API Maintenance Systems AS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
API Maintenance Systems AS Bundle
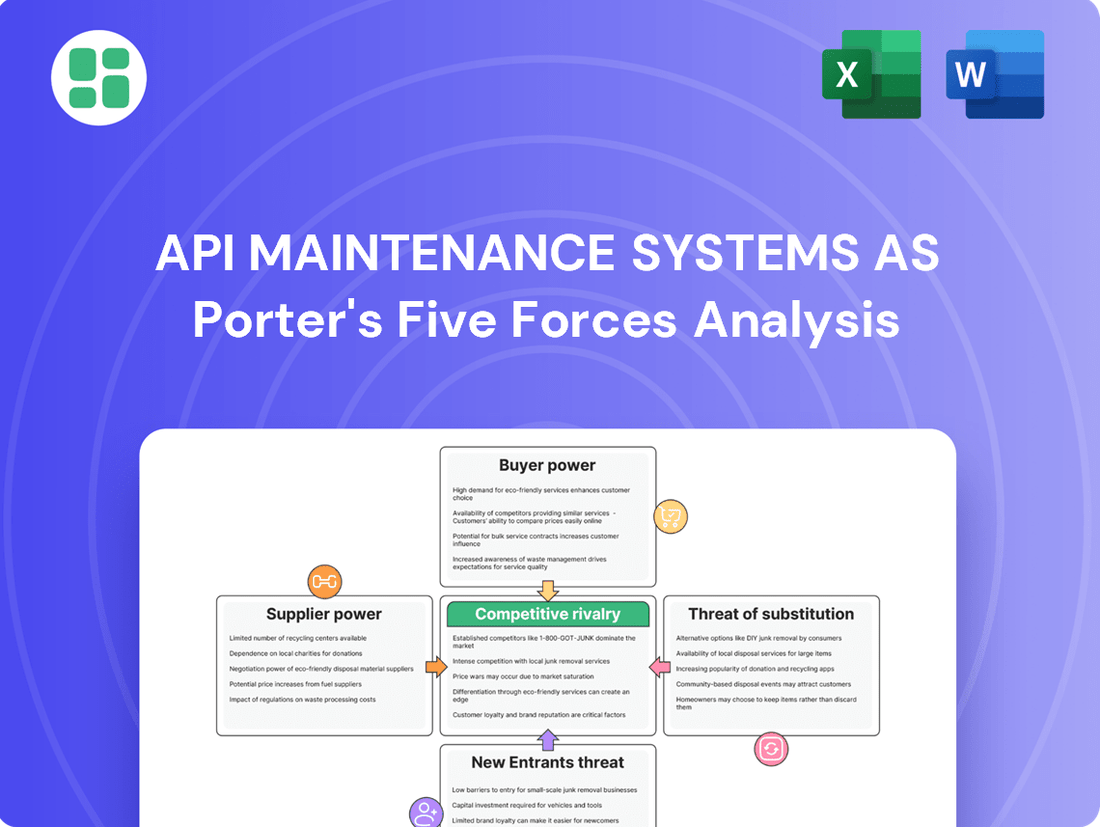
API Maintenance Systems AS operates in a dynamic market influenced by several key forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of substitutes and new entrants is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview only scratches the surface.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore API Maintenance Systems AS’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for critical components like cloud infrastructure or specialized AI modules significantly influences their leverage over API Maintenance Systems AS. When only a few providers offer essential, differentiated technologies, their bargaining power rises, potentially driving up costs or dictating less favorable contract terms. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market, dominated by a few major players, saw price adjustments that could impact service providers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for API Maintenance Systems AS is significantly influenced by switching costs. If it’s difficult and expensive for API Maintenance Systems AS to change its current suppliers, perhaps due to complex integration or specialized software, then those suppliers have more power to dictate terms. For instance, if a switch requires substantial investment in new hardware or extensive employee retraining, suppliers can leverage this to their advantage.
Conversely, if API Maintenance Systems AS can easily transition to alternative suppliers with minimal disruption or cost, the suppliers' bargaining power diminishes. In 2024, many cloud-based API management solutions offer flexible integration options, potentially lowering these switching costs for companies like API Maintenance Systems AS. This flexibility allows API Maintenance Systems AS to negotiate better pricing and service level agreements, as the threat of moving to a competitor remains a viable option.
