Anuvu Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Anuvu Bundle
Anuvu's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the aviation connectivity market.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive, data-driven examination of Anuvu's industry dynamics, revealing the true pressures and opportunities that influence its strategic direction.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Anuvu’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Anuvu's dependence on a select group of global satellite operators for its core connectivity infrastructure means these suppliers hold considerable bargaining power. The limited availability of satellite bandwidth, a critical resource, allows these providers to dictate pricing and service terms, directly impacting Anuvu's operational costs and profitability.
The scarcity of essential satellite assets grants these suppliers significant leverage. Anuvu's ability to secure favorable terms is intrinsically linked to the availability and cost of these satellite resources, especially as new low Earth orbit (LEO) constellations from companies like Starlink and OneWeb are actively reshaping the market landscape by 2024.
Anuvu faces significant bargaining power from proprietary hardware and software vendors, particularly those supplying specialized components for satellite communication and in-flight entertainment. This concentration of suppliers, often holding patents and unique technologies, creates a dependency for Anuvu. For instance, the development and integration of advanced systems, such as those supporting MicroGEO satellites, rely on these specialized inputs, making supplier switching costly and potentially disruptive.
Anuvu's reliance on major studios and media houses for in-flight entertainment content, such as movies and TV shows, grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. Exclusive content deals or the demand for popular franchises can drive up licensing fees, directly affecting Anuvu's operational costs and the breadth of its entertainment offerings. For instance, the increasing demand for premium content across all entertainment platforms, including aviation, means studios can command higher prices, impacting Anuvu's ability to secure a diverse and appealing content library in 2024.
High Switching Costs for Anuvu
Anuvu faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs, particularly when changing core providers for satellite capacity or integrated hardware. These transitions demand substantial financial outlay, intricate technical re-configuration, and carry the inherent risk of service interruptions. The complexity involved in integrating new solutions, especially as Anuvu navigates multi-orbit strategies, further entrenches the bargaining position of its current critical suppliers.
The costs associated with switching suppliers for satellite bandwidth or specialized aviation connectivity hardware can be prohibitive. For instance, a typical integration of a new satellite communication system for an airline fleet can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the complexity and number of aircraft. This financial barrier, coupled with the time and expertise required for technical recalibration and testing, significantly limits Anuvu's ability to negotiate favorable terms or readily move to alternative providers.
- High Financial Investment: Switching core satellite capacity providers can involve upfront costs exceeding $1 million per fleet, covering new hardware and installation.
- Technical Re-configuration: Adapting existing aircraft systems to new satellite frequencies or network protocols requires specialized engineering and can take months.
- Service Disruption Risk: A poorly managed transition can lead to temporary loss of connectivity, impacting Anuvu's service delivery and client satisfaction.
- Multi-Orbit Complexity: Integrating and managing solutions across various satellite constellations (e.g., GEO, MEO, LEO) adds layers of technical complexity, making supplier changes even more challenging.
Supplier Concentration and Specialization
Supplier concentration, particularly in niche areas like specialized aerospace components or unique satellite technology, can significantly bolster supplier bargaining power. When Anuvu relies on a limited number of providers for critical, hard-to-replicate inputs, these suppliers gain leverage. For instance, if only a few manufacturers produce the advanced avionics required for Anuvu's aircraft fleet, they can dictate terms more effectively.
This concentration is amplified by supplier specialization. If a supplier possesses unique expertise or proprietary technology essential for Anuvu's service delivery, their ability to command higher prices or favorable contract conditions increases. This is because Anuvu has fewer viable alternatives for obtaining these specialized capabilities. The dependence on such specialized suppliers reduces Anuvu's flexibility and strengthens the supplier's position in negotiations.
- High concentration in aerospace components: Reports from 2024 indicate that the market for certain advanced aerospace materials and avionics is dominated by a handful of global suppliers, often with lead times exceeding 18 months.
- Specialized satellite technology: The development and deployment of next-generation satellite constellations often depend on a very limited pool of specialized manufacturers for key components, with some suppliers holding patents on critical technologies.
- Increased negotiation leverage: In 2024, companies with fewer sourcing options for specialized inputs faced an average price increase of 7-10% compared to those with diversified supply chains.
