Ascent Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ascent Industries Bundle
Ascent Industries operates in a landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the ever-present threat of new entrants, significantly impacting its pricing power. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this competitive terrain effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ascent Industries’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fluctuating prices for key raw materials like steel scrap, iron ore, and alloying elements directly impact Ascent Industries' cost structure. For instance, global steel prices experienced significant swings in early 2024, with some benchmarks showing a 15-20% increase year-over-year before moderating. This volatility grants suppliers greater bargaining power, especially if Ascent faces challenges in absorbing or passing on these elevated costs to its customers.
Ascent Industries likely faces concentrated supplier power if a limited number of firms dominate the market for critical inputs like specialized steel grades or advanced manufacturing components. For example, if only two or three global producers supply a unique alloy essential for Ascent's high-performance products, these suppliers can dictate terms, potentially increasing prices or restricting availability. This leverage becomes even more pronounced if switching suppliers involves significant costs or lengthy qualification processes.
The increasing global emphasis on sustainability, particularly the push for green steel, could further consolidate supplier power. As of early 2024, major steel producers are investing heavily in decarbonization technologies, which may initially limit the supply of traditional, lower-cost steel grades. This shift could mean that Ascent, to maintain its competitive edge and meet evolving customer demands for eco-friendly products, might have to rely on a smaller pool of suppliers capable of providing certified green steel, thereby amplifying their bargaining strength.
Ascent Industries faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers for critical inputs like steel. These costs can involve substantial investments in retooling manufacturing equipment to accommodate different material specifications, the complex process of re-qualifying new materials to meet stringent quality standards, and the time and resources needed to renegotiate contracts. For instance, in the specialized industrial products and pipe/tube manufacturing sectors, a shift in steel supplier could necessitate millions in capital expenditures for new machinery or extensive testing protocols, directly impacting production timelines and costs.
Uniqueness of Inputs
Ascent Industries' reliance on highly specialized inputs, particularly for its advanced industrial product fabrication, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, if Ascent requires specific, proprietary alloys for its high-precision metal components, suppliers of these unique materials can exert considerable leverage. The scarcity of alternative sources for such specialized inputs, potentially due to patents or complex manufacturing processes, further amplifies this power. In 2024, the global market for specialty metal alloys saw price increases of up to 15% for certain grades due to concentrated production and high demand from advanced manufacturing sectors.
The uniqueness of inputs for Ascent Industries can be observed in several key areas:
- Proprietary Alloys: Ascent's use of patented or uniquely formulated metal alloys for critical components in its specialized industrial products grants significant power to the few suppliers capable of producing them.
- Specialized Machining Services: Certain fabrication processes may require highly specialized machining or finishing services that only a limited number of providers offer, creating a dependence on those suppliers.
- Advanced Composites: If Ascent incorporates cutting-edge composite materials with unique performance characteristics, the suppliers of these advanced materials can command higher prices and dictate terms.
- Limited Substitutability: The inability to easily substitute these specialized inputs with more common alternatives means Ascent has less flexibility in sourcing, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
Forward Integration Threat by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Ascent Industries' core operations, such as pipe and tube manufacturing or industrial fabrication, significantly enhances their bargaining power. This means suppliers could potentially bypass Ascent and sell directly to end customers, thereby capturing more value.
For instance, if a key raw material supplier for Ascent also possesses the capabilities and infrastructure for steel distribution or even basic fabrication, they could choose to compete directly. This would not only reduce Ascent's supplier options but could also lead to increased input costs or restricted access to essential materials, impacting Ascent's profitability and market flexibility.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers may leverage their position to enter Ascent's manufacturing or distribution channels.
- Increased Supplier Power: If suppliers can directly compete, their leverage over Ascent grows, potentially dictating terms.
- Market Impact: Direct competition from suppliers could narrow Ascent's market access and increase operational costs.