Suppliers can become formidable competitors if they choose to integrate forward into the CMMS/EAM software market. For instance, a critical technology provider, such as a leading database vendor or an advanced AI analytics platform supplier, could decide to launch its own comprehensive CMMS/EAM system. This move would directly challenge API Maintenance Systems AS, potentially diminishing the latter's reliance on its existing software, API PRO.
Importance of Supplier's Input to API PRO
The criticality of a supplier's input to the functionality and performance of API PRO directly influences their bargaining power. If API Maintenance Systems AS relies heavily on specialized components or software modules from a particular vendor, that vendor gains considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the industrial automation sector saw continued consolidation, with key component suppliers reporting strong demand, potentially increasing their pricing power for critical inputs used in systems like API PRO.
Consider a scenario where API PRO's advanced predictive maintenance algorithms are deeply integrated with a proprietary data analytics engine from a single provider. This dependency significantly strengthens the supplier's position, as switching to an alternative could involve substantial redevelopment costs and potential performance degradation for API Maintenance Systems AS.
- Criticality of Input: The more essential a supplier's product or service is to API PRO's core functionality, the higher the supplier's bargaining power.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with changing suppliers, such as integration challenges or R&D investment, amplify supplier leverage.
- Supplier Concentration: If only a few suppliers can provide the necessary input, their power increases. For example, specialized sensor manufacturers for industrial IoT applications often operate in concentrated markets.
- Supplier Differentiation: Unique or proprietary technology offered by a supplier can create a strong dependency, boosting their bargaining position.
Cost of Supplier's Product/Service Relative to Total Cost
The proportion of a supplier's cost within API Maintenance Systems AS's overall cost structure for its API PRO solution is a critical factor in determining supplier bargaining power. If a particular supplier's component or service constitutes a significant portion of API PRO's total expenses, that supplier naturally wields greater influence. This is because their pricing decisions can directly and substantially impact API Maintenance Systems AS's profitability and competitive pricing strategies.
For instance, if a key software module or a specialized integration service represents, say, 30% of the total development or operational cost for API PRO, the provider of that module or service has considerable leverage. This leverage allows them to negotiate more favorable terms or potentially increase prices, knowing that API Maintenance Systems AS may find it difficult or costly to switch to an alternative. In 2024, the increasing complexity of enterprise software solutions often means that specialized third-party components can indeed represent a substantial cost element.
- High Component Cost: If a supplier's offering makes up a large percentage of API PRO's total cost, their bargaining power increases.
- Profitability Impact: Suppliers with a significant cost share can directly influence API Maintenance Systems AS's profit margins.
- Switching Costs: High reliance on a specific supplier's component can lead to high switching costs, further empowering the supplier.
- Market Trends: In 2024, the trend towards specialized, integrated software solutions can elevate the cost proportion of key third-party inputs.
The bargaining power of suppliers for API Maintenance Systems AS is amplified when they provide inputs that are critical to the functionality and performance of API PRO. If API Maintenance Systems AS heavily depends on a supplier's specialized technology, that supplier gains significant leverage. For example, in 2024, the industrial automation sector saw continued consolidation, with key component suppliers reporting strong demand, potentially increasing their pricing power for critical inputs used in systems like API PRO.
Suppliers who can easily integrate forward into the CMMS/EAM software market pose a direct threat. A provider of a key technology, like a database or AI analytics engine, could launch its own competing system, reducing API Maintenance Systems AS's reliance on its existing software, API PRO.
The proportion of a supplier's cost within API Maintenance Systems AS's overall cost structure for API PRO is also a key factor. When a supplier's component or service represents a substantial portion of total expenses, their pricing decisions can significantly impact API Maintenance Systems AS's profitability and competitive pricing. In 2024, the increasing complexity of enterprise software often means specialized third-party components can represent a significant cost element.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example Scenario (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Criticality of Input | High | Supplier of proprietary AI module for predictive maintenance in API PRO. |
| Switching Costs | High | API PRO integrated with a single-source data analytics engine requiring extensive redevelopment to switch. |
| Supplier Concentration | High | Few specialized sensor manufacturers for industrial IoT applications in the market. |
| Supplier Differentiation | High | Unique, patented algorithm crucial for API PRO's core function. |
| Cost Proportion | High | A core software module representing 30% of API PRO's total development cost. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of API Maintenance Systems AS's competitive environment examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the API maintenance sector.