Anuvu's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly constrained by the limited number of providers for critical satellite bandwidth and specialized aviation hardware. High switching costs, often exceeding $1 million per fleet for new hardware and installation in 2024, alongside technical re-configuration challenges and the risk of service disruption, reinforce supplier leverage. This dependency is further amplified by supplier specialization and concentration in niche markets, where a few manufacturers dominate advanced aerospace components and satellite technologies, leading to potential price increases for Anuvu.
| Factor | Impact on Anuvu | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited alternatives increase supplier leverage. | Dominance of a few suppliers in advanced aerospace materials and avionics. |
| Switching Costs | High financial and technical barriers to changing providers. | Upfront costs for new hardware and installation can exceed $1 million per fleet. |
| Supplier Specialization | Proprietary technology or unique expertise strengthens supplier position. | Patents on critical technologies for next-generation satellite constellations. |
| Scarcity of Resources | Limited availability of satellite bandwidth allows price dictation. | New LEO constellations are reshaping market dynamics, but core bandwidth remains a key constraint. |
What is included in the product
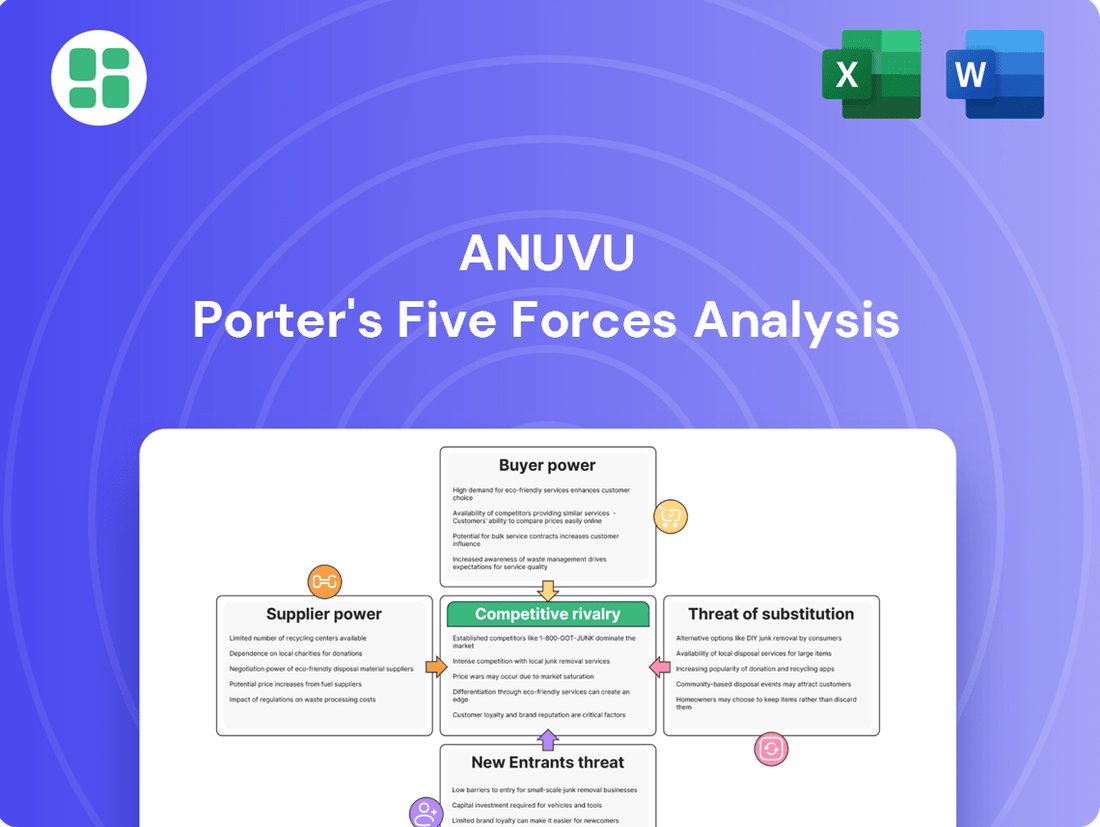
Anuvu's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its operating environment, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Anuvu's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary for quick strategic decision-making, alleviating the pain of complex market assessments.