Ascent Industries faces considerable bargaining power from its suppliers due to the concentration of critical material sources and the high costs associated with switching. For example, in early 2024, the price of specialized steel alloys, crucial for Ascent's advanced products, saw increases of up to 15% from a limited number of global producers. This situation is exacerbated by the unique nature of some inputs, such as proprietary alloys and specialized machining services, where alternative suppliers are scarce. The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Ascent's operations, such as direct sales or basic fabrication, further amplifies their leverage, potentially leading to increased costs and reduced market flexibility for Ascent.
| Factor | Ascent Industries Impact | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited suppliers for specialized alloys grant significant power. | Up to 15% price increase for certain specialized alloys in early 2024. |
| Switching Costs | High costs for retooling, re-qualification, and contract renegotiation. | Millions in potential capital expenditure for equipment changes in niche sectors. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Proprietary alloys and specialized machining create dependence. | Scarcity of alternative sources for unique metal components. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers may bypass Ascent to sell directly to customers. | Potential for raw material suppliers to move into basic fabrication. |
What is included in the product
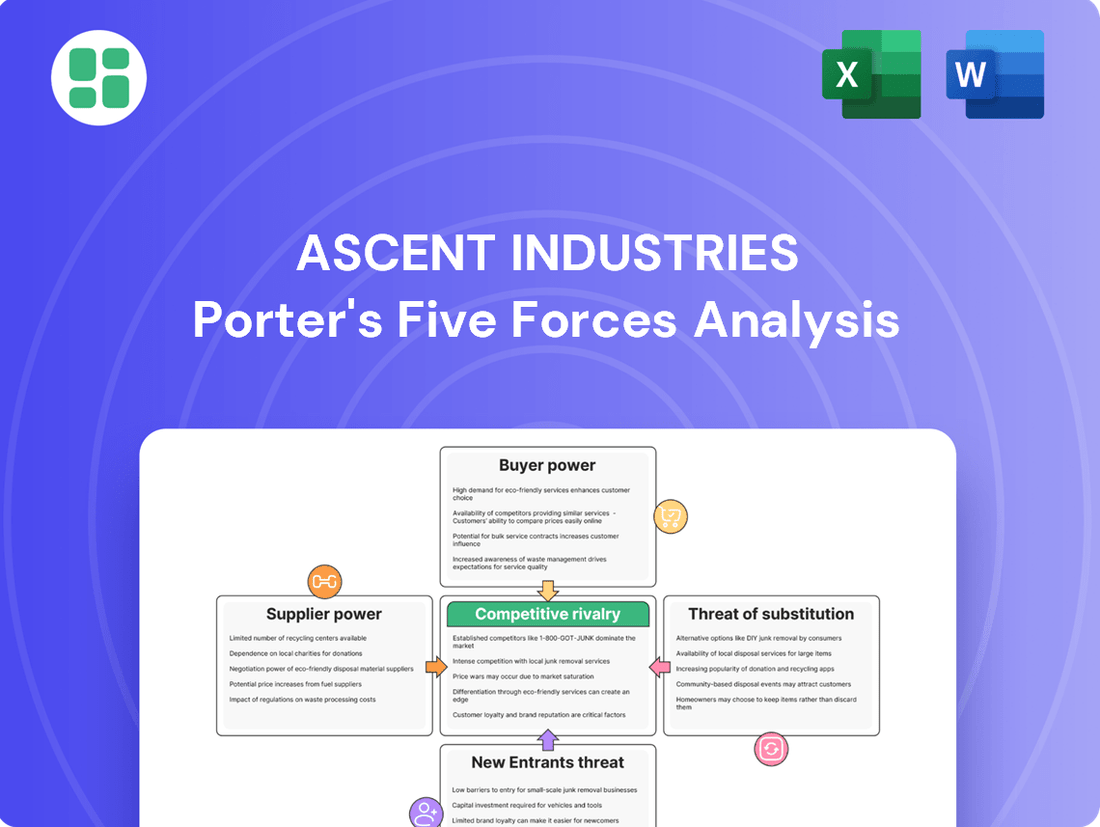
Ascent Industries' Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing a strategic view of its competitive environment.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Ascent Industries' Porter's Five Forces, highlighting areas of potential vulnerability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ascent Industries' reliance on a few major clients in sectors like infrastructure and energy significantly influences its customer bargaining power. For instance, if a handful of large construction companies account for over 40% of Ascent's revenue, these clients can leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate more favorable pricing and contract terms.
