers have numerous providers to choose from, and switching costs are minimal, further amplified by consumer protection efforts in 2024.
The availability of detailed comparison tools and regulatory mandates for clear pricing and performance data in 2024 empowers customers to easily assess Bahnhof's offerings against competitors, directly increasing their leverage.
While Bahnhof's bundled services appeal to customers seeking integrated solutions, this consolidation also grants clients greater bargaining power to negotiate favorable terms for their comprehensive packages.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Competition | High | Sweden's broadband market has multiple major players (Telia, Tele2), leading to intense competition. |
| Customer Switching Costs | Low | Regulatory focus in 2024 aims to simplify provider changes, minimizing barriers. |
| Information Transparency | High | Consumer advocacy groups actively publish comparisons of ISP plans, aiding informed decisions. |
| Bundled Service Demand | Moderate to High | Corporate clients prefer integrated IT solutions, giving them leverage when consolidating with one provider. |
Full Version Awaits
Bahnhof Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Bahnhof Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual, comprehensive document, ready for download and use the moment you buy. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file, professionally formatted and ready for your strategic needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Swedish Internet Service Provider (ISP) market is a crowded space. Major players like Telia, Tele2, and Telenor compete fiercely with a multitude of smaller, specialized providers and municipal networks. This sheer volume and variety of competitors, including publicly owned city networks, create a highly competitive environment.
While Sweden boasts exceptionally high broadband penetration, with near-universal access to high-speed connections, the industry isn't stagnant. Growth continues, fueled by a rising demand for faster speeds, the ongoing rollout of 5G technology, and broader digital transformation efforts across various sectors. This persistent, albeit moderate, expansion creates a dynamic where companies are keenly focused on capturing existing market share rather than solely on acquiring entirely new customer segments, inherently heightening competitive rivalry.
Bahnhof, a Swedish Internet Service Provider, distinguishes itself through a robust emphasis on privacy and data security. This differentiation is built upon their ownership and operation of their own network infrastructure and data centers, a significant departure from many competitors who may rely on leased lines or third-party facilities.
While core broadband services can often be viewed as a commodity, leading to intense price competition within the industry, Bahnhof's strategic focus on privacy and security provides a unique selling proposition. This allows them to attract a segment of the market prioritizing data protection over solely cost-driven decisions.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the Internet Service Provider (ISP) industry, particularly for companies like Bahnhof with extensive physical infrastructure, are substantial. These high exit barriers stem from significant sunk costs associated with building and maintaining vast fiber optic networks, data centers, and other specialized equipment. Disposing of or repurposing this infrastructure often yields a fraction of its original investment, making a complete withdrawal from the market financially punitive.
These considerable sunk costs create a situation where companies are incentivized to remain operational, even during periods of intense competition or economic downturn. The inability to easily recover invested capital means that firms are more likely to continue competing to generate some return on their assets rather than abandoning the market altogether. This persistence fuels ongoing competitive rivalry within the ISP sector.
For Bahnhof, a company known for its substantial data center facilities and network investments, these exit barriers are a defining characteristic. Their strategic decisions are heavily influenced by the need to amortize these large, fixed investments over time. This reality reinforces the competitive dynamic, as exiting would mean crystallizing significant losses.
- High Sunk Costs: ISPs like Bahnhof invest billions in network infrastructure, making it difficult to recover capital upon exit.
- Infrastructure Obsolescence: Specialized network equipment may have limited resale value or become obsolete quickly.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Exiting a market can sometimes involve regulatory approvals or obligations to existing customers.
- Brand and Customer Base: The effort and cost to build a brand and customer base are lost if a company exits.
Pricing Strategies and Promotions
Competitive rivalry within the internet service provider (ISP) market, where Bahnhof operates, is fierce, particularly in the residential broadband sector. This intensity is clearly demonstrated through aggressive pricing strategies and frequent promotions. For instance, in 2024, many ISPs continued to offer substantial discounts on initial subscription periods and attractive bundled packages that include television and mobile services. These tactics are designed to capture market share and foster customer loyalty in a highly competitive environment.
The constant pressure to offer lower prices and more compelling deals directly impacts Bahnhof's revenue streams and overall profit margins. ISPs are continuously introducing limited-time offers and introductory rates, forcing competitors to respond in kind to avoid losing customers. This dynamic means that pricing decisions are critical, and a failure to remain competitive can lead to a significant erosion of market position.