Instantly understand strategic pressure with Anuvu's powerful spider/radar chart, simplifying the visualization of competitive forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Anuvu's primary customers, major airlines and large maritime operators, are highly consolidated entities. These significant buyers of connectivity and entertainment solutions possess substantial leverage, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing and service agreements. For instance, in 2024, the top 10 global airlines accounted for over 40% of global passenger traffic, underscoring their collective bargaining strength.
While replacing an entire in-flight entertainment or connectivity system is a significant undertaking, airlines may find it less costly to switch between different connectivity service providers over time if the core technology remains compatible. This means that if competitors like Viasat or Intelsat offer similar services at more attractive price points or with enhanced features, airlines could be more inclined to switch, thereby strengthening their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the competitive landscape for in-flight connectivity saw ongoing efforts by providers to differentiate through service quality and pricing, directly influencing airline procurement decisions.
Airlines and maritime operators are acutely aware of their own competitive landscapes, which makes them highly sensitive to the costs of essential services like connectivity and in-flight entertainment. This cost-consciousness directly translates into a stronger bargaining position with providers like Anuvu, as they actively seek more favorable pricing or enhanced service packages to maintain their own profitability. For instance, in 2024, the average operating cost per available seat mile for major airlines continued to be a critical metric, and any reduction in ancillary service costs can significantly boost their bottom line.
Customer's Ability to Demand Customization
Large airline and maritime clients frequently require highly customized solutions. These tailor-made offerings are designed to align with their specific operational demands, branding strategies, and desired passenger experiences. For instance, a major airline might need a unique content delivery system that integrates seamlessly with their existing in-flight entertainment platform and reflects their brand identity.
This demand for bespoke services significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. Anuvu must allocate substantial resources to develop and implement these unique requirements, often leading to negotiations on terms that favor the customer. The necessity for these specialized solutions grants customers considerable leverage in price and service level agreements.
- Customization Demand: Major airlines and shipping companies often require bespoke solutions for content delivery, connectivity, and passenger engagement systems.
- Resource Allocation: Meeting these unique client needs necessitates significant investment in research, development, and specialized implementation by Anuvu.
- Increased Leverage: The need for tailored services empowers customers to negotiate more favorable pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Anuvu's profitability.
- Competitive Differentiation: While costly, Anuvu's ability to offer customization can also be a key differentiator, attracting and retaining high-value clients in a competitive market.
Threat of Customer In-house Development
The threat of customer in-house development, while low for complex satellite infrastructure like Anuvu's, can still influence negotiations. Very large airline groups might explore managing parts of their in-flight entertainment (IFE) content or ground operations internally, especially as they prioritize enhanced passenger experiences.
This possibility, even if not fully realized due to significant complexity and cost, creates a latent pressure. Airlines can leverage this theoretical capability to push for more competitive pricing and higher service standards from Anuvu. For instance, in 2024, airlines continued to invest heavily in digital passenger services, with some exploring greater control over their content delivery platforms.
- Potential for partial in-house IFE content management by large airline groups.
- High complexity and cost limit full backward integration for satellite services.
- Theoretical threat influences Anuvu's pricing and service quality negotiations.
- Airline focus on passenger experience drives interest in greater control over digital services.
The bargaining power of Anuvu's customers, primarily major airlines and maritime operators, is substantial due to their consolidated nature and sensitivity to operational costs. In 2024, the significant market share held by the top airlines, exceeding 40% of global passenger traffic, highlights their collective leverage in negotiating terms with service providers.
Airlines can switch between connectivity providers if core technology is compatible, especially if competitors offer better pricing or features. This competitive dynamic in 2024, with providers differentiating on service and price, directly influences airline procurement decisions and strengthens their negotiating position. The ongoing focus on reducing operating costs per available seat mile in 2024 means airlines are highly motivated to secure favorable pricing for services like connectivity.