This customer concentration is particularly impactful if Ascent's specialized components or services lack strong differentiation. Major players in the agricultural machinery sector, for example, might switch suppliers if Ascent doesn't meet their price demands, especially given the competitive landscape where alternative solutions are readily available.
Ascent Industries' steel products, including pipes and tubes, often operate in markets where standardization is prevalent. This means customers can readily compare offerings from various suppliers based on specifications and price, significantly boosting their leverage.
The steel pipe and tube market experienced a notable growth trajectory, with global demand projected to reach USD 198.5 billion by 2028, according to some market analyses. This expansion, fueled by infrastructure and energy projects, also intensifies competition, making it harder for companies like Ascent to differentiate their core offerings and thus increasing customer bargaining power.
Customer switching costs for Ascent Industries are a critical factor in understanding buyer power. If customers can easily transition to a competitor with minimal effort or expense, their ability to negotiate better terms increases significantly, directly impacting Ascent's pricing power.
For instance, if Ascent's clients face low barriers to re-qualifying new suppliers or lack binding long-term contracts, they are more inclined to shop around. This flexibility allows them to leverage competitive offers, potentially forcing Ascent to lower its prices to retain business. In 2024, industries with readily available substitute products often see this dynamic play out, with customer acquisition costs for competitors being relatively low.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Ascent Industries' customers, particularly those in sectors like agricultural machinery manufacturing, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is largely due to their own escalating input costs and the intense competition they face, which directly impacts their profitability.
For example, reports from early 2024 indicated that agricultural equipment manufacturers were grappling with a 15-20% increase in raw material costs. This financial pressure compels them to seek the most competitive pricing for essential components, like those supplied by Ascent. Consequently, Ascent may find itself constrained in its ability to implement price increases without risking substantial order volume reductions.
- High Customer Price Sensitivity: Agricultural machinery manufacturers, facing increased input costs (e.g., steel, labor), are highly sensitive to the prices of components.
- Impact on Ascent's Margins: This sensitivity forces Ascent to maintain competitive pricing, potentially limiting its profit margins on sales to this segment.
- Market Dynamics: The competitive landscape for agricultural equipment manufacturers means they pass cost pressures down the supply chain, directly affecting Ascent's pricing power.
Backward Integration Threat by Customers
Customers' ability to integrate backward, meaning they could produce their own steel components or perform fabrication internally, poses a significant threat to Ascent Industries. This is particularly relevant in sectors like infrastructure and energy where large-scale projects are common.
If Ascent's major clients can credibly threaten to self-supply, their bargaining power over Ascent naturally increases. This leverage can lead to reduced demand for Ascent's products and services as customers seek to control their supply chains and costs.
- Backward Integration Threat: Customers in infrastructure and energy sectors may consider producing their own steel components or undertaking fabrication internally.
- Increased Bargaining Power: A credible threat of self-supply by major customers enhances their leverage over Ascent, potentially impacting pricing and order volumes.
- Impact on Demand: This customer power can lead to a decrease in demand for Ascent's offerings as clients prioritize internal production for large projects.
Ascent Industries faces substantial bargaining power from its customers due to concentrated client bases and the commoditized nature of its steel products. High price sensitivity, especially in the agricultural machinery sector, forces Ascent to maintain competitive pricing, impacting its margins. The potential for customers to integrate backward, producing components internally, further amplifies their leverage, threatening Ascent's order volumes and pricing flexibility.