Visualize competitive intensity across all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments to mitigate threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers for API Maintenance Systems AS is significantly influenced by customer concentration and the volume of purchases. If a few major clients account for a substantial portion of API PRO license sales or service revenue, they gain considerable leverage.
These large-volume customers can effectively negotiate for reduced pricing, specialized functionalities, or more advantageous contract conditions. For instance, if a single client represents over 10% of API Maintenance Systems AS's annual recurring revenue, their ability to influence terms increases dramatically.
Customer switching costs for API Maintenance Systems AS's CMMS/EAM solutions significantly influence customer bargaining power. These costs encompass financial outlays for new software, operational disruptions during transition, and technical challenges related to data migration and integration.
For instance, if a customer needs to migrate years of maintenance history, reconfigure workflows, and retrain staff on a new system, the perceived effort and expense can deter them from switching. This inertia effectively lowers their bargaining power, as the cost of changing providers outweighs the perceived benefits of a competitor's offering.
In 2024, the average cost for a small to medium-sized business to implement a new CMMS can range from $5,000 to $50,000, with larger enterprises facing much higher figures due to complexity and scale. This substantial investment in switching makes customers more likely to remain with their current provider, even if minor issues arise.
Customer price sensitivity for API PRO is a significant factor. In sectors with constrained maintenance budgets, or where Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS)/Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) software is viewed as interchangeable, clients will likely scrutinize pricing more closely, increasing pressure on API Maintenance Systems AS. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 45% of small to medium-sized businesses consider software cost a primary driver in their purchasing decisions for operational tools.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers' capacity to build their own maintenance management systems or improve existing generic software presents a significant threat to API Maintenance Systems AS. This potential for backward integration directly amplifies customer bargaining power.
If clients have the necessary technical expertise and financial resources to develop their own Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) or Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) solutions, they gain a powerful alternative to relying on external providers. This can lead to demands for lower prices or more tailored services from API Maintenance Systems AS.
- Customer In-house Development: The increasing availability of low-code/no-code platforms and cloud-based infrastructure makes it more feasible for larger organizations to develop custom maintenance solutions.
- Technical Skill Availability: A 2024 survey indicated that over 40% of large enterprises reported having dedicated IT teams capable of developing and maintaining custom software applications, including asset management tools.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: For some customers, the long-term cost of developing and maintaining an in-house system might be perceived as lower than ongoing subscription fees and customization costs from a vendor like API Maintenance Systems AS, especially if their needs are highly specialized.
Customer's Information and Market Knowledge
Customers who are well-informed about the CMMS/EAM market, including competitor pricing and features, hold significant sway. This knowledge empowers them to negotiate more effectively with API Maintenance Systems AS. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 70% of enterprise CMMS buyers conduct extensive online research, comparing at least three vendors before making a decision. This transparency in market data allows buyers to demand better value, potentially driving down prices or pushing for enhanced service packages.
The accessibility of detailed competitive intelligence directly impacts the bargaining power of API Maintenance Systems AS's customers. Armed with insights into industry benchmarks and alternative solutions, clients can leverage this information to secure more favorable terms. Consider that in 2024, the average CMMS implementation cost for mid-sized businesses ranged from $50,000 to $150,000, and informed customers can use this data to challenge API Maintenance Systems AS's pricing structures.
- Informed Buyers: Customers with deep knowledge of CMMS/EAM solutions can effectively leverage this information during negotiations.
- Market Transparency: Widespread access to pricing and feature comparisons empowers customers to demand better value.
- Negotiating Leverage: Understanding industry benchmarks, like the 2024 average implementation costs for mid-sized businesses ($50k-$150k), allows for more effective price discussions.
- Demand for Value: Well-informed customers are more likely to push for enhanced service levels or customized features to maximize their return on investment.
The bargaining power of customers for API Maintenance Systems AS is amplified by their ability to develop in-house solutions. With the rise of low-code/no-code platforms, organizations can create custom maintenance management systems, reducing reliance on external vendors. In 2024, over 40% of large enterprises reported having IT teams capable of such development, making them less susceptible to vendor lock-in and more inclined to negotiate favorable terms.
Customers' price sensitivity, especially in sectors with tight maintenance budgets, directly impacts their negotiation leverage. A 2024 survey revealed that 45% of SMBs prioritize software cost in purchasing decisions. This focus on affordability means that API Maintenance Systems AS faces pressure to offer competitive pricing to retain these clients, as switching costs, while present, can be overcome by perceived long-term savings.