| Customer Segment | Key Bargaining Factors | 2024 Data Point / Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Major Airlines | Consolidation, Cost Sensitivity, Switching Potential | Top 10 airlines handled >40% global passenger traffic; focus on reducing operating costs per available seat mile. |
| Maritime Operators | Similar consolidation and cost pressures | N/A (specific data not publicly available for this segment in this context) |
| Anuvu's Response | Customization, Potential for In-house Solutions | Development of bespoke solutions is resource-intensive, granting customers negotiation leverage; airlines explore greater control over digital services. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Anuvu Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Anuvu Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the aviation connectivity and passenger experience sector. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be available for immediate download upon purchase, offering actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The in-flight connectivity and entertainment sector is crowded with established companies. Major players such as Viasat, Inmarsat, Gogo, and Marlink are constantly competing for airline and maritime contracts. This intense rivalry forces companies to offer competitive pricing, cutting-edge technology, superior service, and appealing content to win business.
Anuvu faces intense competition as rivals continuously introduce advanced technologies, offering higher speeds, broader content selections, and improved user interfaces. For instance, Viasat and Intelsat are heavily investing in their satellite networks, with Viasat's ViaSat-3 constellation aiming for global coverage and enhanced capacity, directly challenging Anuvu's market position.
The constant drive to differentiate services, whether through adopting next-generation satellite technology like high-throughput satellites (HTS) or securing exclusive content partnerships, intensifies this rivalry. Companies are locked in a battle for technical supremacy and unique value propositions within a dynamic and rapidly evolving market landscape.
The in-flight connectivity and entertainment sector demands massive initial outlays for satellite infrastructure, ground networks, and content rights. For instance, companies like Viasat have invested billions in their satellite constellations, with their Viasat-3 constellation alone representing a significant capital expenditure. These substantial upfront costs, coupled with long-term commitments and highly specialized assets, erect formidable exit barriers, making it difficult for firms to leave the market.
These high fixed costs and exit barriers often compel companies to pursue aggressive pricing to preserve market share, even when demand falters. This can lead to intense price competition, as seen in the ongoing efforts by providers to secure airline contracts. The pressure to recoup these investments can fuel a fierce rivalry, as firms fight to maintain revenue streams in a capital-intensive industry.
Industry Growth and Market Saturation
While the overall mobility connectivity market is expected to see robust expansion, some areas are nearing saturation. Major airlines, for instance, are increasingly equipped with In-Flight Entertainment and Connectivity (IFEC) solutions, intensifying competition in these established segments. This saturation can transform the market into a zero-sum game, where gains for one company mean losses for another.
In saturated markets, competitive rivalry escalates significantly. Companies engage in aggressive marketing campaigns and price wars to win or retain contracts. For example, by 2024, major players in the aviation connectivity sector are likely to be vying intensely for the remaining unserved aircraft and for upgrades on existing fleets. This dynamic forces providers to innovate rapidly and offer compelling value propositions to stand out.
- Market Saturation: Certain segments within mobility connectivity, particularly among well-established airlines, are approaching saturation.
- Zero-Sum Competition: In these mature segments, market share gains are often at the direct expense of competitors.
- Aggressive Tactics: Expect intensified marketing efforts, price reductions, and aggressive bidding for new contracts.
- Innovation Pressure: Companies must continuously innovate to differentiate their offerings and capture market share.
Global Reach and Regional Competition
Anuvu navigates a complex competitive arena, marked by its global operations encountering both multinational giants and formidable regional competitors. This dynamic means rivalry isn't just about scale, but also about localized expertise and established networks.
Competitors often possess deep-rooted relationships within specific geographic markets or specialize in particular transport sectors, creating intense competition within those specialized niches. For instance, in the aviation sector, while global players exist, regional airlines might offer more tailored services or pricing that directly challenge Anuvu's broader offerings in those areas.
The need to adapt to and compete within diverse regulatory frameworks and varying market conditions across different regions adds significant complexity. This requires Anuvu to maintain flexibility and understanding of local nuances to effectively manage its competitive position globally.
- Global Presence vs. Regional Dominance: Anuvu's worldwide operations are challenged by competitors with deep regional penetration and established customer bases.
- Niche Specialization: Rivalry intensifies in specific transport sectors where competitors focus on specialized services, offering tailored solutions that can outmaneuver broader market approaches.
- Regulatory and Market Diversity: Anuvu must contend with differing legal, economic, and cultural landscapes across its operational territories, each presenting unique competitive hurdles.