| Factor | Ascent Industries Impact | Supporting Data (2024/Recent) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major clients | Over 40% of revenue from a few key infrastructure/energy clients. |
| Product Standardization | Easy price comparison, reduced differentiation | Steel pipes and tubes market characterized by standard specifications. |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on Ascent's pricing | Agricultural equipment manufacturers facing 15-20% raw material cost increases in early 2024. |
| Switching Costs | Increased customer flexibility | Low barriers to re-qualifying suppliers for many clients. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential for reduced demand | Clients in large-scale infrastructure projects may explore self-supply. |
What You See Is What You Get
Ascent Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, ready-to-use Ascent Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within its industry. What you're previewing is precisely the same professionally formatted and detailed analysis that will be available to you instantly after purchase, ensuring no surprises. This comprehensive report is designed to equip you with actionable insights for strategic decision-making regarding Ascent Industries.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Ascent Industries' performance is closely tied to the growth rates in key sectors like infrastructure, energy, and agriculture. While global steel demand saw a dip in 2024, projections indicate a modest recovery for 2025, largely propelled by infrastructure projects. This anticipated growth, particularly in emerging markets, could temper the intensity of competitive rivalry by expanding the overall market pie.
Ascent Industries operates in markets with a significant number of direct competitors. In steel distribution, the landscape includes numerous domestic and international players, many of whom are vying for market share. Similarly, the pipe and tube manufacturing sector is characterized by a diverse range of companies, and industrial fabrication also sees a broad spectrum of participants.
The sheer volume of competitors, both at home and abroad, intensifies rivalry. For instance, the global steel industry in 2024 continues to see participation from countries with lower production costs, potentially impacting pricing dynamics for companies like Ascent. This competitive density can lead to aggressive price wars, especially when international players leverage subsidies or other cost advantages.
Ascent Industries operates in a capital-intensive sector, with industrial manufacturing and steel production demanding significant upfront investment. This naturally results in substantial fixed costs, such as those associated with plant maintenance and machinery. For instance, in 2024, the average capital expenditure for a new steel mill can easily run into billions of dollars, creating a strong pressure to utilize these assets fully.
The high fixed cost structure incentivizes companies like Ascent to maintain high production levels, even when demand softens. This drive to cover overhead can lead to aggressive pricing strategies as firms attempt to offload inventory, potentially triggering price wars. In 2024, reports indicated that certain steel producers were operating at capacity utilization rates below 70%, a clear sign of this pressure to move product and manage fixed costs.
Product Differentiation
Ascent Industries faces a dynamic competitive landscape where product differentiation plays a crucial role in mitigating price-based rivalry. The extent to which Ascent can distinguish its steel products, pipes, tubes, and fabricated items beyond mere cost is a key determinant of its competitive advantage. In markets where products are perceived as commodities, competition often devolves into a price war, intensifying rivalry among existing players.
However, Ascent has opportunities to differentiate. For instance, by focusing on specialized alloys, superior surface finishes, or custom fabrication capabilities, Ascent can command premium pricing and reduce direct price comparisons. In 2024, the global steel market, while competitive, saw demand for specialized steel products grow, indicating a willingness among buyers to pay more for tailored solutions.
- Differentiation Strategy: Ascent can differentiate through product quality, technical support, and customization in its steel, pipe, and tube offerings.
- Impact of Low Differentiation: If products are seen as interchangeable commodities, competition will heavily rely on price, increasing rivalry and potentially eroding profit margins.
- Market Trends: Growing demand for high-strength, corrosion-resistant, or custom-engineered steel components in sectors like automotive and construction supports differentiation efforts.
- Ascent's Position: By investing in R&D and advanced manufacturing, Ascent can create unique value propositions that move it away from pure price competition.
Exit Barriers
Ascent Industries operates within sectors characterized by significant exit barriers, particularly in the steel and industrial manufacturing industries. These barriers can trap companies, even those struggling, within the market.
High capital investment in specialized machinery and facilities means that selling off assets at a reasonable price is often difficult. For instance, the cost of a modern steel mill can run into billions of dollars, making a clean break financially prohibitive for many. Furthermore, regulatory requirements, such as environmental cleanup obligations at former industrial sites, add to the expense of exiting. Long-term contracts with suppliers or customers also create commitments that are costly to break, forcing companies to continue operations even when unprofitable. This situation can lead to persistent overcapacity in the global steel market, a trend that has been evident for years, impacting profitability across the board.
- Specialized Assets: Significant investment in heavy machinery and plant infrastructure, often with limited resale value outside the specific industry.
- Regulatory Obligations: Costs associated with environmental remediation, site decommissioning, and compliance with labor laws upon closure.