Well-informed customers, armed with market data and competitor analysis, possess significant bargaining power. In 2024, 70% of enterprise CMMS buyers researched multiple vendors. This transparency allows them to challenge API Maintenance Systems AS's pricing and service offerings, demanding better value and potentially influencing contract terms based on industry benchmarks, such as the average $50,000 to $150,000 implementation cost for mid-sized businesses.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| In-house Development Capability | Increases power by providing alternatives | 40%+ of large enterprises have capable IT teams |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases power, especially in cost-conscious sectors | 45% of SMBs cite software cost as a primary driver |
| Market Knowledge & Transparency | Increases power through informed negotiation | 70% of enterprise CMMS buyers research multiple vendors |
Preview Before You Purchase
API Maintenance Systems AS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete, professionally written Porter's Five Forces Analysis for API Maintenance Systems, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for businesses in this sector. The document displayed here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you’ll receive, ready for immediate download and use the moment you buy, ensuring you get precisely what you need without any placeholders or samples.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) and Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) software market is a lively space. While there are dominant, established companies, a steady stream of new, innovative businesses are entering the fray. This dynamic means there's a significant number of competitors, each bringing their own unique strengths and focusing on specific market segments.
This sheer volume of competitors, all striving to capture a piece of the market, naturally cranks up the rivalry. Companies are often pushed to compete on price, potentially leading to price wars, or they might focus on out-innovating each other to stand out. For instance, in 2023, the global CMMS market was valued at approximately USD 1.1 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth, fueling this competitive drive.
The CMMS/EAM market is booming, with projections indicating it will surpass $2 billion in 2024. This strong expansion, expected to continue at a 10.4% compound annual growth rate between 2025 and 2035, generally tempers intense rivalry. When the pie is growing, companies can focus on capturing new market segments rather than solely battling for existing share.
Despite the favorable growth environment, the competitive landscape remains active, evidenced by significant merger and acquisition (M&A) activity. This suggests that while the overall market is expanding, consolidation and strategic partnerships are key strategies employed by players to gain or maintain market position.
API Maintenance Systems AS's competitive rivalry is significantly shaped by product differentiation and the associated switching costs for its API PRO software. When API PRO offers unique functionalities, seamless integration capabilities, or superior customer support, it creates a stronger market position.
For instance, if API PRO boasts advanced predictive maintenance algorithms or a more intuitive user interface compared to competitors, customers are less likely to seek alternatives. High switching costs, such as the expense of data migration, retraining staff, or reconfiguring existing systems, further solidify API Maintenance Systems AS's standing by making it more challenging for rivals to poach customers.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the CMMS/EAM market, including substantial investments in specialized hardware and software, alongside deeply integrated workflows, can make it incredibly difficult for companies to leave. For instance, a significant portion of a company's operational data and processes are often tied to their chosen CMMS/EAM system, creating a high switching cost that acts as a strong disincentive to exit.
These barriers mean that even companies experiencing financial distress may continue to operate and compete, rather than incur the costs and disruption associated with leaving the market. This can intensify competitive rivalry, as these trapped competitors may engage in aggressive pricing or service strategies to try and recoup their sunk costs, even if it means operating at low or no profitability.
The CMMS/EAM market has seen substantial investment in recent years. For example, the global Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) market size was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. This ongoing investment by multiple players, coupled with the inherent difficulty in exiting, suggests that competitive pressures stemming from high exit barriers are likely to persist.
- Specialized Assets: Significant capital expenditure on hardware and software tailored for maintenance management.
- Long-Term Contracts: Many CMMS/EAM solutions involve multi-year service agreements and licensing.
- Integration Complexity: Deep integration with other business systems (ERP, IoT platforms) creates operational dependencies.
- Sunk Costs: Extensive investment in customization, training, and data migration makes switching costly.
Strategic Stakes and Market Importance
The strategic importance of the CMMS/EAM market significantly fuels competitive rivalry among key players. When companies like API Maintenance Systems AS, or their direct competitors, consider this sector vital for their long-term growth or as a cornerstone of their broader enterprise software offerings, the intensity of competition escalates. This strategic focus often translates into substantial investments in research and development, alongside aggressive marketing campaigns, to capture and maintain market share.