- 2024 Market Dynamics: Reports from early 2024 indicate continued consolidation pressures in the aviation connectivity market, with regional players actively seeking partnerships to expand their reach against larger incumbents.
The competitive rivalry within the in-flight connectivity and entertainment (IFEC) sector is fierce, driven by significant capital investments and the pursuit of technological superiority. Companies like Viasat and Intelsat are investing heavily in advanced satellite networks, such as Viasat's ViaSat-3 constellation, to enhance capacity and global coverage, directly challenging Anuvu's market position.
Market saturation in certain segments, particularly among major airlines, intensifies this rivalry, often leading to zero-sum competition where market share gains come at the direct expense of rivals. This dynamic forces providers into aggressive marketing, price reductions, and intense bidding for new contracts, as seen in the ongoing efforts to secure airline deals. By 2024, the aviation connectivity market is characterized by intense competition for unserved aircraft and fleet upgrades.
Companies must continuously innovate to differentiate their offerings, whether through next-generation satellite technology or exclusive content partnerships. This constant drive for technical supremacy and unique value propositions creates a highly dynamic and rapidly evolving market landscape. For instance, by mid-2024, the demand for higher bandwidth and enhanced passenger experience continues to fuel innovation, with providers showcasing advancements in Wi-Fi speeds and personalized entertainment.
| Competitor | Key Investments/Strategies | 2024 Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Viasat | ViaSat-3 constellation for global coverage and capacity | Expanding satellite network capabilities, securing new airline contracts |
| Intelsat | Next-generation satellite technology, mobility services | Enhancing high-throughput satellite (HTS) offerings, partnerships for broader reach |
| Gogo | Advanced connectivity solutions for aviation | Focus on in-cabin passenger experience, network upgrades for faster speeds |
| Marlink | Integrated connectivity solutions for maritime and aviation | Leveraging hybrid network solutions, expanding regional service offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For passengers, the most significant substitute for in-flight or on-vessel Wi-Fi is the availability of terrestrial networks. This means passengers can connect before their journey or once they reach their destination, diminishing the immediate need for onboard connectivity. This readily available alternative directly influences how much value passengers place on, and how much they are willing to pay for, in-flight Wi-Fi services.
Passengers are increasingly bringing their own entertainment. In 2024, it's common for travelers to load up smartphones, tablets, and laptops with movies, shows, and games before flying. This personal digital library directly competes with, and often replaces, the need for traditional in-flight entertainment systems, significantly impacting demand for such services.
Some travelers are increasingly choosing to disconnect during their journeys, prioritizing rest or offline activities over constant connectivity. This behavioral shift directly impacts the addressable market for services like Anuvu’s, as it presents a viable alternative to in-flight entertainment and Wi-Fi. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that nearly 30% of air travelers actively seek to disconnect during flights.
Offline Productivity Tools
For business travelers, the ability to work offline using downloaded documents, presentations, and applications on personal devices can act as a substitute for in-flight internet for many productivity tasks. While real-time collaboration and cloud access inherently require connectivity, a significant portion of pre-flight preparation and post-flight follow-up can be managed without it. This capability reduces the perceived necessity for high-speed in-flight Wi-Fi for certain user segments.
The reliance on offline productivity tools is notable. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 65% of business travelers regularly utilize offline versions of productivity suites like Microsoft Office or Google Workspace for tasks such as document editing and presentation creation during flights. This highlights a segment of the market where the value proposition of in-flight internet is diminished for core work functions.
- Offline Productivity Suites: Tools like Microsoft Office 365 (offline versions), Google Workspace (offline mode), and Apple's iWork allow for document creation, editing, and presentation management without an internet connection.
- Note-Taking and Task Management Apps: Many applications such as Evernote, OneNote, and Todoist offer robust offline functionality, enabling users to capture ideas, organize tasks, and review project details during flights.
- PDF Readers and Document Viewers: Business travelers frequently download reports, contracts, and research papers in PDF format, which can be reviewed thoroughly offline.
- Presentation Software: PowerPoint, Keynote, and Google Slides allow for the creation and rehearsal of presentations without requiring an internet connection, a common pre-meeting activity for business travelers.