- Contractual Commitments: Long-term agreements with suppliers, customers, and employees that incur penalties or significant costs if terminated early.
- Industry Overcapacity: The global steel industry, for example, has historically contended with overcapacity, making it harder for struggling firms to exit gracefully without impacting market prices or asset values. In 2023, global crude steel production reached approximately 1.89 billion tonnes, with many regions still facing supply-demand imbalances.
The competitive rivalry for Ascent Industries is amplified by a crowded market with numerous domestic and international players in steel distribution, pipe and tube manufacturing, and industrial fabrication. This density often leads to aggressive price competition, particularly as international competitors leverage cost advantages. For instance, in 2024, the global steel market continued to be influenced by countries with lower production costs, putting pressure on pricing for companies like Ascent.
High fixed costs in capital-intensive sectors like steel production, with new mills costing billions in 2024, compel companies to maintain high utilization rates. This can trigger price wars when demand falters, as firms try to cover overhead. Many steel producers in 2024 were operating below 70% capacity, illustrating this pressure.
Ascent's ability to differentiate its products beyond price is crucial. While the market for many steel products can be commoditized, demand for specialized steel grew in 2024, offering opportunities for companies like Ascent to command premium pricing through unique alloys or custom fabrication.
The intensity of rivalry is further shaped by the presence of numerous competitors, many of whom are actively seeking to gain market share. This dynamic means that Ascent must constantly monitor pricing strategies and product offerings of its rivals to remain competitive.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitute materials for steel in infrastructure, energy, and agriculture is significant. Advanced plastics, composites, and aluminum are increasingly viable alternatives, offering benefits like lighter weight and corrosion resistance. For instance, the global composites market, which includes materials like carbon fiber, is projected to reach over $150 billion by 2027, showcasing strong growth and adoption.
China's expanding role as a major producer of carbon fiber, a key composite material, further amplifies this threat. This indicates a global shift towards material diversification. As these substitutes become more readily available, cost-effective, and technologically advanced, they directly challenge the market share of traditional steel products offered by companies like Ascent Industries.
When considering the threat of substitutes for Ascent Industries' steel products, it's crucial to examine how alternative materials stack up in terms of both cost and performance. For instance, advanced polymers and composites are increasingly offering comparable strength-to-weight ratios to steel, often at a lower overall cost when factoring in installation and maintenance. In 2024, the global market for advanced composites saw significant growth, with demand driven by industries seeking lighter, more fuel-efficient solutions.
If these substitutes provide a superior value proposition, perhaps through enhanced durability in corrosive environments or easier fabrication, customers will naturally gravitate towards them. This shift directly impacts the demand for traditional steel. For example, in the automotive sector, the increasing adoption of aluminum and high-strength plastics for body panels and structural components highlights this trend, with some manufacturers reporting up to a 15% reduction in vehicle weight using these alternatives.
Customers in infrastructure, energy, and agriculture are increasingly open to substitutes, driven by regulatory shifts and sustainability mandates. For instance, the growing emphasis on lighter materials in construction, partly due to energy efficiency goals, encourages the adoption of advanced composites over traditional steel or concrete. In 2024, the global market for advanced composites in construction was projected to reach over $18 billion, indicating a strong customer propensity to explore alternatives.
Innovation in Substitute Technologies
Ascent Industries must closely watch how quickly new technologies emerge that could replace its current offerings. For instance, breakthroughs in biodegradable plastics could significantly impact Ascent's traditional polymer products.
The pace of innovation is accelerating. By mid-2024, reports indicated a 15% year-over-year increase in patent filings for sustainable material alternatives, directly challenging established industrial goods.
This rapid advancement means substitutes can become more competitive, offering better performance or lower costs, thereby intensifying the threat. For example, advancements in 3D printing for metal components are making them a more viable substitute for traditionally manufactured parts in sectors like aerospace and automotive.
Key areas to monitor include:
- Emerging Material Science: Developments in composites, nanomaterials, and bio-based alternatives.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Innovations in additive manufacturing (3D printing) and precision robotics.