For instance, the global Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) market was projected to reach approximately $1.2 billion in 2024, with projections indicating continued growth. This substantial market size and its perceived strategic value mean that established players and emerging companies alike are motivated to invest heavily. This includes not only product innovation but also strategic acquisitions and partnerships to bolster their competitive position.
- Intensified R&D: Competitors are likely to increase spending on developing advanced features, such as AI-driven predictive maintenance and IoT integration, to differentiate their offerings.
- Aggressive Marketing: Companies will likely ramp up marketing efforts to highlight their unique value propositions and expand their customer base in this strategically important sector.
- Market Share Focus: The perception of CMMS/EAM as a critical market segment drives a strong desire among players to gain or defend market share, leading to more aggressive competitive tactics.
The competitive rivalry within the API Maintenance Systems AS market is robust, driven by a substantial number of vendors offering CMMS and EAM solutions. This crowded field necessitates differentiation through features like predictive maintenance and user experience to retain clients, as switching costs, including data migration and retraining, are considerable.
The market's projected growth, with the global CMMS market expected to exceed $2 billion in 2024, fuels this competition. Companies are investing heavily in R&D and marketing to capture market share, leading to strategies like mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their positions.
High exit barriers, such as specialized asset investments and complex integrations, keep even financially strained competitors in the market, potentially intensifying price and service competition.
The strategic importance of CMMS/EAM drives players to invest in innovation and aggressive marketing, aiming to secure dominance in this vital sector.
| Key Competitive Factors | Impact on Rivalry | Example Data (2024 Projections) |
| Number of Competitors | High rivalry due to many vendors | CMMS market projected to exceed $2 billion |
| Product Differentiation | Reduces rivalry if successful | Focus on AI-driven predictive maintenance |
| Switching Costs | Increases customer retention, lowers rivalry | Costs include data migration, training |
| Exit Barriers | Keeps competitors in market, increases rivalry | Specialized hardware/software, integration complexity |
| Market Growth Rate | Can temper rivalry as market expands | Expected CAGR of 10.4% (2025-2035) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The availability of alternative solutions for managing API maintenance presents a significant threat. These substitutes, ranging from manual tracking and spreadsheets to basic ERP modules with limited maintenance features, can fulfill similar needs, albeit with less sophistication. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 35% of small businesses still rely on spreadsheets for asset tracking, highlighting a substantial segment potentially open to simpler, lower-cost alternatives to dedicated API maintenance systems.
The price-performance trade-off is crucial here. If these less advanced substitutes offer a comparable level of essential functionality at a considerably lower cost, the threat to specialized API maintenance systems intensifies. Businesses will weigh the benefits of advanced features against the direct cost savings, making the perceived value of a full-fledged system a key differentiator.
Customer propensity to substitute API maintenance systems hinges on perceived value and integration ease. If a less specialized, simpler alternative meets core needs without major disruption, customers may switch. For instance, in 2024, businesses increasingly sought integrated platforms that reduced the need for multiple specialized API tools, indicating a growing openness to consolidated solutions that offer better value and simpler management.
The threat of substitutes for API maintenance systems is amplified by the growing capability of organizations to develop and enhance their own internal solutions. As digital transformation accelerates, many large enterprises are investing heavily in custom-built platforms or significantly upgrading their existing generic software, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, to meet specific operational needs. This trend means that instead of relying on external API maintenance providers, companies might opt to internalize these functions, thereby reducing the demand for specialized third-party services.
Emergence of Hybrid Solutions or Niche Tools
The emergence of highly specialized niche tools or hybrid solutions poses a significant threat of substitutes for traditional API maintenance systems. These can range from IoT platforms with integrated basic maintenance functionalities to standalone diagnostic software that addresses specific failure points. For instance, a company might opt for a specialized predictive maintenance sensor network that feeds data into a general analytics platform, bypassing the need for a comprehensive CMMS/EAM system for certain operational aspects.
These substitutes often cater to very specific pain points, offering a more focused and potentially less expensive solution than a full-scale API maintenance system. The market for such specialized tools is growing, with venture capital funding increasingly directed towards innovative solutions in areas like AI-driven anomaly detection for industrial equipment. In 2023, investments in industrial IoT and predictive maintenance startups reached over $5 billion globally, indicating a strong trend towards these more targeted alternatives.