- Aggressive Pricing: ISPs routinely employ discounted rates to attract new subscribers.
- Bundled Services: Offering packages of broadband, TV, and mobile services is a common strategy to increase customer value and retention.
- Promotional Offers: Limited-time deals and introductory discounts are prevalent tactics used to gain a competitive edge.
- Impact on Margins: These competitive pressures can compress profit margins for all players in the market, including Bahnhof.
The Swedish ISP market is characterized by intense competition, with numerous players vying for market share. This rivalry is evident in aggressive pricing strategies and frequent promotional offers, a trend that continued strongly into 2024. Many providers, including major players and smaller regional operators, offered significant discounts for initial subscription periods and attractive bundles of services like broadband, TV, and mobile. For Bahnhof, this means constant pressure on pricing and margins, necessitating a focus on its unique value proposition to retain customers.
| Competitor | 2024 Broadband Price (Example) | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|
| Telia | Starting from 399 SEK/month | Extensive network coverage |
| Tele2 | Promotional offer: 299 SEK/month for 6 months | Bundled mobile and broadband deals |
| Telenor | Starting from 349 SEK/month | Focus on customer service |
| Bahnhof | Starting from 329 SEK/month (Privacy-focused) | Emphasis on privacy and security, own infrastructure |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing rollout and adoption of 5G technology present a growing threat of substitutes for traditional fixed-line broadband services. As of early 2024, major telecommunication companies globally are heavily investing in 5G infrastructure, with widespread deployment expected to accelerate throughout the year.
With enhanced speeds and significantly lower latency, 5G mobile broadband is increasingly capable of serving as a primary internet connection for many consumers and businesses. This is particularly true in regions where fiber optic deployment is lagging or for users who prioritize the flexibility and mobility that wireless connections offer, potentially impacting demand for wired broadband subscriptions.
Satellite internet services, exemplified by Starlink, are emerging as a notable, though still niche, substitute. These services are particularly relevant for customers in remote or underserved regions where establishing traditional wired internet infrastructure is prohibitively costly. For instance, as of early 2024, Starlink reported over 2.7 million active users globally, indicating a growing adoption rate.
While satellite internet is not yet a widespread threat in Sweden's more populated areas, its expanding reach presents a potential challenge for providers serving remote user segments. The increasing accessibility and performance improvements in satellite technology could gradually erode the market share for fixed-line providers in these specific geographical niches.
The proliferation of widespread public Wi-Fi networks in urban centers presents a significant threat of substitutes for dedicated fixed-line internet services. By July 2024, many cities boast extensive free Wi-Fi zones in cafes, libraries, and public transport hubs, offering a viable alternative for casual internet users. This trend directly impacts the demand for traditional ISP services, as consumers can increasingly access the internet without a personal subscription.
Furthermore, bundled services from mobile network operators, which often include home internet as part of a mobile data plan, further intensify this threat. As of early 2024, major telecom providers are actively promoting these converged offerings, making it attractive for consumers to consolidate their connectivity needs. This bundling strategy can lead customers to reduce or eliminate their reliance on separate fixed-line internet providers.
Over-the-Top (OTT) Communication Services
The proliferation of Over-the-Top (OTT) communication services, such as WhatsApp, Zoom, and Skype, presents a significant threat to traditional communication revenue streams. These services utilize existing internet infrastructure, effectively bypassing the need for legacy voice and messaging services often offered by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). While they don't substitute the internet itself, they directly compete with and erode the profitability of voice and communication segments.
By 2024, the global OTT market was valued at over $100 billion, demonstrating its substantial reach and impact. This growth is driven by user preference for feature-rich, often free or low-cost communication alternatives. For instance, a significant portion of international voice traffic has shifted to OTT platforms, impacting traditional telcos' revenue.
- Erosion of Voice and Messaging Revenue: OTT services directly substitute traditional voice calls and SMS, leading to declining revenue for ISPs in these areas.
- Increased Data Consumption: While OTTs don't replace internet access, they drive higher data usage, which can be both an opportunity and a challenge for ISPs managing network capacity.
- User Preference for Convenience: Consumers increasingly favor the integrated features and cross-platform compatibility offered by OTT applications.