- Digitalization and AI: How these technologies enable new production methods or improve substitute performance.
- Regulatory Shifts: New environmental or safety standards that might favor alternative solutions.
Switching Costs for Customers to Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Ascent Industries' steel products is moderate, primarily due to the switching costs customers face. Transitioning from traditional steel to alternatives like advanced composites or high-strength plastics often involves significant retooling, redesign, and requalification processes. For instance, in the automotive sector, a shift from steel to aluminum or composites can necessitate billions in new manufacturing equipment and extensive crash-testing to meet safety standards.
These complexities create a barrier to entry for substitutes. While some applications might see easier adoption of alternatives, especially where weight reduction or corrosion resistance are paramount and existing infrastructure is adaptable, many core industries rely on steel's established supply chains and proven performance characteristics. The upfront investment and the potential for disruption in production lines generally keep switching costs relatively high for many of Ascent Industries' customers.
Factors that could lower these switching costs include:
- Standardization of alternative materials: Increased industry-wide adoption of standardized composite or plastic grades that are easily integrated into existing designs.
- Technological advancements in manufacturing: Innovations that simplify the processing and integration of substitute materials, reducing the need for extensive new equipment.
- Development of compatible supply chains: The emergence of robust and readily accessible supply chains for alternative materials, mirroring the widespread availability of steel.
The threat of substitutes for steel remains a significant consideration for Ascent Industries. While switching costs can be high, particularly in established infrastructure projects, advancements in materials science and manufacturing are continuously improving the value proposition of alternatives. By mid-2024, the global market for advanced composites alone was estimated to be worth over $120 billion, demonstrating a strong and growing customer base for these substitute materials.
These substitutes, including advanced plastics and aluminum, offer compelling advantages such as lighter weight and enhanced corrosion resistance, which are increasingly valued across sectors like automotive and construction. For instance, the automotive industry's drive for fuel efficiency has led to a greater adoption of aluminum, with its market share in vehicle production steadily increasing, impacting traditional steel demand.
The availability and cost-effectiveness of these alternatives are also improving. For example, China's significant production capacity for carbon fiber, a key composite material, contributes to broader accessibility. As these trends continue, the competitive landscape for Ascent Industries' steel products will likely evolve, necessitating ongoing adaptation and innovation.
| Substitute Material | Key Advantages | 2024 Market Growth Indicator | Impact on Steel Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Composites | Lightweight, High Strength-to-Weight Ratio, Corrosion Resistance | Global market projected to exceed $150 billion by 2027 | Moderate to High, especially in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, Corrosion Resistance, Recyclability | Increasing adoption in automotive body panels and structural components | Moderate, particularly in transportation and construction |
| High-Strength Plastics/Polymers | Corrosion Resistance, Design Flexibility, Lower Density | Growing use in consumer goods, packaging, and certain industrial applications | Low to Moderate, depending on specific application requirements |
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to enter the steel distribution, pipe and tube manufacturing, or industrial fabrication sectors is substantial. Establishing a modern steel mill, for instance, can easily cost billions of dollars, encompassing land acquisition, construction, heavy machinery, and advanced automation systems. In 2024, new steel plant construction projects globally are frequently cited as requiring investments upwards of $2 billion to $5 billion, creating a significant financial hurdle.
Ascent Industries likely benefits from substantial economies of scale in its production and distribution networks. For instance, in the steel distribution sector, larger players can negotiate better terms with suppliers due to higher volume purchasing, a significant cost advantage.
Newcomers would find it challenging to replicate these purchasing power benefits, especially in commodity markets where price is a key differentiator. This cost disparity makes it difficult for new entrants to compete effectively on price against established firms like Ascent, particularly in segments such as basic pipe manufacturing.
New companies face a significant hurdle in accessing established distribution channels and customer relationships within the infrastructure, energy, and agriculture sectors. Ascent Industries, with its extensive operational history, has cultivated deep-rooted connections that are difficult for newcomers to replicate.
Building comparable market access would demand substantial time and considerable investment from any new entrant. For instance, securing contracts with major utility companies or agricultural cooperatives, key distribution points, often requires years of proven reliability and extensive networking, a significant barrier to entry.