- Niche Software: Tools focusing on specific tasks like vibration analysis or thermal imaging can replace broad maintenance system functionalities.
- IoT Platforms: Integrated sensor data and basic analytics offered by IoT providers can cover routine monitoring needs.
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: Advanced algorithms for fault prediction can act as a substitute for manual inspection scheduling within a CMMS.
- Cloud-Based Analytics: General data analytics platforms can ingest maintenance logs and identify patterns without a dedicated maintenance system.
Technological Advancements in Non-CMMS/EAM Fields
Rapid advancements in adjacent technology sectors present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional CMMS/EAM systems. For instance, the rise of sophisticated AI-powered analytics platforms and advanced operational intelligence tools offers alternative pathways for organizations to manage assets and maintenance processes. These emerging solutions can provide predictive maintenance insights, optimize resource allocation, and streamline workflows, potentially reducing the perceived need for a dedicated CMMS/EAM platform.
The increasing integration of AI and machine learning into general business software, including project management and ERP systems, further blurs the lines. Companies might leverage these broader platforms to handle asset tracking and maintenance scheduling, bypassing specialized CMMS/EAM solutions altogether. This trend is particularly evident as these platforms mature, offering more robust functionalities that can compete with core CMMS/EAM capabilities.
Consider the growing market for IoT-enabled predictive maintenance solutions. These systems can monitor asset health in real-time and trigger maintenance alerts without requiring a full-scale CMMS/EAM. The global IoT market, valued at over $1.1 trillion in 2023, is a testament to the widespread adoption of connected technologies that could serve as substitutes for traditional maintenance management systems.
- AI-driven analytics platforms offer predictive capabilities, potentially reducing reliance on dedicated CMMS/EAM for maintenance scheduling.
- Advanced project management software increasingly incorporates asset management features, acting as a substitute for specialized systems.
- IoT-enabled predictive maintenance solutions provide real-time asset health monitoring, bypassing the need for traditional CMMS/EAM integration for this function.
- The expansion of the global IoT market signifies a growing availability of alternative technologies for asset management and maintenance.
The threat of substitutes for API maintenance systems is significant, driven by readily available, lower-cost alternatives. Many businesses, particularly smaller ones, still rely on simpler methods like spreadsheets for asset tracking, as evidenced by a 2024 survey showing 35% of small businesses using them.
The perceived value and ease of integration of these substitutes heavily influence customer choices. If simpler solutions meet core needs without major disruption, customers may opt out of specialized systems. For instance, the 2024 trend towards integrated platforms highlights a willingness to consolidate tools for better value and simpler management.
The increasing capability of organizations to develop in-house solutions or enhance existing generic software like ERP systems also poses a threat. This internalizing of functions reduces the demand for third-party API maintenance services.
Emerging niche tools and hybrid solutions, such as IoT platforms with basic maintenance features or specialized diagnostic software, offer targeted and potentially less expensive alternatives. The substantial global investment in industrial IoT and predictive maintenance startups, exceeding $5 billion in 2023, underscores the growing market for these focused substitutes.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | Threat Level | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spreadsheets & Manual Tracking | Basic data logging, simple task lists | High for basic needs | Small businesses managing simple asset inventories |
| Integrated ERP Modules | Limited maintenance scheduling, asset databases | Medium | Companies with existing ERP seeking consolidated solutions |
| Niche Diagnostic Tools | Specific fault detection (e.g., vibration analysis) | High for specific issues | Focusing on predictive maintenance for critical machinery |
| IoT Platforms | Real-time monitoring, basic analytics | Medium to High | Utilizing sensor data for operational oversight |
Entrants Threaten
The capital requirements for entering the CMMS/EAM software market are substantial, acting as a significant barrier to new entrants. Developing a robust solution like API PRO demands considerable investment in research and development to ensure advanced features and competitive functionality.
Significant capital is also needed for building and maintaining the necessary infrastructure, particularly for cloud-based offerings which are increasingly prevalent. Marketing and sales efforts to establish brand recognition and acquire customers in this competitive landscape further escalate the initial financial outlay.
For instance, in 2024, the global CMMS market was valued at approximately $2.1 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. This market size reflects the established players and the investment required to gain even a small market share.
Established players like API Maintenance Systems AS leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. This means they can spread costs like software development, customer support, and marketing across a larger customer base, leading to lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, major API management providers reported operating expenses that were a fraction of their revenue, a feat difficult for newcomers to replicate.