Emergence of Next-Generation Ground-Based Alternatives
While not directly competing for connectivity mid-flight or mid-ocean, advancements in ground-based mobile networks, particularly 5G at lower altitudes, present a potential long-term substitute. For instance, by the end of 2024, 5G network coverage is expected to reach over 70% of the global population, increasing the feasibility of seamless ground-to-air connectivity for certain applications.
Future direct-to-device satellite phone services also pose a potential threat. These services, which bypass the need for specialized hardware, could offer an alternative for basic communication needs, potentially impacting the demand for dedicated in-flight connectivity systems over time. Analysts project the direct-to-device satellite market to grow significantly in the coming years, with early partnerships already forming between mobile carriers and satellite providers.
- Emerging 5G Capabilities: Enhanced terrestrial networks offer potential for seamless connectivity at lower altitudes, creating a substitute for certain in-flight communication needs.
- Direct-to-Device Satellite Services: Future satellite phone solutions that eliminate the need for specialized hardware could offer alternative communication channels.
- Long-Term Impact: While not immediate competitors, these evolving technologies represent a potential shift in how connectivity is accessed, impacting demand for traditional in-flight systems.
- Market Growth Projections: The direct-to-device satellite market is anticipated for substantial growth, indicating a growing alternative landscape.
The threat of substitutes for Anuvu's services is significant, primarily stemming from readily available terrestrial networks and the increasing self-sufficiency of travelers. Passengers can leverage their own devices loaded with offline content, diminishing the need for onboard entertainment systems. Furthermore, a growing segment of travelers intentionally disconnects during journeys, opting for rest or offline activities.
Business travelers, in particular, can fulfill many productivity tasks using offline applications on their personal devices, reducing reliance on in-flight internet for core work functions. While advancements in 5G and future direct-to-device satellite services present longer-term potential substitutes, the immediate threat lies in the widespread adoption of offline capabilities and changing passenger preferences.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on Anuvu | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial Networks | Mobile phone data, public Wi-Fi at airports | Reduces immediate need for onboard connectivity | High availability of 4G/5G |
| Offline Entertainment | Downloaded movies, music, games on personal devices | Decreases demand for airline-provided IFE | Prevalence of streaming service downloads |
| Offline Productivity | Microsoft Office, Google Workspace (offline modes) | Lowers perceived value of in-flight Wi-Fi for work | 65% of business travelers use offline suites |
| Behavioral Shift | Choosing to disconnect, rest, or read | Shrinks addressable market for connectivity services | ~30% of air travelers seek to disconnect |
| Emerging Technologies | Enhanced 5G, direct-to-device satellite | Potential long-term competition for connectivity | 5G coverage reaching >70% globally by end of 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a presence in the mobility connectivity and entertainment market, like that of Anuvu, requires a substantial capital investment. This includes securing satellite capacity, building robust ground infrastructure, developing advanced hardware, and obtaining crucial content licensing agreements. For instance, the cost of launching and maintaining a satellite constellation can run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, making it a significant hurdle.
This high financial barrier effectively deters many potential new entrants. Only entities with considerable financial backing can realistically consider entering this competitive landscape. For example, in 2024, the average cost for a new satellite launch alone can range from $50 million to over $200 million, depending on the rocket and payload size, presenting a formidable entry cost.
Operating globally in satellite communications and content distribution means dealing with a maze of international and national rules, spectrum licenses, and aviation or maritime certifications. This complex web of approvals is a significant barrier, making it tough and expensive for newcomers to even get started.
The process of securing these essential approvals can take years and involve substantial legal and consulting fees, effectively deterring many potential new entrants. For instance, obtaining a new satellite orbital slot and associated spectrum rights can cost tens of millions of dollars and require extensive diplomatic negotiations.
The need for highly specialized technical expertise presents a substantial barrier for new entrants in the satellite-based connectivity and IFE systems sector. Developing, deploying, and maintaining these complex systems demands deep knowledge in engineering, telecommunications, and content management. For instance, as of 2024, the global aerospace and defense sector, which heavily relies on such expertise, faces a significant talent shortage, with estimates suggesting a need for millions of skilled workers in the coming years. This scarcity makes it difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to build a competent workforce and acquire the essential technological know-how. This accumulated intellectual capital is not easily replicated, creating a formidable hurdle for potential competitors.