Proprietary Technology/Expertise
Ascent Industries' proprietary technology and accumulated expertise in steel fabrication and tubular products present a significant barrier to new entrants. The company has invested heavily in developing unique manufacturing processes and specialized certifications that are not easily replicated. This deep well of knowledge allows Ascent to offer specialized solutions and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
For instance, Ascent's advanced welding techniques and proprietary coating applications for its tubular products enhance durability and performance, setting a high standard that newcomers would struggle to match. This specialized know-how, built over years of operation, translates into a tangible advantage, making it difficult for new companies to enter and compete effectively on product quality and innovation.
- Proprietary Manufacturing Processes: Ascent utilizes unique steel fabrication techniques that improve efficiency and product quality, making replication costly for new firms.
- Specialized Certifications: The company holds key industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 and API certifications, which are time-consuming and expensive for new entrants to obtain.
- Accumulated Expertise: Decades of experience in tubular product development have resulted in specialized knowledge in material science and application engineering, creating a knowledge moat.
- Innovation in Coatings: Ascent's development of advanced, corrosion-resistant coatings for its steel products offers superior longevity, a feature that requires significant R&D investment to replicate.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation significantly impact the threat of new entrants in the industrial manufacturing and steel sectors. Stringent environmental regulations, such as emissions standards and waste disposal requirements, can impose substantial compliance costs on new players. For instance, in 2024, the European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) began imposing costs on carbon-intensive imports, potentially raising the barrier for steel producers in countries with less stringent climate policies.
Safety standards are another critical factor. Adhering to rigorous occupational health and safety regulations requires significant investment in training, equipment, and operational procedures. Failure to meet these standards can result in fines and operational disruptions, making it challenging for new entrants to compete with established firms that have already integrated these requirements into their operations. In 2024, many countries continued to update their safety protocols for heavy machinery and chemical handling in manufacturing.
Trade policies, including tariffs and import quotas, directly influence the cost competitiveness of new entrants. For example, tariffs imposed on raw materials or finished steel products can increase the cost of entry and make it harder for new companies to price their goods competitively against domestic or existing international suppliers. In early 2024, ongoing trade disputes and the implementation of new tariffs in various global markets continued to shape the accessibility of international markets for nascent industrial manufacturers.
- Environmental Regulations: Increased compliance costs for emissions and waste management, as seen with the EU's CBAM in 2024.
- Safety Standards: High initial investment in training and equipment to meet stringent occupational health and safety requirements.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs and quotas can escalate raw material costs and hinder market access for new entrants.
- Capital Intensity: The need for substantial upfront capital to meet regulatory and operational standards deters many potential new competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Ascent Industries is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. Building new steel facilities in 2024 can cost upwards of $2 billion to $5 billion, a significant barrier. Furthermore, Ascent's established distribution networks and deep customer relationships, cultivated over years, are difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate, especially in sectors like infrastructure and energy.
Ascent's proprietary manufacturing processes and specialized certifications, such as ISO 9001 and API certifications, also deter new entrants. These require substantial investment and time to obtain, creating a knowledge and quality moat that is challenging to overcome. For example, their advanced welding techniques and proprietary coatings offer superior product performance, demanding significant R&D to match.
Government regulations, including environmental standards and safety protocols, add further complexity and cost for potential new players. In 2024, the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) increased compliance costs for carbon-intensive imports, while updated safety standards necessitate significant upfront investment in training and equipment. Trade policies, such as tariffs, can also inflate raw material costs, impacting new entrants' price competitiveness.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Estimated Cost/Time (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing new steel production facilities | $2 billion - $5 billion+ |
| Distribution Channels & Relationships | Building market access and customer trust | Years of operation and networking |
| Proprietary Technology & Expertise | Replicating unique manufacturing processes and certifications | Significant R&D and certification costs |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting environmental and safety standards | Substantial investment in training, equipment, and compliance |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ascent Industries is built upon a foundation of robust data, including their annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms like IBISWorld. We supplement this with insights from competitor financial statements and trade publications to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.