The experience curve further solidifies the advantage of incumbents. API Maintenance Systems AS, having operated for years, possesses accumulated knowledge regarding efficient development practices, customer needs, and market trends. This deep understanding translates into optimized processes and better product-market fit, creating a substantial barrier for new entrants attempting to match their operational efficiency and service quality.
For API Maintenance Systems AS, the threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the high barriers to entry related to product differentiation and brand loyalty. Established players, such as the well-regarded API PRO, have cultivated strong brand recognition and a loyal customer base over time. This makes it difficult for newcomers to gain traction without a similarly proven product and established customer relationships.
Access to Distribution Channels and Partnerships
New players in the CMMS/EAM space often face significant hurdles in securing essential distribution channels and forging strategic partnerships. These relationships, vital for reaching key markets, can be difficult to establish for those without an existing footprint.
Securing effective distribution channels and forming strategic partnerships, such as with hardware manufacturers, ERP providers, or system integrators, is crucial in the CMMS/EAM market. New entrants may struggle to establish these relationships, which are often key to reaching target customers. For instance, in 2024, the CMMS market was valued at approximately $1.2 billion, with growth driven by the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions and the need for efficient asset management across industries. Gaining access to established reseller networks or integration partners can be a significant barrier.
- Distribution Channel Access: New entrants may find it challenging to gain shelf space or partnerships with established IT resellers and VARs (Value-Added Resellers) who already carry incumbent CMMS/EAM solutions.
- Partnership Development: Building trust and securing integration partnerships with major ERP vendors like SAP or Oracle, or with large system integrators, requires time, proven success, and often significant investment.
- Customer Reach: Without these established channels and partnerships, new entrants are often limited to direct sales efforts, which can be slow and costly, hindering their ability to scale and compete effectively against established players.
Regulatory and Legal Barriers
Compliance with stringent data security and privacy regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants in the API maintenance systems sector. These regulations mandate robust data protection measures, increasing development costs and the time required to bring a new system to market. For instance, the average cost of a data breach in 2024 was estimated at $4.73 million globally, highlighting the financial implications of non-compliance.
Furthermore, industry-specific standards and certifications add another layer of complexity. API maintenance systems often need to adhere to standards set by bodies like ISO or specific financial or healthcare industry regulators. Achieving these certifications requires substantial investment in infrastructure, processes, and ongoing audits, making it challenging for smaller, less-resourced newcomers to compete effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants must allocate significant capital to ensure adherence to data privacy laws like GDPR, impacting initial investment.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Meeting sector-specific certifications (e.g., ISO 27001 for security) requires advanced technical capabilities and financial resources.
- Time-to-Market Delays: Navigating complex regulatory landscapes and certification processes can extend the development cycle, delaying market entry.
The threat of new entrants for API Maintenance Systems AS is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements for market entry, including R&D, infrastructure, and marketing. For example, the global CMMS market, valued at approximately $2.1 billion in 2024, indicates the significant investment needed to gain market share.
Established players benefit from economies of scale and an experience curve, making it difficult for newcomers to match operational efficiency and product-market fit. Major API management providers in 2024 demonstrated operating expenses that were a fraction of their revenue, a cost advantage hard for new entrants to overcome.
Product differentiation and brand loyalty further deter new entrants, as established companies like API PRO have cultivated strong customer bases. Securing distribution channels and strategic partnerships, crucial for market reach, also poses a significant hurdle for those without an existing footprint.
Compliance with stringent regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, alongside industry-specific standards, adds substantial costs and time-to-market delays. The average cost of a data breach in 2024 was around $4.73 million globally, underscoring the financial risk of non-compliance for new players.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High R&D, infrastructure, and marketing costs. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established players. | Price competition challenges for newcomers. |
| Brand Loyalty & Differentiation | Established reputation and customer relationships. | Difficulty in acquiring customers. |
| Distribution Channels & Partnerships | Access to resellers, ERP vendors, and integrators. | Limited market reach for new entrants. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to data privacy and industry standards. | Increased costs and delayed market entry. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for API Maintenance Systems is built upon a foundation of industry research reports, competitor financial statements, and market intelligence platforms. We also incorporate data from technology trend analyses and user community feedback to capture the nuances of this evolving sector.