- Market Penetration: By late 2024, it's estimated that over 80% of smartphone users globally regularly utilize at least one OTT communication service.
Alternative Data Transmission Technologies
While fiber optics currently dominate high-speed data transmission, advancements in alternative technologies pose a potential threat. Emerging wireless mesh networks and the latest cable broadband iterations, like DOCSIS 4.0, are improving their capabilities. These could offer competitive alternatives, impacting the long-term demand for dedicated fiber services.
For instance, DOCSIS 4.0 promises symmetrical multi-gigabit speeds over existing cable infrastructure. This could reduce the perceived need for costly fiber deployments for many consumers and businesses. By 2024, the global fixed wireless access market was projected to reach over $100 billion, indicating significant growth in wireless alternatives.
- Advancing Wireless Technologies: Continued development in 5G and future wireless standards could offer competitive speeds and lower latency, potentially serving as substitutes for fiber in certain applications.
- Cable Broadband Evolution: DOCSIS 4.0's ability to deliver multi-gigabit symmetrical speeds over existing coaxial cable networks presents a significant competitive alternative to fiber.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For many users, the lower deployment cost and existing infrastructure of advanced wireless and cable technologies could make them more attractive substitutes than fiber.
- Market Penetration: The widespread availability and increasing performance of these alternative technologies could capture market share from fiber providers, particularly in less densely populated areas.
The threat of substitutes for traditional fixed-line broadband is multifaceted, encompassing advancements in wireless technologies, evolving cable infrastructure, and the increasing prevalence of public Wi-Fi. These alternatives offer competitive speeds, greater flexibility, and often lower costs, directly challenging the market position of dedicated wired services. By 2024, the global fixed wireless access market was projected to exceed $100 billion, highlighting the significant growth of wireless alternatives.
5G mobile broadband, with its enhanced speeds and reduced latency, is increasingly viable as a primary internet connection, especially where fiber deployment is limited. Satellite internet services like Starlink are also expanding, particularly serving remote areas. As of early 2024, Starlink reported over 2.7 million users globally, indicating a growing adoption trend.
Furthermore, the widespread availability of public Wi-Fi and bundled service offerings from mobile operators present compelling alternatives. Many urban centers by mid-2024 boasted extensive free Wi-Fi zones, reducing the need for personal subscriptions for casual users. These evolving substitutes directly impact the demand and revenue potential for traditional fixed-line providers.
| Technology | Key Substitute Feature | 2024 Market Data/Projection |
|---|---|---|
| 5G Mobile Broadband | High speeds, low latency, mobility | Significant global infrastructure investment and accelerated deployment expected. |
| Satellite Internet (e.g., Starlink) | Broad coverage, especially in remote areas | Over 2.7 million active users globally as of early 2024. |
| Public Wi-Fi Networks | Free access in public spaces | Extensive availability in urban centers by mid-2024. |
| Bundled Mobile Services | Integrated connectivity, convenience | Active promotion by major telecom providers as of early 2024. |
| DOCSIS 4.0 Cable | Multi-gigabit symmetrical speeds over existing infrastructure | Potential to reduce the perceived need for fiber deployments. |
Entrants Threaten
The internet service provider (ISP) industry, particularly for companies like Bahnhof that manage their own network infrastructure and data centers, demands immense capital. Laying fiber optic cables across vast distances, constructing state-of-the-art data centers, and procuring essential core network equipment represent substantial upfront investments. For instance, the global spending on data center construction alone was projected to reach over $270 billion in 2024, highlighting the sheer scale of required capital.
This high capital intensity acts as a significant barrier, deterring potential new entrants. The sheer cost of replicating Bahnhof's extensive network and data center footprint makes it exceedingly difficult for smaller or less capitalized companies to compete effectively. Building a comparable infrastructure would likely require billions of dollars in investment, a sum that many aspiring ISPs simply cannot raise.
New entrants into the Swedish telecommunications market, where Bahnhof operates, must contend with significant regulatory hurdles and licensing requirements overseen by the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS). These regulations cover a broad spectrum, including network security standards, data retention mandates, and crucial consumer protection measures. For example, in 2023, PTS continued its rigorous oversight of licensed operators, ensuring compliance with directives like the NIS2 directive which enhances cybersecurity across critical infrastructure, including telecom networks.