Established Customer Relationships and Brand Loyalty
Anuvu and existing players have deeply entrenched relationships with major airlines and maritime operators, often solidified by multi-year agreements. For instance, Anuvu's extensive partnerships are a testament to this, with many contracts running for several years, ensuring recurring revenue and a stable customer base.
Newcomers must overcome the significant hurdle of displacing these established connections and earning the trust and reputation necessary in an industry where dependability and a track record of performance are critical. The cost and effort required to build this level of credibility are substantial deterrents.
Brand recognition and existing contractual obligations serve as powerful barriers to entry. A new entrant would need to offer a demonstrably superior product or service, or a significantly lower price point, to even begin chipping away at the loyalty Anuvu and its competitors enjoy. The market's inherent conservatism further reinforces these existing relationships.
- Long-term contracts: Many agreements with airlines and maritime clients are multi-year, locking in revenue and customer loyalty for incumbent providers.
- Trust and reputation: The industry demands proven reliability, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction without a solid performance history.
- Brand loyalty: Established brands have cultivated strong customer loyalty, requiring significant investment for new players to overcome.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Existing players like Anuvu leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in securing satellite bandwidth and content licensing. For instance, Anuvu’s established relationships allow for bulk purchasing, driving down per-unit costs. New entrants would face the immediate challenge of achieving comparable scale, making it difficult to match the cost efficiencies enjoyed by incumbents.
Furthermore, Anuvu benefits from economies of scope by offering integrated passenger experience solutions, bundling connectivity, content, and software. This diversification creates a more robust value proposition and further entrenches its market position. A new competitor would need substantial investment to replicate this breadth of offering, creating a considerable barrier to entry.
- Economies of Scale: Anuvu’s bulk purchasing power for satellite bandwidth and hardware components significantly lowers operational costs compared to potential new entrants.
- Economies of Scope: The ability to offer integrated passenger experience solutions, combining connectivity and content, provides Anuvu with a competitive advantage that is costly for new firms to replicate.
- Cost Disadvantage for Entrants: New companies would operate at a higher cost base initially, struggling to compete on price with established, scaled providers like Anuvu.
The threat of new entrants in the mobility connectivity and entertainment sector, where Anuvu operates, is significantly mitigated by extremely high capital requirements and complex regulatory landscapes. For instance, the cost of launching a single geostationary satellite can exceed $200 million in 2024, a substantial barrier for any newcomer. Navigating the intricate web of international spectrum licenses and aviation certifications further adds to the financial and temporal hurdles, often taking years and millions in legal fees to secure.
The need for specialized technical expertise and established customer relationships also acts as a formidable deterrent. Anuvu's existing, long-term contracts with airlines, often spanning multiple years, create a stable revenue base and a significant hurdle for new players attempting to gain market share. Building the necessary trust and reputation in an industry where reliability is paramount requires substantial time and proven performance, which new entrants lack.
Economies of scale and scope further solidify Anuvu's competitive position. Bulk purchasing of satellite bandwidth and content licenses allows incumbents to operate at lower costs. For example, Anuvu's integrated offerings, combining connectivity and entertainment solutions, create a more attractive and cost-effective package for clients, making it difficult for new entrants to match this breadth of service and achieve comparable cost efficiencies.
| Barrier Type | Description | Estimated Cost/Time (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Satellite launch, ground infrastructure, hardware development, content licensing | Satellite launch: $50M - $200M+; Spectrum rights: Tens of millions |
| Regulatory Hurdles | International and national rules, spectrum licenses, aviation/maritime certifications | Years for approvals, millions in legal/consulting fees |
| Technical Expertise | Engineering, telecommunications, content management | Talent shortage in aerospace/defense sector |
| Customer Relationships | Long-term contracts with airlines/maritime operators | Multi-year agreements, trust and reputation building |
| Economies of Scale/Scope | Bulk purchasing, integrated service offerings | Cost advantage for incumbents, difficult for new entrants to replicate |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Anuvu Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Anuvu's annual reports, industry-specific market research from sources like OAG and Cirium, and regulatory filings from aviation authorities. This ensures a robust understanding of competitive pressures.