The complexity and time-intensive nature of navigating these stringent regulations can act as a substantial deterrent for potential new market participants. Successfully obtaining the necessary licenses and demonstrating ongoing compliance requires considerable investment in legal expertise, technical infrastructure, and administrative processes, thereby raising the barrier to entry for smaller or less established companies looking to compete with incumbents like Bahnhof.
Established internet service providers (ISPs) like Bahnhof leverage extensive networks and existing customer relationships, creating significant barriers for newcomers. Their established agreements with city networks and property owners grant them access to prime distribution channels that are difficult for new entrants to replicate. For instance, in 2024, the continued consolidation within the fiber optic infrastructure market means that securing rights-of-way and physical access points is increasingly challenging and costly.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Incumbent Internet Service Providers (ISPs) like Deutsche Telekom and Vodafone in Germany benefit significantly from economies of scale. Their vast existing network infrastructure, covering extensive fiber optic and copper lines, allows for lower per-unit costs in operation and maintenance compared to a newcomer needing to build out from scratch. For instance, in 2024, major German ISPs continued to invest billions in network upgrades, a cost that is spread across millions of existing subscribers, making it harder for new entrants to achieve comparable cost efficiencies.
Furthermore, incumbents possess a substantial experience curve advantage. Years of managing complex network operations, troubleshooting technical issues, and refining customer service processes have honed their operational expertise. This accumulated knowledge translates into more reliable service delivery and efficient customer support, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly. By mid-2024, the average customer churn rate for established ISPs remained significantly lower than what new market entrants typically experience, underscoring this advantage.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbent ISPs leverage massive network investments, reducing per-subscriber costs for infrastructure, operations, and customer service.
- Experience Curve: Decades of network management and customer relationship building provide incumbents with operational efficiencies and service quality advantages.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants face substantial hurdles in matching the cost-effectiveness and service reliability built through scale and experience.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Start-ups struggle to compete on price or service quality against established players who have already amortized their infrastructure and operational learning.
Brand Loyalty and Switching Costs for Customers
While the direct financial cost of switching internet providers might not be prohibitive, Bahnhof's established brand loyalty and the inherent inertia customers experience in changing services present a significant barrier to new entrants. This loyalty, cultivated through a strong emphasis on privacy and security, means newcomers must offer compelling advantages or substantial incentives to lure away existing users. For instance, in 2023, the average consumer stayed with their primary internet service provider for approximately 4.1 years, indicating a degree of customer stickiness that new competitors must overcome.
Bahnhof's commitment to privacy and security has fostered a dedicated user base. This focus differentiates them in a market where data protection is increasingly valued. Consequently, new companies entering the space face the challenge of not only matching Bahnhof's service offerings but also building trust and demonstrating a comparable commitment to user privacy, which is a considerable hurdle.
- Customer Inertia: Many users prefer the convenience of sticking with their current provider, even if slightly better options exist.
- Brand Reputation: Bahnhof's strong reputation for privacy and security acts as a significant deterrent to potential new market entrants.
- Acquisition Costs: New entrants would need to invest heavily in marketing and promotional offers to attract customers away from a trusted provider like Bahnhof.
The threat of new entrants for an ISP like Bahnhof is considerably low due to immense capital requirements for infrastructure development, such as fiber optic networks and data centers, with global data center construction spending projected to exceed $270 billion in 2024. Significant regulatory hurdles and licensing complexities, overseen by authorities like the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS), further deter new players, especially with ongoing compliance demands like the NIS2 directive for cybersecurity. Established players benefit from economies of scale, with major German ISPs investing billions in network upgrades in 2024, spreading costs across millions of subscribers, and possess an experience curve advantage, reflected in lower customer churn rates for incumbents compared to new entrants by mid-2024.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for network and data center infrastructure. | Global data center construction spending projected over $270 billion. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and compliance with standards like NIS2. | PTS continued rigorous oversight of licensed operators. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large existing customer base and infrastructure. | Major German ISPs invested billions in network upgrades. |
| Experience Curve | Operational efficiencies and customer service expertise gained over time. | Incumbent churn rates significantly lower than new entrants. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bahnhof is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Bahnhof's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld, and publicly available regulatory filings.